Chapter: Organic Chemistry: Structure and bonding
Bonds and hybridized centers
BONDS AND HYBRIDIZED CENTERS
Key Notes
σ and π bonds
Every
bond in an organic structure is aσ bond or a π bond. Every atom in a structure is linked to
another by a single σ bond.
If there is more than one bond between any two atoms, the remaining bonds are π bonds.
Hybridized centers
All
atoms in an organic structure (except hydrogen) are either sp, sp2 or sp3 hybridized. Atoms linked by single bonds are sp3 hybridized, atoms linked
by double bonds are sp2
hybridized* and atoms linked by triple bonds are sp hybridized.*
Shape
sp3Hybridized
centers are tetrahedral, sp2hybridized
centers are trigonal planar and sp
centers are linear. This determines the shape of functional groups. Functional
groups containing sp2 hybridized
centers are planar while functional groups containing sp hybridized centers are linear.
Reactivity
Functional
groups containing π bonds
tend to be reactive since the π bond is weaker than aσ bond and is more easily broken.
σ and π bonds
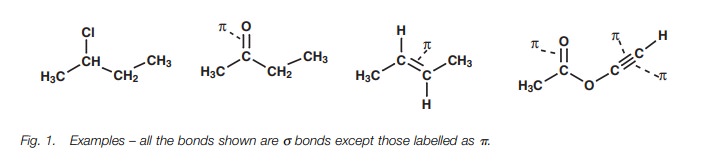
Identifying σ and π bonds in a molecule (Fig. 1) is quite easy as long as you remember the following rules:
·
all bonds in organic structures are either sigma (σ) or pi (π) bonds;
·
all single bonds are σ bonds;
·
all double bonds are made up of one σ bond and one π bond;
·
all triple bonds are made up of one σ bond and two π bonds.
Hybridized centers
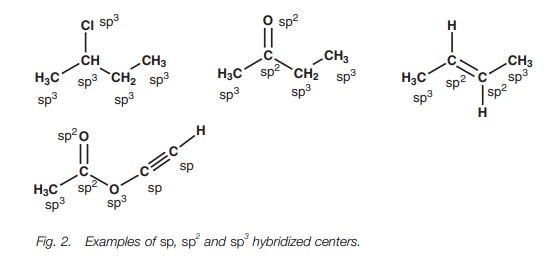
All the atoms in an organic structure (except
hydrogen) are eithersp sp2or sp3
hybridized (Fig. 2).
The identification of sp, sp2 and sp3 centers is simple if you
remember the following rules:
·
all atoms linked by a single bond are sp3 hybridized (except hydrogen).
·
both carbon atoms involved in the double bond of an alkene (C=C)
must be sp2 hybridized.*
·
both the carbon and the oxygen of a carbonyl group (C=O) must be sp2 hybridized.
·
all aromatic carbons must be sp2
hybridized.
·
both atoms involved in a triple bond must be sp hybridized.
·
hydrogen uses a 1s
orbital for bonding and is not hybridized.
Hydrogen atoms cannot be hybridized. They can
only bond by using an s orbital since
there are no p orbitals in the first
electron shell. It is therefore impossible for a hydrogen to take part in π bonding. Oxygen, nitrogen and halogens on the other hand can form
hybridized orbitals which are either involved in bonding or in holding lone
pairs of electrons.
Shape
The
shape of organic molecules and the functional groups within themis determined
by the hybridization of the atoms present. For example, functional groups
containing trigonal planar sp2 centers are planar while functional groups
containing sp centers are linear:
● planar functional groups
– aldehyde, ketone,
alkene, carboxylic acid,
acid chloride, acid anhydride, ester, amide, aromatic.
● linear functional groups – alkyne, nitrile.
● functional groups with tetrahedral carbons – alcohol, ether, alkyl
halide.
Reactivity
Functional groups which contain π bonds are reactive since the π bond is weaker than aσ bond and can be broken more easily. Common
functional groups which contain πbonds are aromatic rings,alkenes,alkynes,
aldehydes,ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, acid chlorides, acid
anhydrides, and nitriles.
Related Topics