Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology
Autonomic Receptors
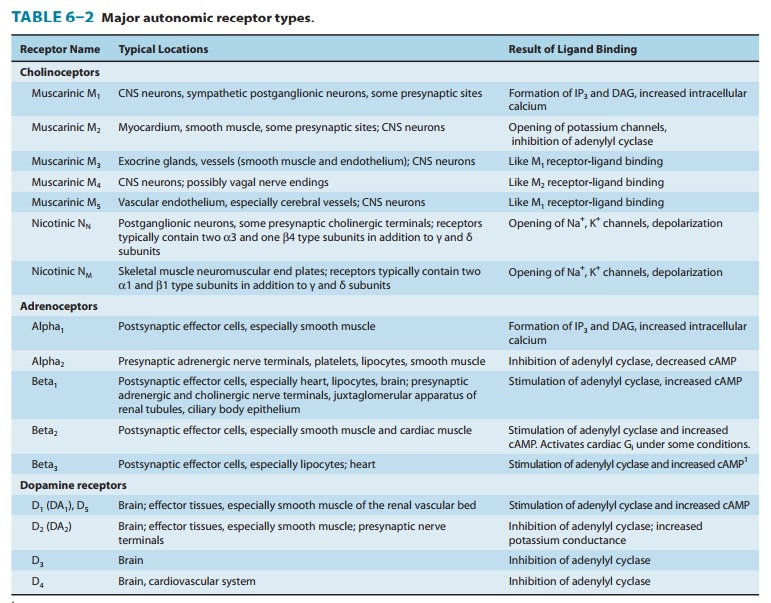
AUTONOMIC RECEPTORS
Historically,
structure-activity analyses, with careful comparisons of the potency of series
of autonomic agonist and antagonist analogs, led to the definition of different
autonomic receptor subtypes, including muscarinic and nicotinic cholinoceptors,
and α,
β,
and dopamine adrenoceptors (Table 6–2). Subsequently, binding of
isotope-labeled ligands permitted the purification and characteriza-tion of
several of the receptor molecules. Molecular biology now provides techniques
for the discovery and expression of genes that code for related receptors
within these groups .
The
primary acetylcholine receptor subtypes were named after the alkaloids
originally used in their identification: muscarine and nicotine, thus muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. In the case of receptors associated with
noradrenergic nerves, the use of the names of the agonists (noradrenaline,
phenylephrine, isoprotere-nol, and others) was not practicable. Therefore, the
term adreno-ceptor is widely used to
describe receptors that respond tocatecholamines such as norepinephrine. By
analogy, the term cholinoceptor denotes
receptors (both muscarinic and nicotinic)that respond to acetylcholine. In
North America, receptors were colloquially named after the nerves that usually
innervate them; thus, adrenergic (or
noradrenergic) receptors and cholinergicreceptors. The general class
of adrenoceptors can be further sub-divided into `-adrenoceptor,a-adrenoceptor,
and dopamine-receptor types on the
basis of both agonist and antagonistselectivity and on genomic grounds.
Development of more selec-tive blocking drugs has led to the naming of
subclasses within these major types; for example, within the α-adrenoceptor class, α1and α2receptors differ in
both agonist and antagonist selectivity.
Related Topics