Political Ideologies - Communitarianism | 11th Political Science : Chapter 8 : Political Ideologies - Part-II
Chapter: 11th Political Science : Chapter 8 : Political Ideologies - Part-II
Communitarianism

Communitarianism
Communitarianism emerged as a political doctrine during the 1980s when
Michael Sandel authored the book ‘Liberalism and the Limits of Justice’. He
criticised the libertarianism and its thinker John Rawls in that work. The
other political scientists supporting communitarianism include Alisdair
MacIntyre, Michael Walzer, Charles Taylor, Amitai Etzioni nd Will Kymlicka.
Though the British Socialist Goodwyn Barmy coined the word “communitarian” in
the 1840s, the doctrine of communitarianism emerged only towards the end of the
20th century
Communitarianism rose as a revolt against the prevailing two ideologies
of libertarianism and Marxism. It criticised the thinkers of libertarianism for
their over emphasis on individuals. It rejected Marxism for being committed to
class-based action and analysis. However, the opposition was directed against
Libertarianism that had become the ruling philosophy of mankind especially in
the western world.
Importance of Community
Communitarianism argues that man is not born in a vacuum. He is a social and cultural animal. Individuals are born in a community or culture and therefore inherit it. Their beliefs, behavior, skills, capacities, attitudes etc are predominantly influenced by the community. Every individual builds on these commonly available and acquired capacities to make a mark in his or her life time. Man is not an atomistic entity existing alone but is embedded in the community. The individual is not ‘unencumbered self ’ (completely free) from society but ‘situated self ’ (rooted and planted) in society
Communitarianism Meaning
Communitarianism is a philosophy that emphasizes the
connection between the individual and the community.
Although the community might be a family UNIT,
Communitarianism usually is understood, in the wider, philosophical sense, As a
collection of interactions, Among a Communitarian philosophy is based upon the
belief that a person's social identity and personality are largely molded by
community relationships, with a smaller degree of development being placed on
individualism.

In short Balancing the Rights and Responsibilities of
Individual with Rights and Responsibilities of Community.
For example a child born in Tamil Nadu speaks Tamil language fluently
and not Japanese where as a child born in Japan speaks Japanese fluently and
not Tamil. A man living in a community where computer technology is already
available in developed form may become a skilled person in software domain. On
the contrary, a man living in a remote community that has not witnessed the
growth of information technology will not have adequate software skills.
Concept of State
Communitarianism considers the State as a positive instrument that
promotes the idea of the common good. The concept of common good is present in
every community. The community develops a set of goals, practices and measures
that collectively promote the fundamental welfare of all. The State should
promote the realisation of the common good and act against the activities that
promote individual good in contradiction with common good. It should protect
and promote those cultural traditions of the community that symbolise and
sustain the common good. Communitarianism supports a State that is
democratically elected and constituted. They strongly aspire for a State that
is responsible and responsive to demands of the community.
Concept of Rights
Communitarianism believes that rights and responsibilities are
intimately related. It rejects the excessive reliance of libertarianism on the
concept of individual autonomy and rights. Instead, it focuses on a new concept
of rights where common good is given importance. They strongly contend that the
common good of the community has supremacy and priority over the rights of the
individuals as it is prior to them. Every person may have his own conception of
good but such individual good must be subordinated to the idea of common good.
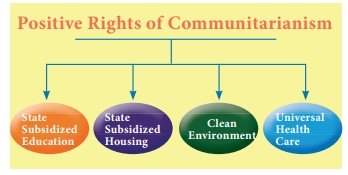
A new concept of positive rights is propagated where in a wide variety of
rights like State-subsidised education, State-subsidized housing, safe
environment, universal healthcare are demanded for the community members. A
synthesis between rights and responsibilities is advocated by certain thinkers
who belong to Responsive Communitarianism.
Concept of Justice
Communitarians attack John Rawls and other libertarian thinkers on the
concept of justice. They reject universalism of libertarianism, their argument
that the concept of justice is universally applicable as it is based on reason.
On the contrary, communitarians articulate the particularistic view of justice.
Every community develops its own notions of justice and therefore it differs
from society to society.
Therefore, we can conclude that Communitarianism as a political doctrine
believes in the indispensability of community for the development of the
‘situated and embedded man’. The positive State should concentrate on the
provision of positive rights to community and its people so that common good
can be preserved and promoted. But Libertarianism still criticises
Communitarianism as preparing the path for the emergence of collectivism and
authoritarianism.
Related Topics