Physical properties, Chemical properties, Uses of Acids - Bases | 8th Science : Chapter 14 : Acids and Bases
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 14 : Acids and Bases
Bases
Bases
We use soaps for bathing as well as
washing. Soaps are slippery in nature. Do you know why? Soaps are slippery due
to the presence of ‘base’. Bases are chemical substances that are corrosive and
bitter in taste. A lot of bleaches, soaps, detergents, toothpaste, etc. ,
contain bases. In contrast to acids which release hydrogen ions in water, bases
release hydroxide ions in water.
Thus, the chemical substances that
release hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called as bases. Examples:
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and Potassium hydroxide (KOH).
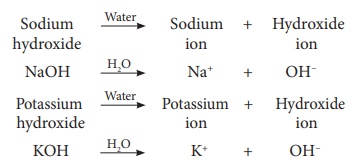
Water soluble bases are called
Alkalis. Bases like sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide
and ammonium hydroxide are highly soluble in water and hence they are called
alkalis. Certain chemical substances which do not release hydroxide ions when
dissolved in water also behave as bases. Examples: Sodium carbonate, Sodium
bicarbonate, Calcium carbonate etc.
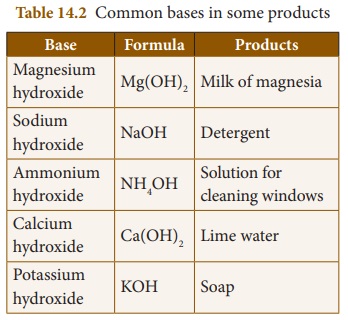
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
is commercially called as washing soda. Similarly sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
is commercially called as baking soda. Caustic soda is sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and
caustic potash is potassium hydroxide (KOH).
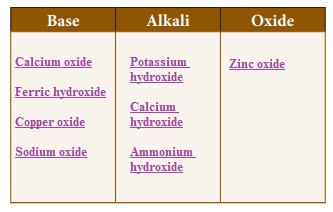
Activity 3
Classify the following
substances.Sodium oxide, Potassium hydroxide, Calcium oxide, Copper oxide, Calcium
hydroxide, Ammonium hydroxide, Ferric hydroxide, Zinc oxide
Properties of Bases
a. Physical properties
• Bases generally exist in solid state
but some bases exist in liquid state also. E.g. Ammonium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide
• Bases give soapy touch only in aqueous
medium not in dry nature.
• Bases are bitter in taste.
• Bases are corrosive in nature.
When come in contact with the skin frequently they form painful blisters.
• Bases are generally colourless
• Bases also change the colour of
the indicators. Red litmus paper turns blue when treated with bases. Similarly,
they turn methyl orange to yellow and phenolphthalein to pink colour
• Bases also conduct electricity in aqueous
solution.
b. Chemical properties
i.
Reaction with metals
Generally metals do not react with
bases. Metals like aluminium and zinc react with bases like sodium hydroxide
forming aluminates and release hydrogen.
Aluminum + Sodium hydroxide + Water
→ Sodium aluminate + Hydrogen
2Al + 2NaOH + 2H2O → 2NaAlO2+
3H2↑
ii. Reaction
with non-metal oxides
All bases react with non metallic
oxides to form salt and water. For example, sodium hydroxide reacts with carbon
dioxide to form sodium carbonate.
Sodium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide →
Sodium carbonate + Water
2NaOH + CO2 → Na2CO3
+ H2O
iii. Reaction
with ammonium salts
Bases react with ammonium salts to
form metal salts, ammonia gas and water.
Sodium hydroxide + Ammonium chloride
→ Sodium chloride + Ammonia + Water
NH4Cl + NaOH → NaCl + NH3↑
+ H2O
Though acids and bases have some
unique properties there are certain similarities between them. Some of them are
given below.
* They are corrosive in nature.
* They undergo ionization in aqueous
solution
* They conduct electricity in
aqueous solution.
* They undergo neutralization
reaction.
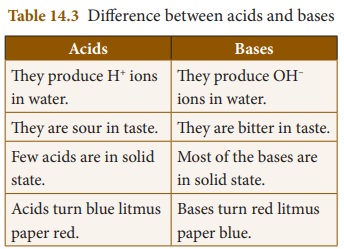
* Some of the differences between
acids and bases are given in Table 14. 3.
Uses of Bases
i. Potassium hydroxide is used to
make bathing soaps.
ii. Sodium hydroxide is used to make
washing soaps.
iii. Sodium hydroxide is also used
in paper industries, textile industries and in the preparation of medicines.
iv. Calcium hydroxide is used for
white washing.
v. Aluminum hydroxide and magnesium
hydroxides are used in antacids to cure acidity problems.
vi. Ammonium hydroxide is used to
manufacture fertilizers, nylon, plastics and rubber.

Related Topics