Information Processing | Chapter 7 | 8th Maths - Cryptology | 8th Maths : Chapter 7 : Information Processing
Chapter: 8th Maths : Chapter 7 : Information Processing
Cryptology
Cryptology
In today’s
world, security in information is a fundamental necessity not only for military
and political departments but also for private communication. Today’s world of communication
has increased the importance of financial data exchange, image processing, biometrics
and e-commerce transaction which in turn has made data security an important issue.
Cryptology is defined as the science which is concerned with communication in secured
form.
1. Cryptology
– Some technical details
Plain text: The original message is called
plain text.
Cipher text or Cipher number:
The encrypted output (converted
message into code) is called Cipher text or Cipher number. Cipher text is written
in capital letters, while plain text is usually written in lowercase. A secret key
is to use something to generate the Cipher text from the plain text.
Encryption and Decryption:
The process of converting
the plain text to the Cipher text is called encryption and the
vice versa is called decryption.
Let us try
to create some Cipher text that we use in the form of coded message at some point
in our real life.
2. Examples
of Cipher Code
1. Shifting Cypher Text
Ceasar Cipher
The Ceasar
Cipher is one of the earliest known and simplest ciphers. It is a type of substitution
cipher in which each letter in the text is “shifted”
a certain number of places down the alphabets.
To pass an
encrypted message from one person to another, it is first necessary that both parties
have the ‘key’ for the cipher, so that
the sender may encrypt it and the receiver may decrypt it. For the Caesar Cipher,
the “key” is the number of characters
to shift the cipher alphabet. So, we have to know how big the switch is to break
the code.
Let us know
about more Ciphers from the following examples and situations.
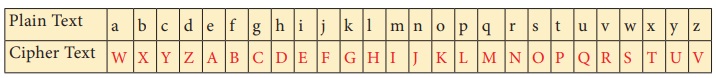
Example 7.8
Use Ceasar
Cipher table set +4 and try to solve
the given secret sentence.
fvieo mr gshiw ger fi xvmgoc
Solution:
Let us make
Ceasar Cipher table first. Here, we have to set to +4 table.
For that,
we have to start letter e to set as A, f
as B … likewise d as Z.
Now, the
+4 Ceasar Cipher table looks like
The given
plain text is
fvieo mr gshiw ger fi xvmgoc
To crack
this secret code, follow the steps given below.
Step 1: Using Ceasar Cipher table,
let us first match the most repeated letters. This will help us to progress faster.
fvieo mr gshiw ger fi xvmgoc
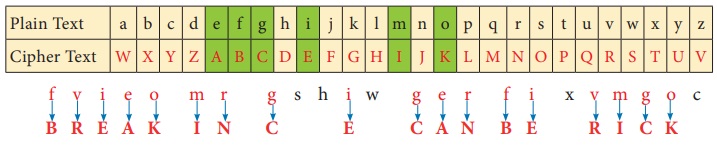
Step 2: Then, let us find remaining
letters to complete the code.
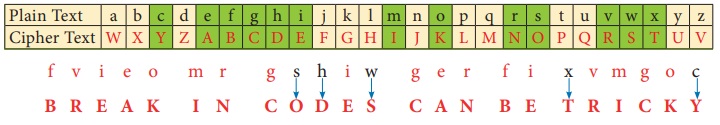
Thus, the
secret sentence is decoded as, BREAK IN CODES CAN BE TRICKY
2. Substituting Cypher
Text
Each letter
in a text is “substituted” by certain pictures and symbols, a key message, group
of words, letters or a combination of these can be used to encode or decode the
information. Let us learn more from the following situation.
Situation:
The teacher
divides the class into two teams and displays a worksheet given in the figure below
for students to complete. Play a game, teams take turns suggesting letter substitutions
and someone entering your suggestions in the table. Teams earn points for correct
letter guesses.
Worksheet 1 :- Additive
Cipher [key = 5]
Convert a given plain text into Additive
Cipher text (number) code.
“ mathematics is a unique
symbolic language in which the whole world works and acts accordingly.”
Tips for cracking additive
ciphers:
• Especially for additive Ciphers, you only need key number. You can complete the cipher
table by filling in the rest of the numbers in order.
• If you can, find and make frequency
table for alphabets, it is help you to get started.
• Match the most repeated
letters first and fill the Cipher number.
• Look for familiar one-letter words like a or i. common two and three
letter words like of, to, in, it, at, the,
and, for, you …..
• Look for consecutive numbers
in the Cipher text and match them with possible consecutive letters in the plain text.
Now, to start
converting a plain text into Cipher number, first we have to make a cipher table
as shown below. Here there key is 5.
As per key number, we have to start and fill a = 05, b = 06 …….. z = 04 respectively.
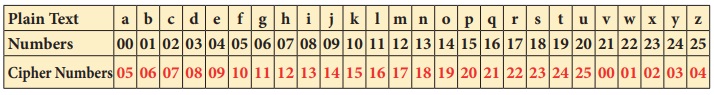
To start
encoding the text, let us count the frequency of alphabets and frame frequency table
as shown below.
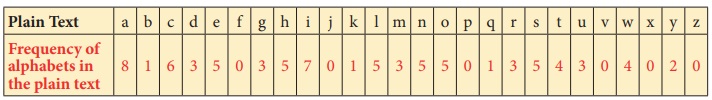
With the
help of Cipher table and frequency table, let us fill the Cipher numbers for the
plain text. Let us first match the most repeated letters (5 times and above), then
2 to 4 times repeated letters and finally remaining letters step by step as shown
in given figure.
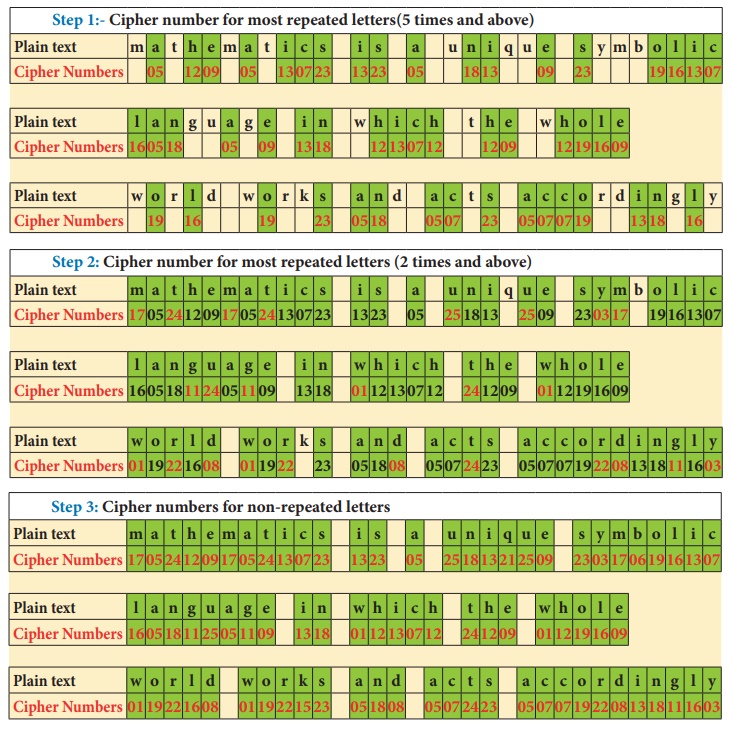
Thus, the
Additive Cipher text for plain text is as follows:
“17 05 24 12 09 17 05 24 13 07 23 13 23 05 25 18 13 21 25 09 23 03
17 06 19 16 13 07
16 05 18 11 25 05 11 09 13 08 01 12 13 07 12 24 12 09 01 12 19 16
09 01 19 22 16 08
01 19 22 15 23 05 18 08 05 07 24 23 05 07 07 19 22 08 13 18 11 16 03”
Activity
TREASURE HUNT
Treasure in the Mathematics
Club room
The teacher divides the students into four groups and gives each
group a code and a clue and then asks them to cracking the clues to find
(i) the identity of the treasure
(ii) the place of the treasure
(iii) the room in which the treasure is present.
You may take notes on this piece of paper as you proceed through
the search
Code 1: Pigpen
Message:- If you decode the clue
here you can get the four expected treasure names
I. Fill in the blank boxes and decode
The Pigpen code looks
like meaningless writing, but it is quite easy to catch on to.
Each letter is represented by the part of the “Pigpen” that surrounds
it.
The first code uses the following key. To complete the code, you need to work out how to use the key to
decode the message.
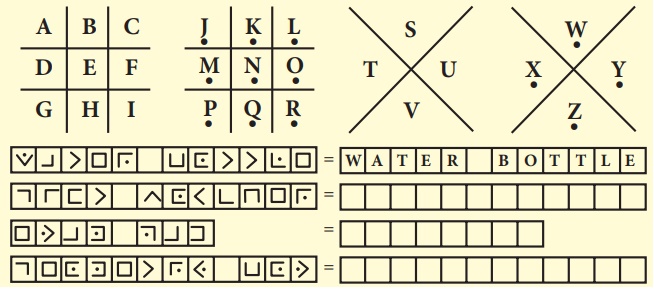
Answer:
Code 2: Polybius Square
Cipher
Message:- If you decode this you
can get the clue to identify the name of the treasure name
II. Fill in the blanks
A Polybius Square is a table that allows someone to convert letters
into numbers.
Use the Polybius square rows and column values to find the code

Answer:
Using this a set of numbers can be used to denote a letter and
vise versa
(4, 2) represent T, (3, 4) represent H, (5, 5) represent E Likewise,
when we solve for the remaining, we get
THE NAME OF TREASURE DOES NOT HAVE B AND D.
Since clue 2 gives that the treasure item does not have the
letters b & d, therefore "exam pad" & "geometry
box" cannot be the treasure item.
Hence, the treasure item is "gift voucher"
Code 3: Atbash Cipher
Message:- If you decode this you
can get the clue room number where the treasure is present
(It may be 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 or 29 or 30)
III. Find the code using the key as shown in given figure:
Atbash cipher is a substitution cipher with just one specific key
where all the letters are reversed that is A
to Z and Z to A.

GSV ILLN MFNYVI RH Z NFOGRKOV LU ULFI ZMW HVEVM
Answer:
The given Cipher is:
GSV ILLN MFNYVI RH Z NFOGRKOV LU ULFI ZMW HVEVM
Decoded Message :
THE ROOM NUMBER IS A MULTIPLE OF FOUR AND SEVEN
Since room number is a multiple of 4 & 7,
The room number is 4 × 7 = 28.
Code 4: Using a Key – Reflection
Table
Message:- If you decode this clue
you can get the possible place where the treasure is located (It used to sit)
Use the reflection table which is given below and find the correct
word by using a reflected alphabet.
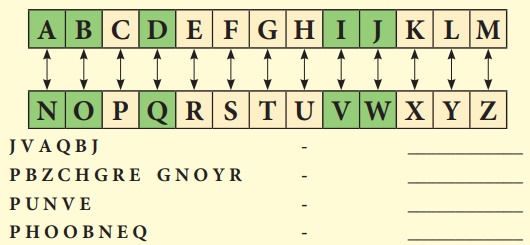
J V A Q B J − WINDOW
P B Z C H G R E G N O Y R − COMPUTER TABLE
P U N V E − CHAIR
P H O O B N E Q − CUPBOARD
After finding
the codes, the teacher then asks students to rearrange the clues one by one
The 4 clues are :
1. Water bottle, Gift voucher, Exam pad, Geometry box
2. The name of the treasure does not have 'b' & 'd'
3. The room is a multiple of four and seven − 28
4. Window, Computer table, Chair, Cupboard
RESULT
(i) The room
in which the treasure took place :- 28
(ii) The
place of the treasure :- Chair.
(iii) The
identity of the treasure :- Gift voucher.
(Hint:- If
you answered the question number 6 in Exercise 4.3, you can compare and verify your
results) The gift voucher contains (20 full marks awarded).
Try these
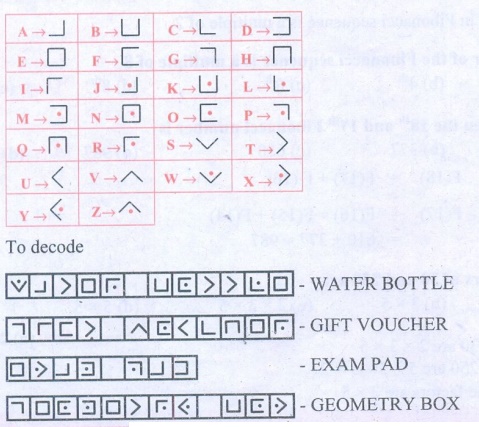
1. Use Pigpen Cipher code
and write the code for your name ________and your chapter names
(i) LIFE MATHEMATICS
(ii) ALGEBRA
(iii) GEOMETRY
(iv) INFORMATION PROCESSING
Solution:
For Pigpen, we should first construct the Criss Cross pattern
& then fill with alphabets.
Step 1: 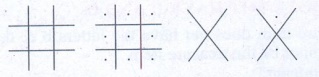
Step 2: Fill the above with all the alphabets from A to Z.
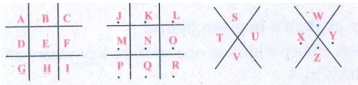
Step 3: So, the secret code is got by the outline of each letter
in the above patterns.
So for 
Similarly for all the others. Therefore Pigpen code is
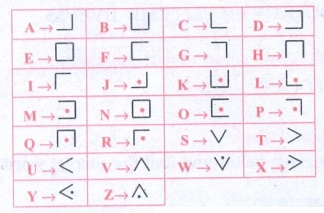
Hence if your name is RAM, the corresponding pattern is 
Let us now write the given words with Pigpen code.
(i) LIFE MATHEMATICS (ii) ALGEBRA (iii) GEOMETRY (iv) INFORMATION PROCESSING

2. Decode the following
Shifting and Substituting secret codes given below. Which one is easier for you?
(i) Shifting method:- M
N S G H M F H R H L O N R R H A K D
(ii) Substituting method:- 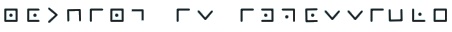
Solution:
Decode using shifting method. Let us shift & see by trial
& error method.
Let us substitute 'b' for 'a', 'c' for 'b'
& so on

Message : M N S G H M F H R H L O N R R H A K D
Decoded text: NOTHING IS IMPOSSIBLE
Decode using substituting method : 
We find that Pigpen code has been used, by substituting for the
symbols from the table that we constructed earlier, we go the message.
NOTHING IS IMPOSSIBLE
3. Write a short message
to a friend and get him to decipher it.(use either shifting or substituting code
method)
(by Student)
Related Topics