Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs
Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs
Cholinoceptor-Activating &
Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs
Acetylcholine-receptor
stimulants and cholinesterase inhibitors make up a large group of drugs that
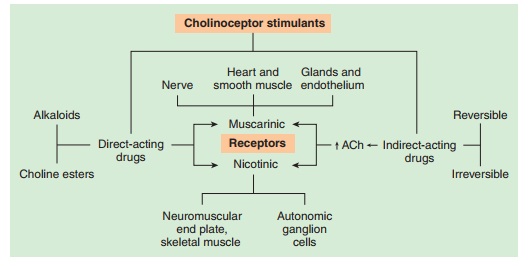
mimic acetylcholine (cholinomimetic agents) (Figure 7–1). Cholinoceptor
stimulants are classified phar-macologically by their spectrum of action,
depending on the type of receptor—muscarinic or nicotinic—that is activated.
Cholino-mimetics are also classified by their mechanism of action because some
bind directly to (and activate) cholinoceptors whereas others act indirectly by
inhibiting the hydrolysis of endogenous acetylcholine.
CASE STUDY
In mid-afternoon, a coworker brings 43-year-old JM to the emergency department because he is unable to continue pick-ing vegetables. His gait is unsteady and he walks with support from his colleague. JM has difficulty speaking and swallow-ing, his vision is blurred, and his eyes are filled with tears. His coworker notes that JM was working in a field that had been sprayed early in the morning with a material that had the odor of sulfur. Within 3 hours after starting his work, JM complained of tightness in his chest that made breathing dif-ficult, and he called for help before becoming disoriented.
How would you proceed to evaluate and treat JM? What should be done for his coworker?
Related Topics