Chapter: Mobile Networks : Wireless Networks
Bluetooth
BLUETOOTH
INTRODUCTION
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data
over short distances (using short-wavelength radio transmissions in the ISM
band from 2400–2480 MHz) from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area
networks (PANs) with high levels of security. Different type of
network is needed to connect different small
devices in close proximity (about 10 m) without expensive wiring or the need
for a wireless infrastructure .Bluetooth is a new standard suggested by a group
of electronics manufacturers that will allow any sort of electronic tools from
computers and cell phones to keyboards and headphones to make its own
connections, without wires, cables or any direct action from a user. A key
distinction with other offered wireless technologies is that bluetooth enables
combined usability models based on functions provided by different devices.
Bluetooth was invented in1994 by L.M.Ericson of Sweden. The name is attributed
to Harald Bluetooth was king of Denmark around the turn of the last millennium.
Choosing this name for the standard indicates how important companies from the
Baltic region (nations including Denmark, Sweden, Norway and Finland) are to
the communications industry.
As famous
as the name is the bluetooth symbol. Bluetooth icon can be recognized by all.
The main strength of bluetooth is its ability to simultaneously handle both
data and voice transmissions. It is capable of supporting one asynchronous data
channel and up to three synchronous voice channels, or one channel sup-porting
both voice and data. This ability combined with ad hoc device connection and
automatic service discovery make it a superior solution for mobile devices and
Internet applications. This grouping allows such novel solutions as a mobile
hands-free headset for voice calls, print to fax capability, and automatically
synchronizing PDA, laptop, and cell phone address book applications.
BLUETOOTH FEATURE:
It is Wireless
and automatic
Bluetooth
is inexpensive (< $5 per unit) It Handles both data and voice
Signals
are omni-directional and can pass through walls and briefcases Bluetooth uses
frequency hopping at rate of 1600 Lops/sec
It
operates on 79 channels in 2.4GHZ band with 1MHZ carrier spacing Pi-conet is
the important terminology
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
Piconet:
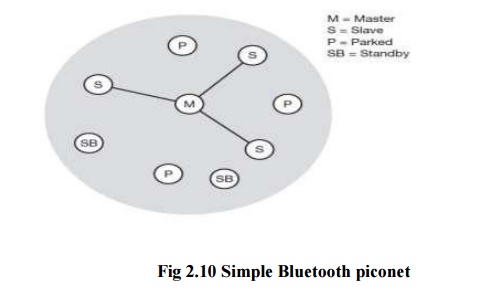
A set of
bluetooth devices sharing a common channel is called piconet. A piconet is a
collection of devices connected via Bluetooth technology in an ad hoc fashion.
A piconet starts with two connected devices, and may grow to eight connected
devices. All Bluetooth devices are peer units and have identical
implementations. However, when establishing a piconet, one unit will act as a Master
and the other(s) as slave(s) for the duration of the
piconet connection. Master is a Bluetooth device that sets the frequency hopping
sequence. The Slave synchronizes to the Masters in time and frequency by
following the Master‘s frequency hoping sequence. Every Bluetooth device has a
unique
Bluetooth
device address and a 28-bit Bluetooth clock. The baseband part of the Bluetooth
System uses a special algorithm, which calculates the frequency hop sequence
from the masters clock and device address. In addition to controlling the
frequency hop sequence, the Master controls when Slaves are to transmit using
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM).
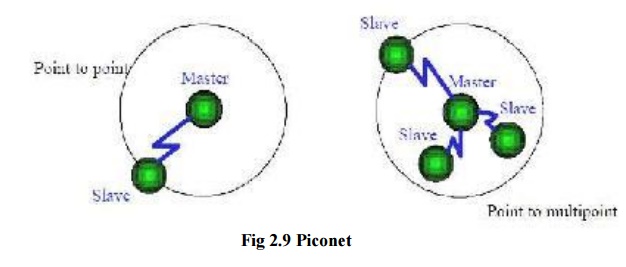
When
there is just one Master and one Slave the system is called a Point to Point connection. When many Slaves are connected to one Master, the
system is called a Point to Multipoint. Both these types
are referred to as a Piconet and all
follow the frequency hopping sequence of the Master. The Slaves in the Piconet
only have links to the Master and no direct links between Slaves.
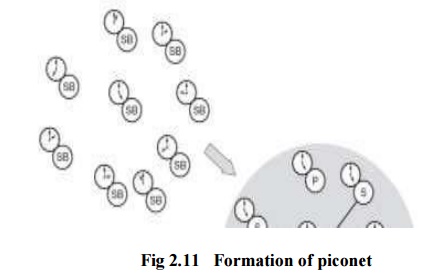
Formation of piconet:
Two
parameters are needed for the formation of piconet
Hopping
pattern of the radio it wishes to connect.
Phase
within the pattern i.e. the clock offset of the hops.
The
global ID defines the hopping pattern. The master shares its global ID and its
clock offset with the other radios which become slaves. The global ID and the
clock parameters are exchanged using a FHS (Frequency Hoping Synchronization)
packet.
There is
no difference between terminals and base stations, two or more devices can form
a piconet. The unit establishing the piconet repeatedly becomes the master, all
other devices will be slaves. The hopping pattern is determined by the device
ID, a 48-bit worldwide unique identifier. The phase in the hopping pattern is
determined by the master‘s clock. After altering the interior clock according
to the master a device may take part in the piconet. All active devices are
assigned a 3-bit active member address
(AMA). All parked devices use an 8-bit parked
member address (PMA). Devices in stand-by do not need any address. All
users within one piconet have the same hopping sequence and share the same 1
MHz channel. As more users join the piconet, the throughput per user drops
quickly.
Scatternet :
Bluetooth
defines a structure called scatternet to facilitate inter piconet
communication. A scatternet is formed by interconnecting multiple piconet. A
group of piconet is called scatternet.
If a
device wants to take part in more than one piconet, it has to coordinate to the
hopping sequence of the piconet it wants to take part in. If a device acts as
slave in one piconet, it just starts to synchronize with the hopping sequence
of the piconet it wants to join. After synchronization, it acts as a slave in
this piconet and no longer participates in its former piconet. To permit
synchronization, a slave has to know the uniqueness of the master that
determines the hopping sequence of a piconet. Before leaving one piconet, a
slave informs the current master that it will be unavailable for a certain
amount of time.
The left
over devices in the piconet continue to communicate normal.
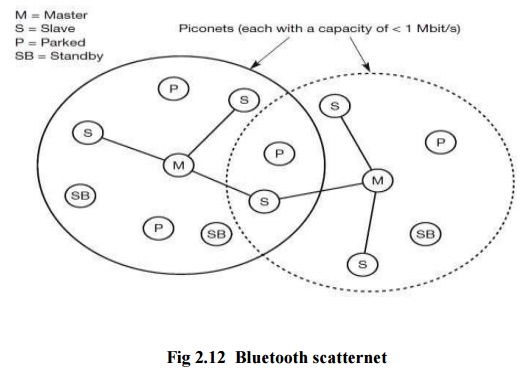
A master
can also go away from its piconet and act as a slave in another piconet. It is
obviously not possible for a master of one piconet to act as the master of
another piconet as this would direct to identical behavior. As soon as a master
leaves a piconet, all traffic within this piconet is balanced until the master
returns. Communication between different piconets takes place by devices
jumping back and forth between these nets. If this is done occasionally, for
instance, isochronous data streams can be forwarded from one piconet to
another. On the other hand, scatternets are not yet supported by all piconet.
BLUETOOTH PROTOCOL STACK
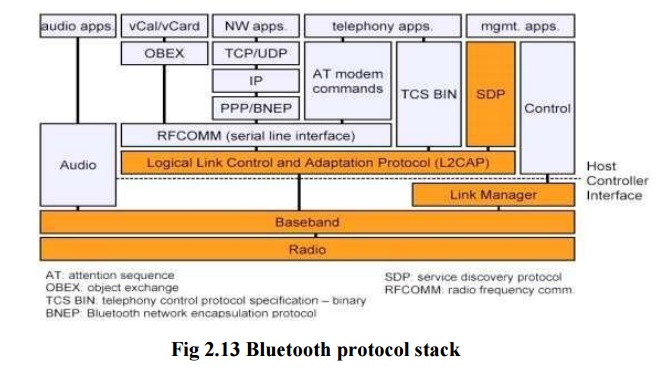
The
Bluetooth protocol stack can be divided into:
Core
Specification -Deals with the lower layers of the architecture
and describes how the technology
works. It describe the protocol from physical to data link layer along with
management functions.
Profile
Specification -Focuses on how to build interoperating devices
using the core technology.
Bluetooth
Radio : specifics details of the air interface, including frequency, frequency hopping, modulation scheme,
and transmission power.
Baseband:
concerned with connection establishment within a piconet, addressing, packet format, timing and power control.
Link
manager protocol (LMP): establishes the link setup between Bluetooth devices and manages ongoing
links, including security aspects (e.g. authentication and encryption), and
control and negotiation of baseband packet size
Logical
link control and adaptation protocol (L2CAP): adapts upper layer protocols to the baseband layer.
Provides both connectionless and connection-oriented services.
Service
discovery protocol (SDP): handles device information, services, and queries for service characteristics
between two or more Bluetooth devices.
Host Controller Interface (HCI): provides
an interface method for accessing
the Bluetooth hardware capabilities. It contains a command interface, which
acts between the Baseband controller and link manager
TCS BIN
(Telephony Control Service): bit-oriented protocol that defines the call control signaling for the
establishment of voice and data calls between Bluetooth devices.
OBEX(OBject
EXchange) : Session-layer protocol for the exchange of objects, providing a model for object and operation representation
RFCOMM: a
reliable transport protocol, which provides emulation of RS232 serial ports over the L2CAP protocol
WAE/WAP:
Bluetooth incorporates the wireless application environment and the wireless application protocol into its architecture.
Physical links
Different
types of links can be established between master and slave. Two link types have
been defined they are:
Synchronous
Connection-Oriented (SCO) link. Asynchronous Connection-Less (ACL) link.
1.Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO): It
Support symmetrical, circuit-switched, point-to-point connections . It is
typically used for voice traffic. The Data rate is 64 kbit/s.
2.Asynchronous Connection-Less (ACL): It
Support symmetrical and asymmetrical,
packet-switched, point-to-multipoint connections. It is typically used for data
transmission .Up to 433.9 kbit/s are used in symmetric or 723.2/57.6 kbit/s are
used in asymmetric. The master uses polling. A slave may answer if it has used
the preceeding slot.
Connection establishment states:
Standby : The State in which Bluetooth
device is inactive, radio not switched on,
enable low power operation.
Page : The Master enters page state
and starts transmitting paging messages to
Slave using earlier gained access code and timing information.
Page Scan : The Device periodically enters
page state to allow paging devices to establish
connections.
Inquiry: The State in which device tries
to discover all Bluetooth enabled devices
in the close vicinity.
Inquiry scan : Most
devices periodically enter the inquiry scan state to make themselves available to inquiring devices.
Slave connection state modes:
Active –It
participates in piconet It Listens, transmits and receives frames
Sniff – It only
listens on specified slots
Hold –It does
not support ACL frames. It has reduced power status. It May still participate in SCO exchanges
Park – It does not
participate on piconet and it Still retained as part of piconet
Bluetooth security:
There are
three modes of security for Bluetooth access between two devices.
Non-secure
Service level enforced security Link level enforced security
The following
are the three basic security services specified in the Bluetooth standard:
Authentication : It
verify the identity of communicating devices. User authentication is not provided natively by Bluetooth.
Confidentiality : It
prevent information compromise caused by eavesdropping by ensuring that only authorized devices can access and view data.
Authorization :It allow
the control of resources by ensuring that a device is authorized to use a service before permitting it to do so.