Man and Environment - Classification of Human settlements | 9th Social Science : Geography: Man and Environment
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography: Man and Environment
Classification of Human settlements
Human settlements
A settlement can be described as any temporary or permanent unit
area where people live, work and lead an organized life. It may be a city,
town, village or other agglomeration of buildings. During the early days, man
preferred tree branches, caves, pits or even rock cuts as his shelter. As days
passed by, man slowly learnt the art of domesticating animals and cultivating
food crops. The evolution of farming took place along four major river basins
i.e. the Nile, Indus, Hwang Ho, Euphrates - Tigris. Man built huts and mud
houses. Slowly settlements came into existence. A settlement generally
consisted of a cluster of houses, places of worship and a place of burial.
Later, small settlements developed into villages. Several villages together
formed a town. Bigger towns developed into cities. Settlements were formed in different
shapes, sizes and locations.
Classification of settlements
On the basis of occupation, settlements may be classified as rural
and urban settlements.
(A) Rural Settlements
Any settlement where most of the people are engaged in primary
activities like agriculture, forestry, mining and fishery is known as a rural
settlement. Most of the world's settlements are rural, that are mostly stable
and permanent. The most important and unique feature of rural settlements is
the vast, open spaces with green, pollution-free environment.
Patterns of rural settlements:
Rectangular pattern:
Rectangular pattern of settlements are found in plain areas or
valleys. The roads are rectangular and cut each other at right angles.

Linear pattern:
In a linear pattern, the houses are located along a road, railway
line and along the edge of the river valley or along a levee.

Circular or semicircular pattern:
The pattern of settlement that is found around the lakes, ponds
and sea coasts are called circular or semi circular pattern.

Star like pattern:
Where several metalled or unmetalled roads converge, star shaped
settlements develop. In the star shaped settlements, houses are spread out
along the sides of roads in all directions.

Triangular pattern:
Triangular patterns of rural settlement generally develop at the
confluence of rivers.

T-Shaped, Y-Shaped, Cross-Shaped or Cruciform settlements:
T-shaped settlements develop at tri- junctions of the roads (T),
while Y-shaped settlements emerge as the places where two roads converge with
the third one. Cruciform settlements develop on the cross-roads which extend in
all four directions.

Nebular pattern:
The arrangement of roads is almost circular which ends at the
central location or nucleus of the settlement around the house of
the main landlord of the village or around a mosque, temple or church.

(B) Urban Settlements
Urban is the term related to cities and towns where people are
primarily engaged in non-agricultural activities, such as secondary, tertiary
and quaternary activities. The common characteristic feature of an urban unit
is that they are compact, congested and liable to a large number of population.
They comprise of mostly man-made structures that fulfill the requirements of a
society's administrative, cultural, residential and religious functions. The
factors responsible for urbanization are better employment opportunities,
suitable conditions for business, education, transport, etc.
Classification of Urban Settlements
Urban centres are classified as towns, cites, metropolitan cities,
mega cities, conurbation, etc., depending on the size and services available
and functions rendered to it.
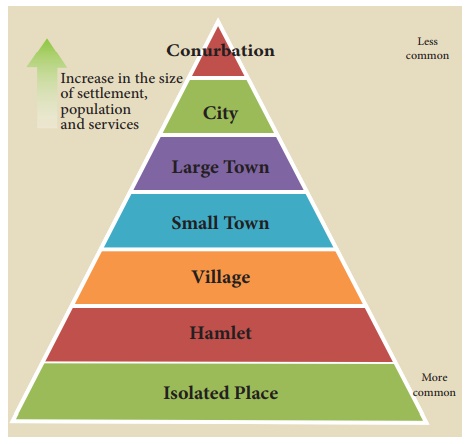
Town: A town is generally larger than a village, but smaller than a
city. It has a population of less than 1 lakh. E.g.: Arakkonam near Chennai
City: Cities are much larger than towns and have a greater number of
economic functions. The population in cities are estimated to be more than 1
lakh. E.g.: Coimbatore
Metropolitan cities: Cities accommodating population between 10 lakhs
and 50 lakhs are metropolitan cities. E.g.: Madurai
Megacities: Cities with more than 50 lakh population are called Megacities.
E.g.: Greater Chennai
Conurbation: A conurbation is a region comprising of a number of cities, large
towns and other urban areas. E.g.: Delhi conurbation
Related Topics