Polymer Chemistry | Term 3 Unit 3 | 7th Science - Student Activities | 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 3 : Polymer Chemistry
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 3 : Polymer Chemistry
Student Activities
ACTIVITY 1
Compare the following things. Ice cubes and a polythene bag. In both the materials, there are large number molecules combined together. Are both polymers?

Nylon is very strong and can be used for rock climbing!
Nylon is a plastic polymer made of chemical units called polyamides. olyamides are made with monomers – hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. Solid chips of these polyamides are melted and forced through a heated spinneret which has very, very tiny holes.

ACTIVITY 2
How Strong is Nylon?
Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take samples of cotton, wool, nylon and silk threads of about 50cm in length.
First tie cotton thread to the stand so that it hangs freely from it. At the free end, attach a CD as plate so that weights can be placed on it. Add weights starting from 10 grams one by one, untilthe thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the cotton thread. Repeat the same activity with the wool, silk and nylon threads.
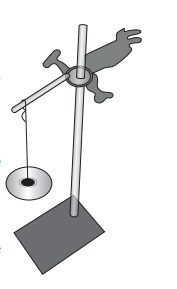
Iron clamp with a hold weights
NOTE: All the varieties of threads should be of same thickness.
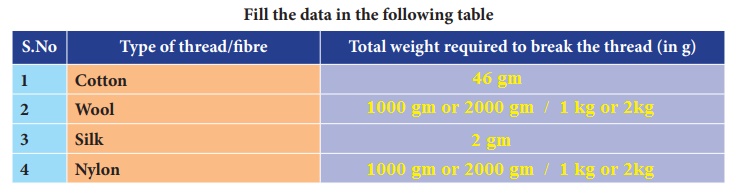
Arrange the threads in the order of increasing strength.
Answer: Cotton, Wool, Silk, Nylon.
What do you infer from the above activity?
Answer: Nylon thread is the strongest thread.
Which type of fibre is the strongest?
Answer: Nylon.
Which type of fibre is the weakest?
Answer: Cotton.
ACTIVITY 3
Identify The Fibre : Let us do an activity. Look at the images below and identify and write down the name of the different types of fibre observed.

Answer:
1. Jute -
2. cotton -
3. silk saree -
4. Rayon material -
5. wool -
6. polyester -
ACTIVITY 4
Synthetic or Natural Fibres : The teacher can give the learner a piece of each and every type of fibre. The learner can feel the fibre and write down the name of the fibre and state whether it is natural or synthetic fibre.
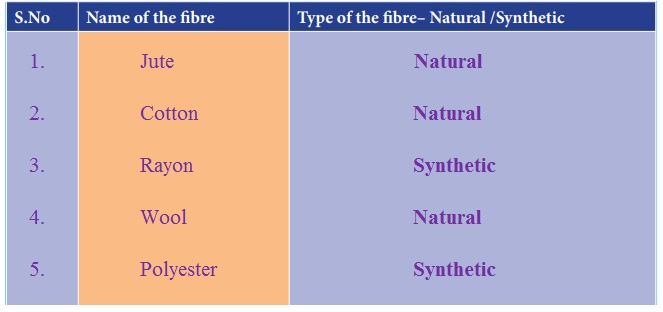
1. Jute – Natural
2. Cotton – Natural
3. Rayon – Synthetic
4. Wool – Natural
5. Polyester – Synthetic
We have done four activities so far. Which activity helped you better to identify the type of fibre? Answer: Activity 3, 4
(Both the use of familiar images as well as touch can help us to identify the different types of fibres. Right!) We have learned about fabrics such as polyester, nylon and acrylic and their common uses. These synthetic fibres are polymers which we will learn about later in this chapter.
ACTIVITY 5
Burning A Piece of natural fibre and a synthetic Fibre
Note: This activity should be performedonly by the teacher.
Take a piece of cotton cloth and a piece of polyester cloth. Both the pieces of cloth can be of same size (2cm x 2cm is enough). Hold the pieces of cloth using tongsto protect yourself from the flame and heat. Burn both the pieces of cloth one by one and see what happens when they burn.
What do you observe while the cotton cloth burns?
Answer: The cotton cloth burns completely. Does not melt and has the odour of burning paper.
What do you observe while the polyester cloth burns?
Answer: Polyester cloth melts on burning and giving off black smoke.
You must have noticed that natural (cotton) fibresburn very differentlycompared tosynthetic (polyester) fibres.

The cotton cloth will burn when it is held in flame. On the other hand, the synthetic polyester cloth will melt on burning. This is one of the disadvantages of wearing clothes madeout of synthetic fibres. If a synthetic cloth comes into contact with fire the fabric melts and sticks to the body causing severe burns. Therefore, one should not wear synthetic clothes while cooking or working in a laboratory.
ACTIVITY 6
Wetting A Cotton Cloth And An Umbrella Cloth
We use an umbrella on rainy days. What kind of umbrella do we use?
Answer: Nylon or Polyester
Can you use an umbrella made of cotton?
Let us do an activity to see why we do not use a cotton umbrella to protect ourselves from the rain. Take a piece of cotton cloth of approximately 10 cm X 10 cm size and a piece of nylon or polyester cloth 10 cm X 10 cm in size from an old unusable / untorn umbrella. Ask four students to hold the four corners of the piece of cotton cloth and pour a glass of water over it. Then ask four students to hold the piece of umbrella cloth and pour a glass of water over it. Compare the effect of water on the piece of cotton cloth and umbrella cloth and record your observation in the notebook.
Which of these fabrics allows water to pass through?
Answer: Cotton cloth allows water to pass through whereas umbrella cloth does not allow water to pass through.
Cotton cloth or Umbrella cloth (nylon or polyester) Now ask the students to put both the pieces of cloth in the hot sun to dry. Which of these fabrics dries the fastest? The cotton cloth or the umbrella cloth?
Answer: Umbrella cloth dries the fastest.
Synthetic fibres are made from the byproducts of processing petroleum oil and gas. You will learn about fractional distillation of petroleum in your higher classes.

It is estimated that every year we use a trillion plastic carry bags (2 million a minute) around the world and out of which only 1 to 3% are recycled.

Plastic has been around for less than 200 years. Edmund Alexander Parkes was the creator of the first plastic called ‘Parkesine’

ACTIVITY 7
Right and wrong application of plastics
Look at the list of eight plastic items. Decide which fourplastic itemsare used for the right application and which four are used for the wrong application by filling in the chart below:
Plastic items: straws, helmets, cutlery, thin carry bags, syringes, electrical wires,tea cups and blood bags
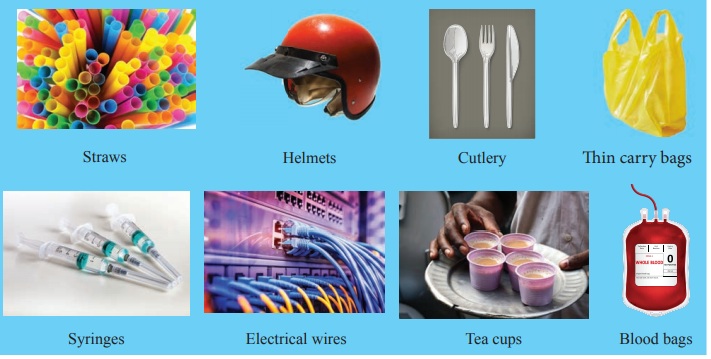
Right application : Wrong application
Helmets : Straws
Syringes : Thin carry bags
Electrical wires : Cutlery
Blood bags : Tea cups
ACTIVITY 8
Identify the different types of plastics
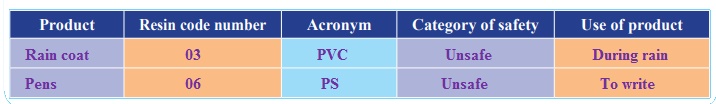
Collect different kinds of plastic products and look carefully for the resin code and/or acronym on them. With the help of the resin code chart,mark the resin code number, acronym, if you think it is a safer, unsafe or questionable (when you cannot find the resin code on the article) type of plastic. What resin codes do you find? Is the resin code safer,unsafe or questionable?
A recipe for PLA a compostable plastic!
What you need
i. 1 tablespoon of corn starch
ii. 1 teaspoon of vegetable glycerin (available at the pharmacy)
iii. 1 teaspoon of vinegar (5% acidity)
iv. 4 Tablespoons of water.
v. Cooking spoon
vi. Cooking pot
vii. Stove
viii. Aluminium foil
Method
Mix the water with the starch in a cooking pot. Add the vinegar and the glycerin. Mix all the ingredients on medium heat. Make sure you continuously stir. The mixture should turn from liquid white into a clear gel. When it begins to bubble, then it is ready and should be taken off the stove.
Spread the gel onto the aluminium foil. Let it cool down for one hour. You can then shape the material to form a cup or bowl. Let the article you made cool for another 24 hours before you try and use it.
Related Topics