Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Biological value of protein
BIOLOGICAL VALUE OF PROTEIN
Biological value of protein is the
percentage of a protein nitrogen that is absorbed and available for use by the
body for growth and maintenance.
Proteins are functionally divided into complete, partially
complete and incomplete proteins. A complete protein contains all essential
amino acids in relatively the same amounts as human beings require to promote
and maintain normal growth. (eg) Protein derived from animal foods. A partially
complete protein contains sufficient amounts of amino acids to maintain life
but fail to promote growth. (eg) Gliadin in wheat. Incomplete proteins are
incapable of replacing or building new tissue and cannot support life or
growth. (eg) Protein in Wheat germ.
The quality of a protein is determined by the kind and
proportion of amino acid it contains. Proteins that contain all essential amino
acids in proportions capable of promoting growth are described as complete protein,
good quality protein, or proteins of high biological value.
A
good quality protein is digested and utilized well. Egg protein is a complete
protein and is considered as a reference protein with the highest biological
value. The quality of other proteins is determined based on their comparison
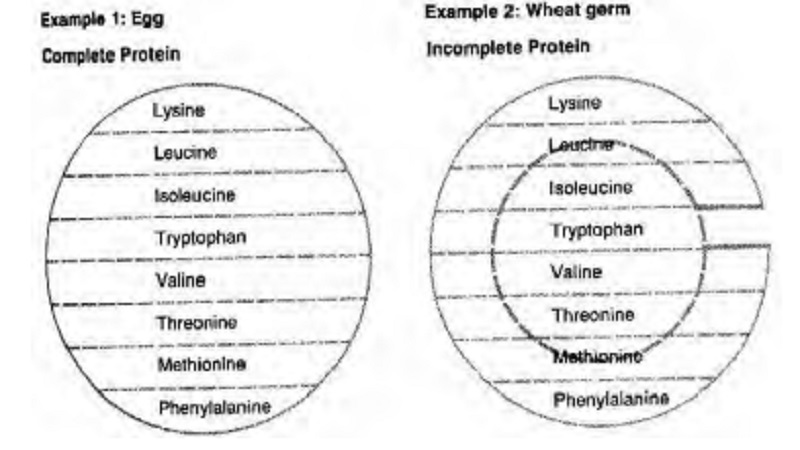
with egg protein as in figure.
The eight essential amino acids (EAA)
must be present in a protein in specific ratios. Egg protein has all eight in
the correct proportions used most efficiently and completely by the body.
Wheat germ is an incomplete protein
because it is deficient in tryptophan (incomplete circle). As a result of this
deficiency only less of the total protein can be used (as represented by the
inner dotted circle).
The protein of animal foods like milk, meat, and fish
generally compare well with egg in the essential amino acid composition and are
categorized as good quality proteins.
Plant proteins are of poor quality, since the essential
amino acid composition is not well balanced.
The
amino acid, which is not present in sufficient amount in food protein, is
called the limiting amino acid of that food. For (eg) Lysine in cereal protein,
Tryptophan in Wheat germ.
Biological
value of food proteins.
Food
Stuff Biological Value
I Animal
Protein
Egg 96
Milk 90
Meat 74
Fish 80
II Vegetable
Protein
Cereals
Rice 80
Wheat 66
Maize 50
III Pulses
Bengal
gram 74
Red
gram 72
IV Oil
Seeds
Ground
nut 55
Gingelly 62
The limitation in cereals can be
overcome by a judicious combination with pulses, which are rich in lysine.
The resulting mixture of cereals and pulse will have an
amino acid pattern better than either of the constituents. Thus a combination
of cereal and pulse has a supplementary effect. For (eg) recipes like, Pongal,
Idli, dhokla are based on cereal pulse combination.
Thus the habitual diets in India
based on cereal and pulse have indeed a rational basis. The biological value of
some important food proteins is given in table-18A.
Related Topics