Chemistry in Daily Life | Term 3 Unit 4 | 7th Science - Flame | 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 4 : Chemistry in Daily Life
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 4 : Chemistry in Daily Life
Flame
Flame

Flame is actually a chemical reaction.
To be specific, the flame is a mixture of gases (vaporized fuel, oxygen, carbon
dioxide, carbon monoxide, water vapor, and many volatile materials) and so is
matter. The light and heat produced by the flame is energy, not matter. But
fire is a matter.
Fact
Fire chemical Reaction
Oxygen + Heat + Fuel = Fire
Flame and its
structure

Which is the festival of light? What
is the specialty of that festival? Yes. We will light more lamps to decorate
the houses. Won’t we? Now how do the lights glow? Yes, with flame.

Here is an experiment with colorful flame
*
White flame – Epsom salt (MgSO4)
*
Violet flame – Lithium Chloride
*
Indigo flame – Potassium Chloride
*
Blue flame – Bleaching powder
*
Green flame – Borax powder
*
Yellow flame – Calcium chloride
*
Orange flame – Table salt
*
Red – Strontium chloride
Teacher
shows the experiment with these salts soaked in alcohol and makes fire.
Flame:
Flame is a zone of combustions of a
combustible substance. Substances which vaporize during burning produce flames.
E.g. Wax, Kerosene etc.
Substances which do not vaporize
during burning do not produce flames e.g. coal.
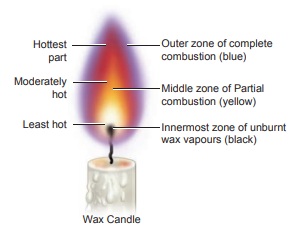
Structure of a Candle flame
A
candle flame has three main zones, theyare
i.
The outer zone – complete combustion of the fuel takes place and the colour of
the flame is blue and is the hottest part of the flame. It is the non-luminous
part of the flame.
ii.The
middle zone -partial combustions of the fuel takes place and the colour of the
flame is yellow and is moderately hot part of the flame. It is the luminous
part of the flame.
iii.
The inner zone: There are unburnt vapours of the fuel and the colour is black
and is least hot part.

A candle flame is caused by vapour burning above the candle.
This burning vapour is hotter than the surrounding air and is therefore less
dense. So, by the principle of convection, it “rises” so the flame is always
upwards
Calorific
value of different fuels
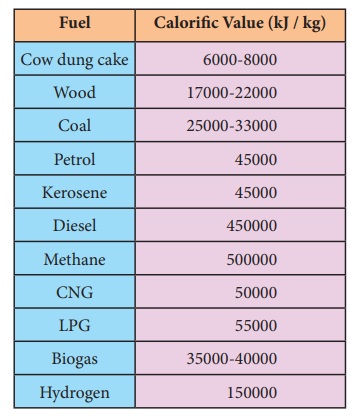
The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1kg of fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilo joule per kg (kJ/kg)
Calorific value = Heat produced / Amount of
fuel used for burning in kJ/kg
If
4.5kg of fuel is completely burnt and the amount of heat produced stands
measured at 1, 80,000 kJ what is its calorific value.
Calorific
value = 1, 80,000 / 4.5 = 40,000 KJ/Kg

Related Topics