Chapter: 11th Computer Technology : Chapter 9 : Introduction to Spreadsheet
Creating Formulae - OpenOffice Calc
Creating
Formulae
After
entering the data in worksheet, you can perform calculations on the data in the
worksheet. In order to create formulae, you first need to know the syntax that
describes the format for specifying a formula.
In
Calc, you can enter formulas in two methods, either directly into the cell or
at the input line. Formula in Calc may start with equal (=) or plus(+) or
minus(–) sign followed by a combination of values, operators and cell
references. But, as a general practice, all formulas should start with an equal
sign. If any formula starts with a + or –, the values will be considered as
positive or negative respectively.
Operators
Operators
are symbols for doing some mathematical, statistical and logical calculations.
Combination of values, operators and cell references is called as “Expression”.
Calc supports a variety of operators which are categorized as:
(1)
Arithmetic Opertors
(2)
Relational Operators
(3)
Reference Operators
(4)
Text Operator
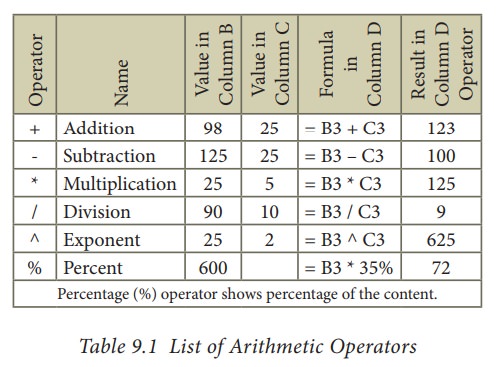
1. Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic
operators are symbols for performing simple arithmetic operations such as
addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc., These operators return a
numerical result.
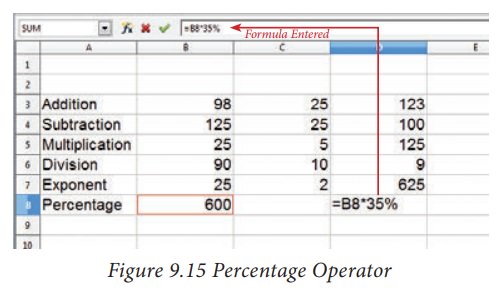
Formula
bar shows the formula what the user had entered. But, the cell shows the resulted
value (Figure 9.15).
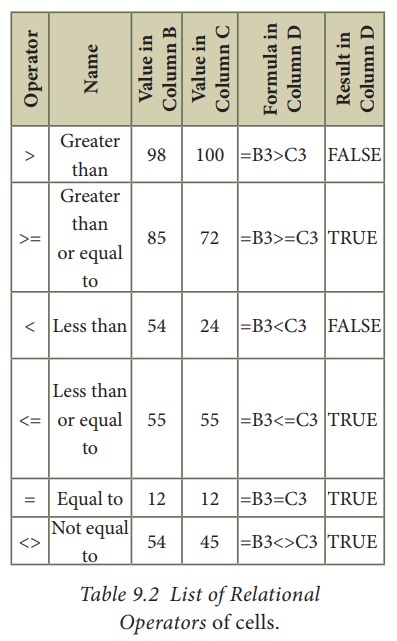
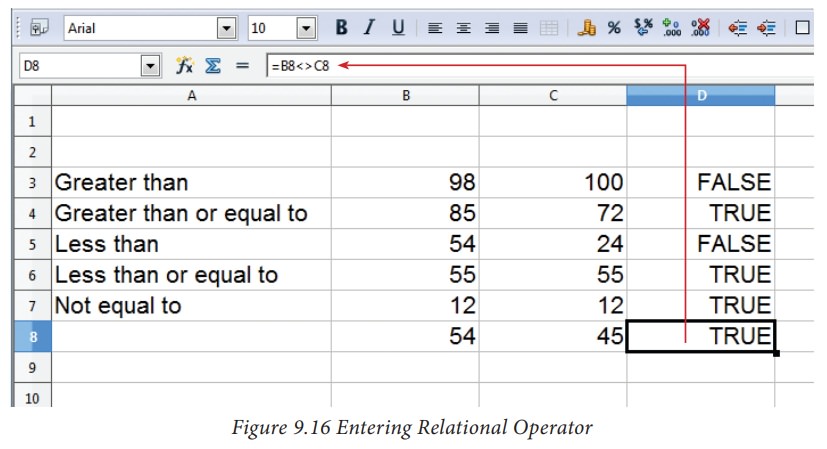
2. Relational Operators
Relational
operators are symbols used for comparing two values such as greater than, less
than, equal to etc. The relational operators are also called as "Comparative
operators". These operators return either a True or a False.
3. Reference Operator
Reference
operators are used to refer cell ranges. A
continuous group of cells is called
as “Range”. There are three
types of reference operators that are used to refer cells in calc; they are
Range Reference Operator, (2) Range Concatenation (3) Intersection Operator.
Range Reference Operator
Colon
(:) is the range reference operator. It is used to group a range of cells. An
expression using a range operator has the following syntax:
reference left : reference right
where
reference left is the starting cell address of a linear group of cells or upper
left corner address of a rectangular group Reference right is the last cell
address of a linear group or lower right corner address of a rectangular group
of cell.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Example:
(i)
Linear group of cells A1, A2,A3,A4,A5 is referred as A1:A5
(ii)
Rectangular group of cells A2, A3, A4, ….. B2, B3, B4,….D5, D6 is referred as
A2:D6 (Refer Figure 7.17)
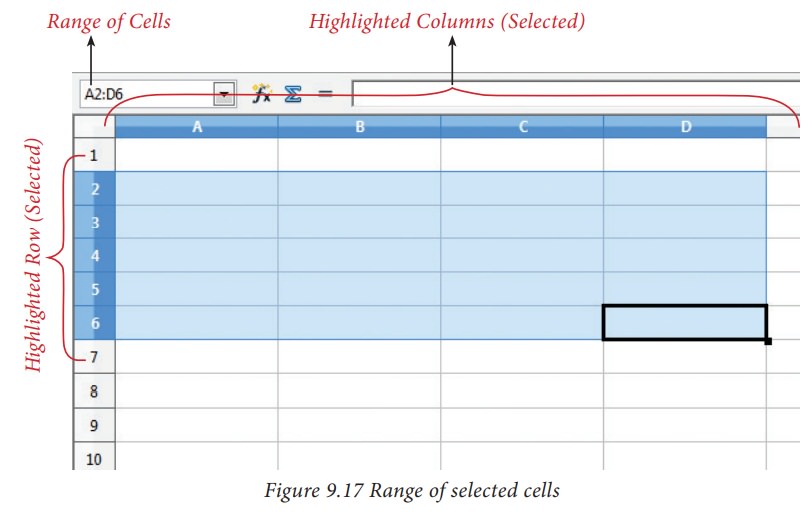
Name
box shows the reference A2:D6 corresponding to the cells included in the drag
operation with the mouse to highlight the range.
Reference concatenation operator:
Concatenation
means joining together. Tilde (~) symbol is used as a concatenation operator in
calc. An expression using a concatenation operator has the following syntax:
reference left ~ reference right
Example:
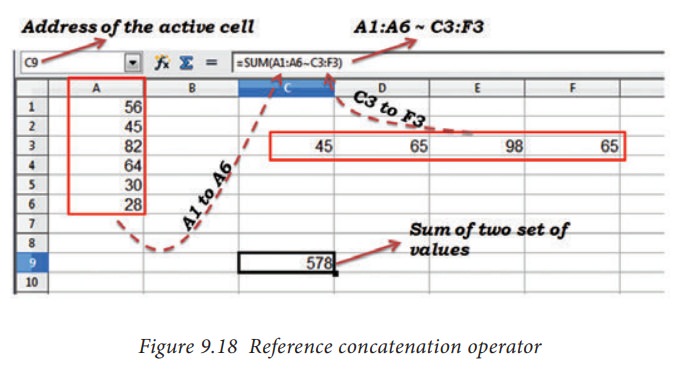
If
you want to find the sum of the values from A1 to A6 and C3 to F3. The formula
is =SUM(A1:A6 ~ C3:F3)
SUM
is a function to find the sum of a group of values. (Refer Figure 9.18)
Intersection Operator:
Intersection
operator is used to join two set of groups. It is very similar to Range
concatenation operator. The intersection operator is represented by an
exclamation
reference
left ! reference right
Example: (A2:D3 ! B2:E4)
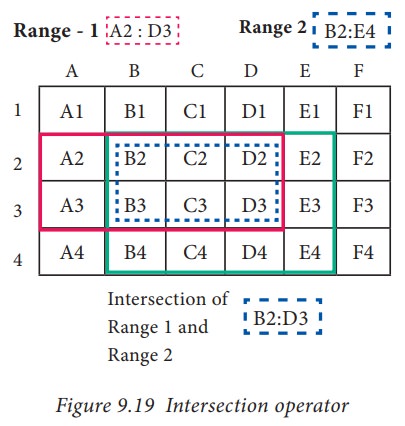
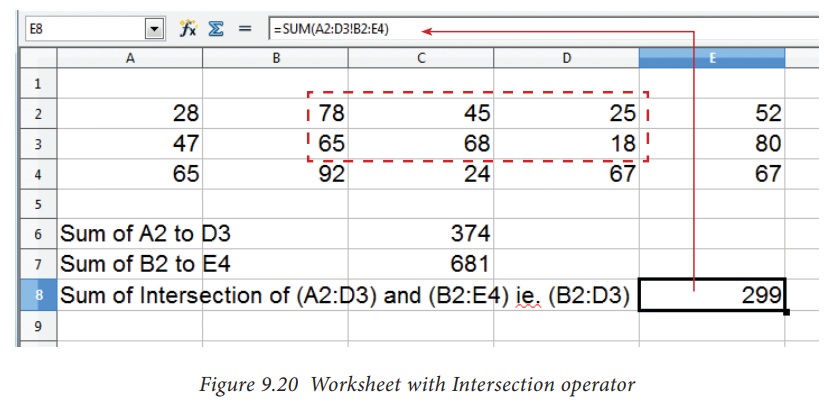
The
result of (A2:D3 ! B2:E4) is referred by the range B2:D3, because these cells
are both inside A2:D3 and B2:E4 (Refer Figure 9.19 and 9.20).
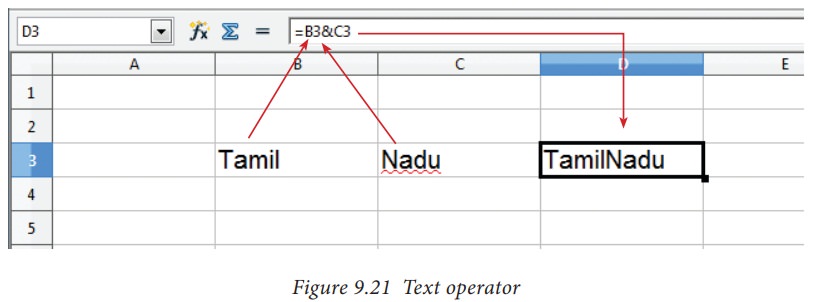
4. Text Operator:
In
Calc, “&” is a text operator which is used to combine two or more text.
Joining two different texts is also known as “Text Concatenation” (Refer Figure 9.21). An expression
using the text operator has the following syntax:
text reference1 & text reference2
When
arithmetic operators are used in a formula, Calc calculates the results using
the rule of precedence followed in Mathematics. The order is:
I. Exponentiation ( ^ )
II. Negation ( - )
III. Multiplication and Division ( *, /)
IV. Addition and Subtraction (+, -)
Here
is an example to illustrate how to create a formula:
Illustration 1:
Create
a Marks worksheet with the following data:
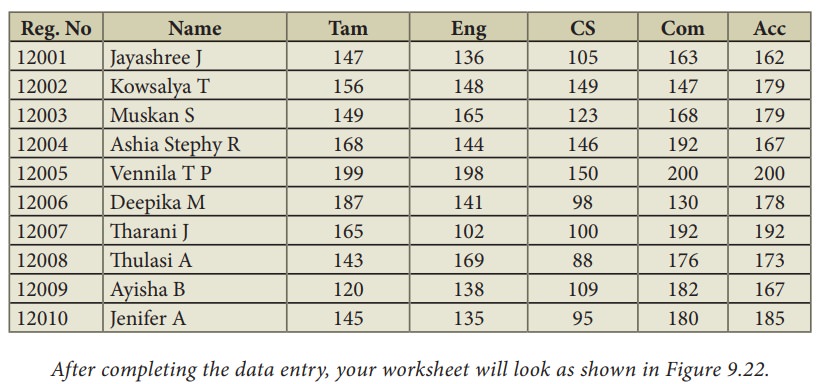
After completing the data entry,
your worksheet will look as shown in Figure 9.22.
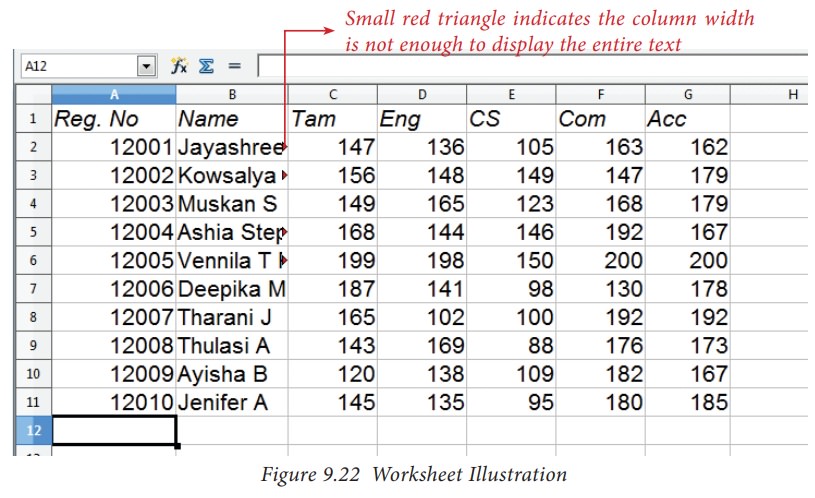
Construction of formula
To construct a formula, follow the steps below:
•
Cell pointer should be in the cell in which you want to display the result.
•
Formula should begin with an = sign.
•
In a formula, use only cell reference (cell address) instead of the actual
values within the cells.
• While constructing a formula, BODMAS rule should be kept in mind.
• eneral Syntax of constructing a formula is: = cell reference1 <operator> cell reference2 <operator> ……………….
•
Cell references are of two types (i) Relative cell reference (ii) Absolute Cell
reference.
•
If you refer cell addresses directly while constructing formulae, it is called
as “Relative Cell addressing”.
•
Examples of Relative Cell addressing:
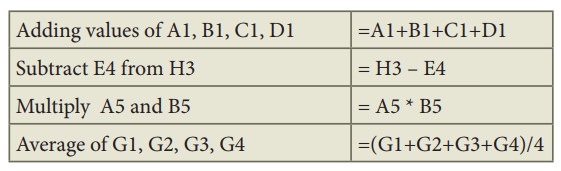
Adding
values of A1, B1, C1, D1 =A1+B1+C1+D1
Subtract
E4 from H3 = H3 – E4
Multiply
A5 and B5 = A5 * B5
Average
of G1, G2, G3, G4 =(G1+G2+G3+G4)/4
•
In the above table, all cell references are “Relative cell addressing:”.
•
While writing a formula, if you use the $ symbol in front of a column name and
row number, it will become an “Absolute Cell addressing”.
•
Examples of Absolute cell addressing:
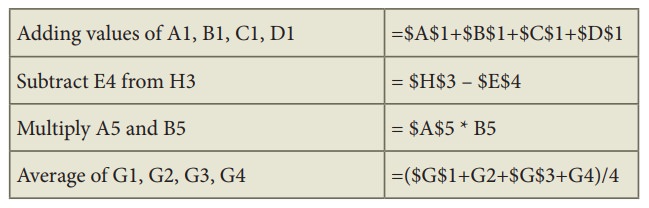
Adding
values of A1, B1, C1, D1 =$A$1+$B$1+$C$1+$D$1
Subtract
E4 from H3 = $H$3 – $E$4
Multiply
A5 and B5 = $A$5 * B5
Average
of G1, G2, G3, G4 =($G$1+G2+$G$3+G4)/4
•
In an expression, all cells need not necessarily be relative or absolute. You
can mix both type of references.
•
The following section explains the use of relative cell addressing. About
“Absolute cell addressing”, you will be learn later in this chapter.
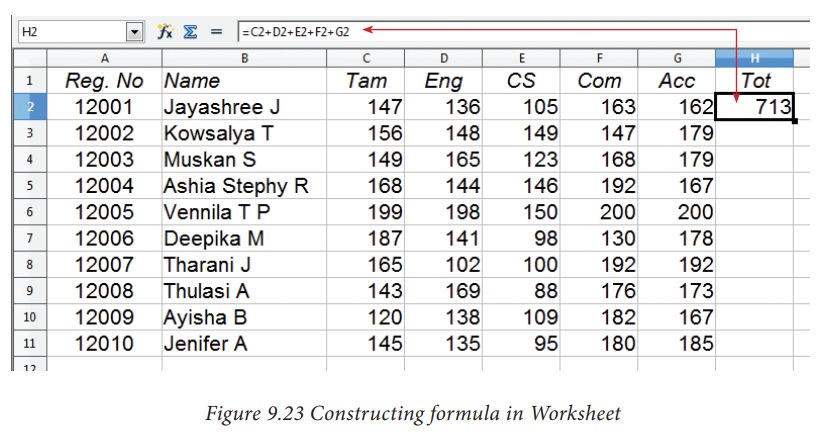
Finding Total to the above Illustration:
•
Move the cell pointer to H2 (Total column)
•
Type the following formula; after entering the formula, press “Enter” key =
C2+D2+E2+F2+G2 (Refere Figure 9.25)
•
Now, you will get the sum of all the values of C2, D2, E2, F2 and G2
•
The above-mentioned formula clearly stated that, how worksheets are working
with cells.
•
While referring to the cell addresses in a formula, the spreadsheet reads the
value inside the cell that you refer. This is a good practice of constructing a
formula. Because, if you change any value, the spreadsheet recalculates with
that new value.
After
entering a formula the result is display as in Figure 9.23
Related Topics