Polymer Chemistry | Term 3 Unit 3 | 7th Science - Fibres | 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 3 : Polymer Chemistry
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 3 : Polymer Chemistry
Fibres
Fibres
We wear clothes, use bags, rope,
blankets, etc. in our daily life. They are made of fibres. Once upon a time,
people used natural fibres such as cotton and wool. Nowadays, we use a lot of
synthetic fibres. All natural and synthetic fibres are polymers.
Observe the difference between the
natural and synthetic fibres:
Natural Coconut Rope vs. Nylon
Fishing rope

1. Natural and Synthetic Fibres
Fibres are long strands of polymers
interwoven to form linear, string-like structures. Fibres that are obtained
from plant or animal sources are called natural fibres. Examples include
cotton, coconut fibre, hair, wool and silk. Fibres that are made using raw
materials from petroleum are synthetic fibres. Examples include polyester,
acrylic and nylon. Historically, humans used natural plant fibres and animal
fur for shelter, clothing and protection from the weather. Today, a large
variety of natural fibres are still grown and processed such as cotton, silk,
and wool. Natural fibres can be spun into filament, thread or rope. Then they
can be woven, knitted, matted or bondedand are used to make clothing,
containers, insulation materialand many other products we use in our daily
life. Three main sources of natural fibres are : (i) Animal (e.g.) wool and
silk.

The discovery of making synthetic
fibres out of petrochemicals has replaced the use of many natural fibres.
Synthetic fibres such as nylon, polyester and acrylic are used to make many
different plastic items you use in your daily life such as clothing, blankets,
tooth brushes and stuffing in cushions.
2. Types and Uses
Silk:
Natural Fibre
Natural silk fibres are obtained
from boiling the cocoons of silk worms from specific species of moths. There
are four types of natural silk: Mulberry silk, Tasar silk, Muga silk and Eri
silk. Most of the mulberry silk worldwide is produced in India. Silk is one of
the strongest natural fibres and has many uses such as clothing, carpets and
parachutes.

Rayon: A
Semi-synthetic Fibre
In the 19th century scientists were
successful in producing the first artificial silk known as rayon. The first
rayon factory in India was established in Kerala in 1946. Rayon is a man-made
fibre, but it is not considered fully synthetic as it is made out of natural
cellulose collected from wood pulp. The cellulose that is
collected from wood
or bamboo pulp is treated with several chemicals. First sodium hydroxide is
added followed by carbon disulphide. The cellulose dissolves in the chemicals
added to it and produces syrup called Viscose. Viscose is forced through a
spinneret (a device made of metal plates with very tiny holes) into a solution
of dilute sulphuric acid. This produces silk-like threads that are cleaned with
soap and dried. This new fibre is called rayon.
Some types of rayon are made from
the short cotton fibres left on cottonseeds after ginning. Rayon is cheaper
than silk, can be woven like natural silk fibre and can be dyed in a wide
variety of colours. It can be mixed with cotton to make bed sheets or with wool
in the production of carpets and home furnishing products. Rayon is also found
in sanitary products, diapers, bandages and gauze for dressing wounds.
Nylon:
Synthetic Fibre
Nylon is the first fully processed
synthetic fibre. It was popular during the Second World War for the use of
parachutes and rope materials for climbing. Nowadays, nylon has replaced
natural silk in many textiles, and has become one of the most commonly used
synthetic fibres.
Nylon fibre is strong, elastic and
light. It islustrous and easy to wash, which has made it popular for the
clothing industry.We use many products made from nylon such as socks, ropes,
tents, toothbrushes, car seatbelts, sleeping bags, curtains, etc. Nylon thread
is actually stronger than a steel wire.

Nylon is very
strong and can be used for rock climbing!
Nylon is a plastic polymer made of chemical units called
polyamides. olyamides are made with monomers – hexamethylenediamine and adipic
acid. Solid chips of these polyamides are melted and forced through a heated
spinneret which has very, very tiny holes.

ACTIVITY 2
How Strong is Nylon?
Take an iron stand
with a clamp. Take samples of cotton, wool, nylon and silk threads of about
50cm in length.
First tie cotton
thread to the stand so that it hangs freely from it. At the free end, attach a
CD as plate so that weights can be placed on it. Add weights starting from 10
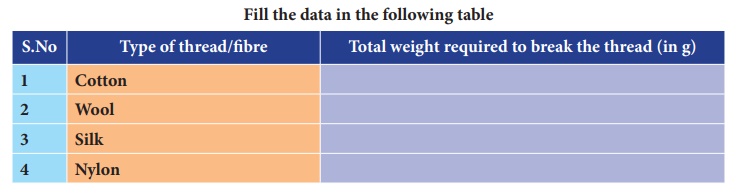
grams one by one, untilthe thread breaks. Note down the total weight required
to break the cotton thread. Repeat the same activity with the wool, silk and
nylon threads.
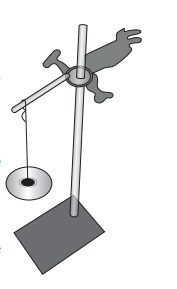
Iron clamp with a hold weights
NOTE: All the varieties of
threads should be of same thickness.
Arrange
the threads in the order of increasing strength.
Answer: Cotton,
Wool, Silk, Nylon.
What
do you infer from the above activity?
Answer: Nylon
thread is the strongest thread.
Which type of fibre is the strongest?
Answer: Nylon.
Which type of fibre is the weakest?
Answer: Cotton.
Polyester and
Acrylic:
Synthetic Fibres
Polyester is another synthetic
fibre. It can be drawn into very fine fibres that can be woven like any other
yarn. Polyester is sold in the name of polycot, polywool, terrycot, etc.
Polycot is a mixture of polyester and cotton; Polywool is a mixture of
polyester and wool. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a very familiar form of
polyester. It is used for making water and soda bottles, utensils, films and
wires amongst many other useful products. Many of the clothes we wear are made
out of polyester fibres. Fabrics made from this fibre do not get wrinkled
easily and are easy to wash making polyester fabrics suitable for dress
materials.
We wear sweaters and use shawls and
blankets in the winter. Many of these are not made from natural wool although
they appear to resemble wool. These are prepared from another type of synthetic
fibre called acrylic. The wool obtained from natural sources is quite
expensive, where as clothes made from acrylic are relatively cheap because they
are a byproduct of the production of plastics. They are available in a
variety of colours. Synthetic fibres are more durable and affordable which has
contributed to their widespread use.

ACTIVITY 3
Identify The Fibre : Let us do an activity.
Look at the images below and identify and write down the name of the
different types of fibre observed.

Answer:
1. Jute -
2. cotton -
3. silk saree -
4. Rayon material -
5. wool -
6. polyester -
ACTIVITY 4
Synthetic or Natural
Fibres : The teacher can give the learner a piece of each and every type
of fibre. The learner can feel the fibre and write down the name of the
fibre and state whether it is natural or synthetic fibre.
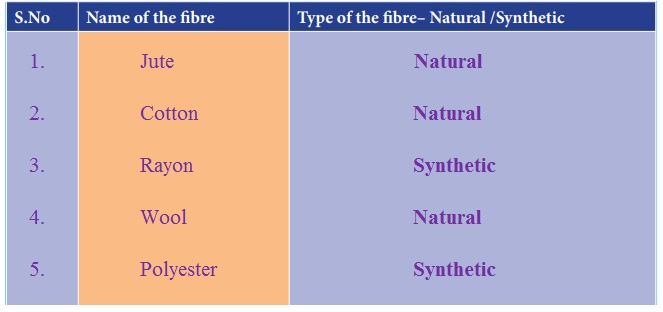
1. Jute – Natural
2. Cotton – Natural
3. Rayon – Synthetic
4. Wool – Natural
5. Polyester – Synthetic
We have done four activities so far. Which activity helped you better to identify the type of fibre? Answer: Activity 3, 4
(Both the use
of familiar images as well as touch can help us to identify the different types
of fibres. Right!) We have
learned about fabrics such as polyester, nylon and acrylic and their common
uses. These synthetic fibres
are polymers which we will learn about later in this chapter.
Related Topics