Chapter: Biochemistry: Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane: Chemical Composition
Chemical Composition
To study the chemical composition of the cell
membrane, the preferred source is RBC, because they lack cell organelles and
thus no contamination of other cellular organelle membranes. The membranes of
the RBCs devoid of cytosol are called as ‘ghosts’.
Four major constituents are present in the cell
membrane. They are (i) lipids (28 – 79%) (ii) proteins (20 – 70%). (iii)
oligosaccharides (only 1 – 5%) and (iv) water (20%).
Lipids
Depending upon the tissue from which the cell
membrane is isolated, the composition also differs. Nearly 80% of the myelin
sheath is made up of lipids, while in liver, it constitutes only 28%.
The main lipid components of the membranes are
phospholipids, cholesterol and glycolipids. The major phospholipids present are
phophatidyl choline (lecithin), phophatidyl ethanolamine, phophatidyl serine
and phophatidyl inositol.
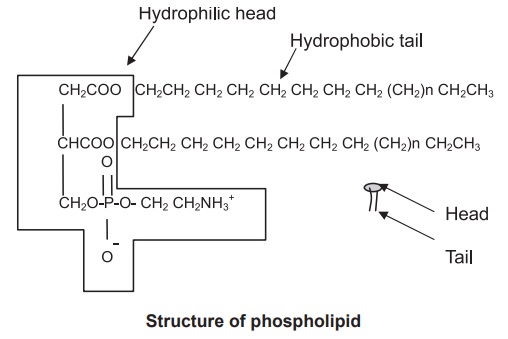
Membrane lipids are amphipathic in nature and
they have a head portion, which is hydrophilic and a tail portion which is
hydrophobic. As the membranes are exposed to the hydrophilic environments, the
lipids arrange themselves to form a bilayer in which the hydrophobic core is
buried inside the membrane.
Proteins
All the major functions of the plasma membrane
are executed by the proteins present in the membrane. Proteins account for
about 20 – 70% of the membrane depending on the type of the cell. They can be
classified into two types. Integral membrane proteins and peripheral membrane
proteins.
Integral Proteins
Some of the membrane proteins are tightly
embedded in the membrane and they cannot be isolated unless, the membrane is
disintegrated. They are called as Integral or Intrinsic membrane proteins. They
are again classified into two. (a). Transmembrane proteins, which traverse
(pass through) or span the membrane. These proteins will have domains on either
side of the membrane. Many cell surface receptors belong to this class. (b).
Lipid anchored proteins that are present either on the cytosolic side or on the
extracytosolic side. They insert themselves in the membrane by a lipid (acyl
chain) attached to the N terminal end.
Transmembrane proteins are of two types. Single
pass transmembrane proteins that traverse the membrane only once.Multipass
transmembrane proteins that traverse the membrane more than once.
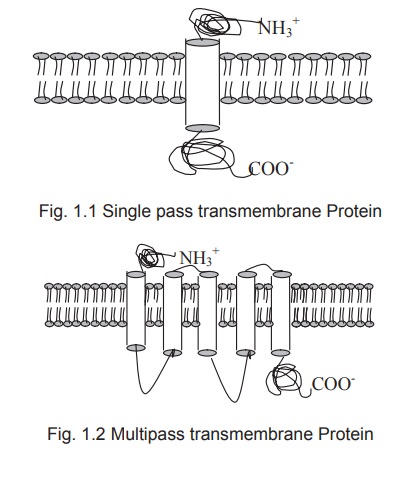
Peripheral Proteins
Those proteins that are present on the surface
of the membrane are called as peripheral proteins. They can be easily isolated
from the membrane. eg. spectrin present in the RBC membrane.
Related Topics