Physical properties, Chemical properties, Uses of Acids - Acids | 8th Science : Chapter 14 : Acids and Bases
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 14 : Acids and Bases
Acids
Acids
The term acid is derived from the
Latin word ‘acidus’ which means sour. Thus, the chemical compounds which have
sour taste are generally called as acids. All acids contain one or more
replaceable hydrogen atoms in their molecules and when dissolved in water they
release H+ ions. For example, Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
and Nitric acid (HNO3) release hydrogen ions (H+) when
dissolved in water.
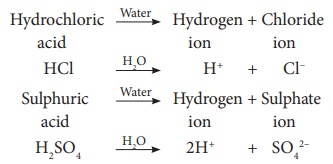
Hydrochloric acid --Water→
Hydrogen ion + Chloride ion
HCl ---H2O→ H+ + Cl–
Sulphuric acid --Water→ Hydrogen
ion + Sulphate ion
H2SO4 ---H2O→ 2H+ + SO42–
Swedish chemist Svante
Arrheniu proposed a theory on acids. According to him,an acid is a substance
which furnishes H+ ions or H3O+ ions in
aqueous solution.

Thus, acids are defined as the
chemical substances which release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
Acids can be classified into organic
acids and inorganic acids depending on the sources. Some acids occur naturally
in fruits and vegetables. These are called organic acids. Examples: Citric
acid, tartaric acid etc. ,
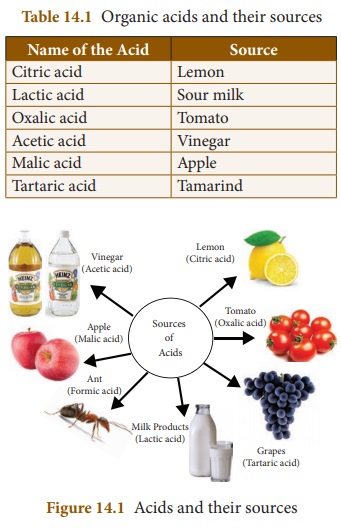
On the other hand, acids are
produced artificially in industries. These acids are called mineral acids or
inorganic acids. Examples: Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4),
Nitric acid (HNO3) etc. , There are many more classifications of
acids. You will study about them in your higher classes.
Properties of Acids
a. Physical properties
Acids are sour in taste.
* They are corrosive in nature.
Strong acids can spoil substances like human skin, clothes and paper.
* Generally acids exist in liquid
state but few acids exist in solid state as well. E.g. Benzoic acid
* Acids are colourless.
* Acids change the colour of the
indicators. Blue litmus paper turns red and methyl orange turns pink when
treated with acids.
* They are soluble in water.
* Solutions of acids conduct
electricity due to ionisation in water.

We feel hungry due to thecorrosive
action of hydrochloric acid on the inner lining of the stomach. When the level
of hydrochloric acidgoes higher, it causes ulcer.
b. Chemical properties
i. Reaction
with metals
Metals like zinc, magnesium,
aluminum, iron etc. , react with acids like hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid
to form metal salts and release hydrogen gas.
Metal + Dilute acids → Metal salt +
Hydrogen
Examples
Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc
chloride + Hydrogen
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2↑
Iron + Sulphuric acid → Ferrous sulphate +
Hydrogen
Fe + H2SO4 →
FeSO4 + H2↑
Activity 1
Take a clean test tube
with holder and pour some dilute hydrochloric acid. Add few pieces of magnesium
ribbon slowly. What do you observe? Now show a burning match stick near the
mouth of the test tube. Do you hear any sound? The gas burns with a pop sound. From
this it is observed that hydrogen gas is formed due to the reaction between
acid and metal (Do it under the supervision of the teacher).
Copper or brass
cooking vessels are coated with tin metal (eyam). If it is not coated the
organic acids present in the food materialswill react with copper and make the
food poisonous. The tin isolates the vessel from the action of acids and
prevents food poisoning.
Answer: The gas burns with a pop sound. From this it is observed that hydrogen
gas has been formed due to the reaction between acid and metal.
ii. Reaction
with metal carbonates and bicarbonates
When carbonates and bicarbonates
come into contact with dilute acids carbon dioxide is given out along with
water. For example, limestone (calcium carbonate) reacts with dilute sulphuric
acid to form calcium sulphate, carbon dioxide and water.
Calcium carbonate + dil Sulphuric acid →
Calcium sulphate + Carbon dioxide + Water
CaCO3 + H2SO4
→
CaSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Activity 2
Take some lemon juice
in a tumbler and add baking soda slowly. What do you see? What do you infer
from this?
Answer:
Inference : When lemon juice is mixed
with baking soda, the new product CO2 is formed with water and salt.
iii. Reaction with metal oxide
Oxides of various metals react with
dilute acids to form their metallic salts and water.
Metal oxides + dilute Acid → Metal
salts + Water
Example:
Calcium oxide + Hydrochloric acid →
Calcium chloride + Water
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
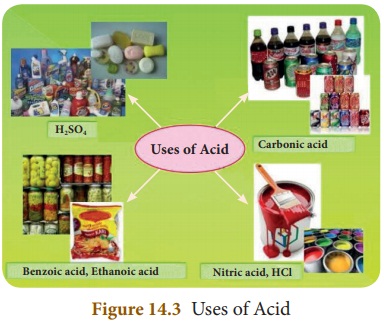
Uses of Acids
* Hydrochloric acid present in our
stomach helps in the digestion of food materials.
* Vinegar (acetic acid) is used to
preserve food materials.
* Benzoic acid is also used to
preserve food materials like pickles.
* Sodium or potassium salts of
higher fatty acids are used to make washing and bathing soaps.
* Sulphuric acid is called the king
of chemicals. It is an effective dehydrating agent. It is used in various
industries to make detergents, paints, fertilizers and many more chemicals.
* Hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and
sulphuric acid are important laboratory reagents.
* Cells of all living organisms
contain the fundamental nuclear material called nucleic acids. Animals have
deoxy ribo nucleic acid (DNA) whereas plants contain ribo nucleic acid (RNA) .
Pickles remain in good condition for long time because they contain vinegar (acetic acid) or benzoic acid.

Related Topics