Term 3 Unit 4 | 7th Science - Chemistry in Daily Life | 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 4 : Chemistry in Daily Life
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 4 : Chemistry in Daily Life
Chemistry in Daily Life
Unit 4
Chemistry
in Daily Life

Learning Objectives
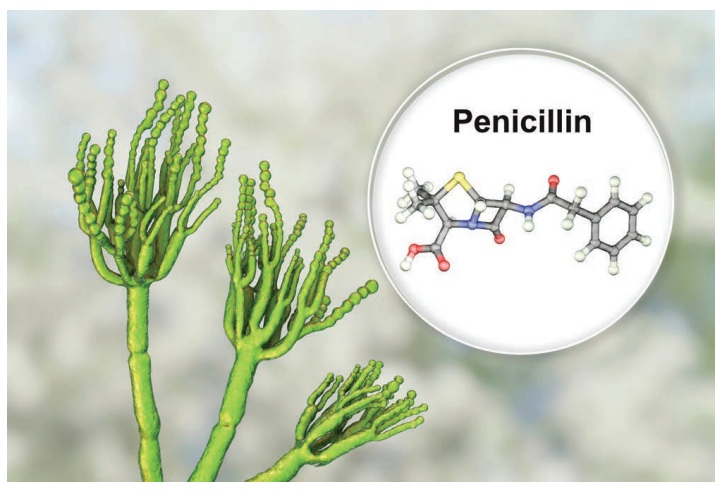
*Understand the
meaning of Medicines, Antibiotics, Analgesics, Antiseptics, Antihistamines,
Antacids and Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS).
* Understands
combustion and its types
* Recognizes flame and
its structure.
Introduction
During
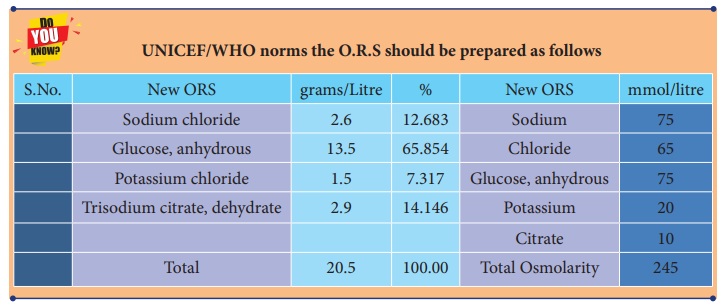
the Bangladesh liberation war, Therapy with Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) in
1971 reduced cholera death rates from 50% to 3% among thousands of refugees. An
Indian doctor, Dilip Mahalanabis, had to manage the shortage of saline bottles
and coup up with the dehydration faced by the refuges. Dr. DilipMahalanabis showed the efficacy of
ORS in cholera cases among Bangladeshi refugees (1971-72). Further field trial
during the cholera epidemic in Manipur attested to its efficacy, ORS has since
saved the lives of millions of children around the world.
Look at the above information. What
do you infer from this? Now you get the curiosity to know about ORS and its
function. Don’t you? In addition to this, let us know about some of the common
medicines and how do they work.
In the normal healthy intestine,
there is a continuous exchange of water through the intestinal wall. Up to 20 liters
of water is secreted and very nearly as much is reabsorbed every 24 hours. This
mechanism allows the absorption of soluble metabolites into the bloodstream
from digested food. However when a person becomes sick, due to diarrhea, water
is expelled and the body is not able to retain the liquid balance. This is
called as ‘dehydration’. It is not the diarrhea that kills, but the
dehydration’ resulting from the infection that kills. If more than 10% of the
body’s fluid is lost death occurs.
Related Topics