Chapter: Biochemistry: Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane: Viscosity
Viscosity
If two tubes, one containing water and the other
containing castor oil are tilted together, the latter will flow slowly, when
compared to the former. This is because of the frictional force that exists
between liquid layers. This resistance for the flow of the liquid is termed as
Viscosity.
Viscosity is defined as the internal resistance
against the free flow of a liquid to the frictional forces between the fluid
layers moving over each at different velocities. Each and every liquid has its
own characteristic viscosity co-efficient. The co-efficient of viscosity of a
liquid is defined as the force in dynes required to maintain the streamline
flow of one fluid layer of unit area over another layer of equal area separated
from one another by 1 cm at a rate of 1cm/sec. Viscosity is measured in poises
or millipoises.
Factors affecting viscosity
1. Density
Density and viscosity are directly proportional
to each other. They are related by Stoke’s law. If a small sphere of radius ‘r’
and density ‘r’ falls vertically through a liquid with the density ‘r’at a
steady velocity ‘u’, inspite of the acceleration due to gravity (g), the co-efficient
of viscosity and density are related as follows.
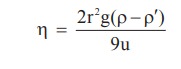
2. Temperature
Temperature and viscosity are inversely related
to each other. As temperature increases, viscosity of the liquid decreases.
3. Solute
Dissolved substances in the pure solvent
increases the viscosity of the solvent.For eg.a protein solution is highly
viscous than pure water. Size and Shape of the solute particles also affect the
viscosity of the solution.
Biological Applications
·
Carbohydrate
and protein solutions are highly viscous in nature.
·
Blood
plasma has a normal viscosity of 15 – 20 mpoises. Alterations in the viscosity
is an indication of diseased condition. Viscosity increases during
macroglobulinemia, retinal hemorrhages and congestive heart failure.
·
Viscosity
of blood is 30 – 40 mpoises and is due to the red blood cells. Viscosity of
blood decreases during anemia.
·
Blood
viscosity is useful in streamlining the blood flow.
·
The
lubricating property of the synovial fluid is achieved mainly by the viscous nature
of the mucopolysaccharides present in the synovial fluid.
Related Topics