Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 1 : Fundamentals of Geography
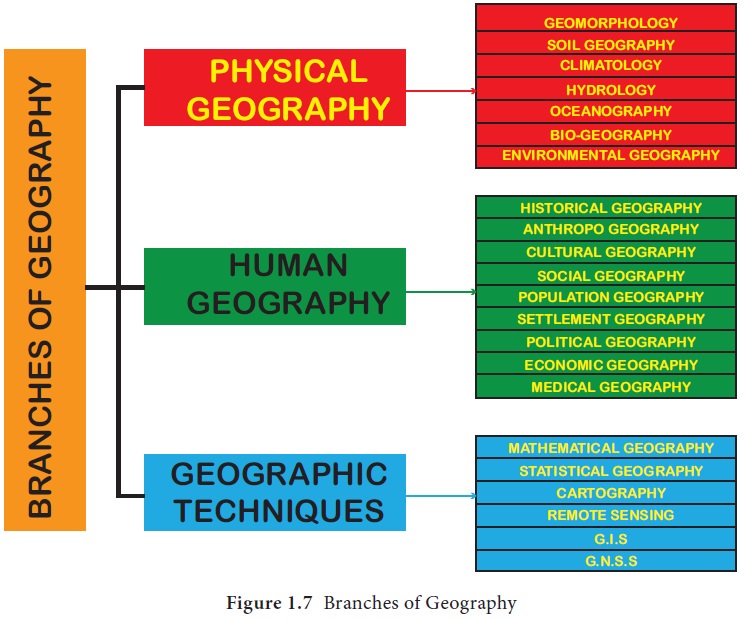
Branches of Geography
Branches
of Geography
Based on content and the available techniques, the
discipline can be divided into three major domains. Each one has many sub
divisions which deal with specific objectives (Figure 1.7). a. Physical Geography b. Human Geography
and c. Geographic Techniques.
Physical Geography
It is the study of natural features of the earth
such as land, water, air and living organisms. The changes taking place within
and among these natural features and their resultant features are studied under
its various branches. The branches of physical geography are:
1.
Geomorphology deals
with the distribution of land forms, their origin and the
forces causing changes over these landforms. Geology provides basic information
to the study of geomorphology.
2.
Soil Geography is a
study related to soil formation, soil profile, soil
types, their fertility level and distribution. Soil erosion and conservation
measures are also dealt in this branch.
3.
Climatology deals
with the study of global and regional weather and
climatic conditions by analysing relevant statistical data. Meteorology
provides basic information on the composition, structure and the changes in the
atmosphere.
4.
Hydrology encompasses
the study of earth’s realm of water such as oceans and surface
water bodies like rivers, reservoirs and ponds. It also makes a study of
underground water and its recharge and also pollution of water bodies.
5.
Oceanography is the
study of seas and oceans. The shape, size, depth
and bottom relief of ocean, distribution of oceans, ocean currents and various
6.
Biogeography is a
study of ecosystems over geographical space. It also
analyses the changes in the ecosystems. Phytogeography
or plant Geography, Zoo Geography or
animal geography and Ecology are the
branches of biogeography.
7.
Environmental Geography is the study of
environmental issues arising out of misuse of various spheres of the earth and
their implications. The ozone layer depletion, global warming, melting of polar
ice caps, rising sea level and other related aspects are also given due
importance. It also tries to give sustainable solutions to these problems.
Human Geography
Human Geography is concerned with the changes made
by the humans over the natural or physical landscape. The ethnic and political
aspects are taken into consideration. The issues like climatic change, natural
and anthropogenic disasters are also the major concerns.
1.
Population Geography is the study of distribution and density of population, the
changing patterns in age and sex composition, birth and death rates, life
expectancy, literacy level and dependency ratio, migrations at national and
international level and the causes and consequences of migration.
2.
Settlement Geography deals
with the characteristics of rural and urban settlements and
transportation network. It seeks better understanding of the present landscape
and plans for the future. The study is more important for town and country
planning.
3.
Historical Geography tries to picturise the geography of an area or region as it
was in the past and studies how it has evolved over time. The forces involved
in transforming region such as colonisation by the Europeans or a natural
disaster are also included in the study.
4.
Anthropo Geography deals
with the distribution of human communities on the earth in
relation to their geographical environment.
5.
Cultural Geography gives
emphasis on the location and diffusion of customs and
cultural traits such as food habits, skills, clothing and beliefs and social
organisations and their developments in different parts of the earth.
6.
Social Geography is
closely related to cultural geography. It examines
the relationships among the social groups and their social relationships in the
places of their living.
7.
Political Geography tries
to understand the countries and their neighbours,
problems of resources sharing, boundaries and territorial limits. This branch
is also concerned with understanding the political behaviour of the population,
relations between independent states, and patterns of voting and delimitation
of electoral constituencies.
8.
Economic Geography deals
with the distribution of economic activities such as,
primary, secondary and tertiary. The primary activities include food gathering,
hunting, animal rearing, agriculture, and mining. The secondary activities
include manufacturing and the tertiary activities include the service sectors
such as trade, transport, communication and other related areas.
9.
Medical Geography mainly
deals with study of geographical aspects of origin,
diffusion and distribution of various communicable diseases and health care
planning.
Geographic Techniques
Geography has developed a number of methods and
tools to investigate and identify the spatial structures and patterns. Besides,
it also lends or borrows some methods and tools to measure and investigate
precise understanding of the spatial locations and patterns.
1.
Mathematical Geography deals
with the study of earth’s size and shape, motions of the
earth, concept of time and the time zones.
2.
Statistical Geography is
concerned with the practice of collecting, analysing and
presenting data that has a geographic or areal dimension, such as census data.
3.
Cartography is the
study of making maps of various scales using
authentic information.
4.
Remote Sensing is the
art, science and technique of capturing the earth surface
features using sensors or cameras in airplanes or satellites, processing and
presenting the spatial information tousers.
5.
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer-based tool of the recent decades for geographical studies. It is
used for storing, retrieving, transforming, analysing, and displaying data to
prepare useful thematic maps.
6.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is used to pinpoint the geographic
location of a user anywhere in the world. Airlines, shipping, travel agencies
and automobile drivers use the system to track the vehicles and follow the best
routes to reach the destination in the shortest possible time.
Global Navigation Satellites System
GNSS is the standard generic term
for satellite navigation systems that provide geo-spatial positioning
with global or regional coverage. This term includes the GPS (USA), GLONASS
(Russia), Galileo (Europe), Beidou (China), IRNSS (India) and other systems.
The GPS was the first GNSS system of the United States and originally used for
military applications. Today it is commonly used in mobiles, vehicles,
agriculture and other areas that allow us to use it in all fields of mapping.
Geography is undergoing frequent changes to tackle
the challenges of the dynamic world. The subject is more flexible and
accommodates many principles of related subjects. At the same time, it lends
concepts and knowledge to many related disciplines. Owing to these changes, the
subject is attaining more refinement, accuracy, precision, depth and scientific
rationale.
Related Topics