Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 12 : Mineral Nutrition
Critical concentration and toxicity of minerals - Plants
Critical concentration and
toxicity of minerals
1. Critical Concentration
To
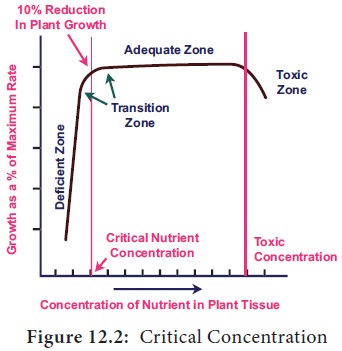
increase the productivity and also to avoid mineral toxicity knowledge of critical
concentration is essential. Mineral nutrients lesser than critical
concentration cause deficiency symptoms. Increase of mineral nutrients more
than the normal concentration causes toxicity. A concentration, at which 10 %
of the dry weight of tissue is reduced, is considered as toxic. Figure 12.2
explains about Critical Concentration.
2. Mineral Toxicity
a. Manganese toxicity
Increased
Concentration of Manganese will prevent the uptake of Fe and Mg, prevent
translocation of Ca to the shoot apex and cause their deficiency. The symptoms
of manganese toxicity are appearance of brown spots surrounded by chlorotic
veins.
b. Aluminium Toxicity
Aluminium
toxicity causes precipitation of nucleic acid, inhibition of ATPase, inhibition
of cell division and binding of plasma membrane with Calmodulin.
For
theories regarding, translocation of minerals please refer Chapter- 11.
Iron and Manganese toxicity
Iron and Manganese exhibit competitive behaviour. Deficiency of
Fe and Mn shows similar symptoms. Iron toxicity will affect absorption of
manganese. The possible reason for iron toxicity is excess usage of chelated
iron in addition with increased acidity of soil (PH less than 5.8) Iron and
manganese toxicity will be solved by using fertilizer with balanced ratio of Fe
and Mn.
Related Topics