Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Iodimetric and Iodometric Titrations
Argentometric Precipitation Methods
ARGENTOMETRIC PRECIPITATION METHODS
INTRODUCTION
In general, titrations governed by precipitation reactions
do not really constitute an appreciable number in volumetric determinations in
comparison to either redox or acid-base reactions. The interaction between
silver-nitrate and sodium chloride in solutions result into the precipitation
of silver chloride as shown below :
NaCl + AgNO3
→ AgCl ↓ + NaNO3
In actual practice, however, such titrations are more or
less restricted to those involving precipitation of Ag+ with anions,
for instance : halogens (Cl–, Br–, I–) and
thiocyanate (SCN–). Generally, it is quite difficult and tedious to
locate the exact point at which further addition of reagent affords no more
precipitation. There-fore, the choice and wisdom of a chemical reaction is
preferably sought so as to result in either a coloured solution or a coloured
precipitate at the end point. A typical instance may be cited by application of
potassium chromate (K2CrO4) solution in the above case
whereby any extra drop of silver nitrate, after all the chloride has been
precipitated, immediately causes precipitation of red chromate showing that the
end point has been duly achieved.
It is, however, interesting to observe here that such
reactions do offer limited usage because of the following two facts, namely :
(i)
Co-precipitation effects do not give a real composition of the precipitate, and
(ii) Choice of
appropriate indicator is very much limited.
Besides, the foregoing facts another vital aspect to be
taken into consideration is the solubility
product that plays a major role in such titration. Hence, the equilibrium
constant of the reaction giving the precipitate of AgCl may be expressed as :
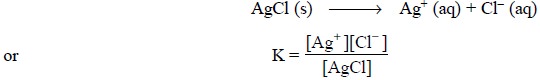
From the above expression the solubility product constant
Ksp may be designated as :
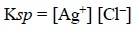
assuming the activity of solid AgCl being constant.
Following are the four
cardinal parameters that may be considered for a feasible argentometric
analysis, namely :
(i) Precipitate
formed must be insoluble,
(ii)
Precipitation process should be fast and rapid,
(iii)
Co-precipitation effects must be minimal, and
(iv) Detection
of equivalence point must be apparently visible.
Related Topics