Chapter: Mechanical : Manufacturing Technology : Metal Joining Process
Arc welding
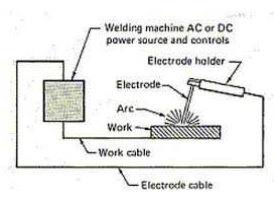
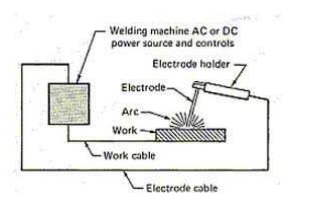
ARC WELDING
Uses an electric arc to coalesce metals
Arc welding is the most common method of welding metals
Electricity travels from electrode to base metal to ground
1.Arc welding Equipments
• A welding generator (D.C.) or Transformer (A.C.)
• Two cables- one for work and one for electrode
• Electrode holder
• Electrode
• Protective shield
• Gloves
• Wire brush
• Chipping hammer
• Goggles
2.Electrode
Electrode is a thin rod made up of same as that of parent material. Flux is coated over the electrode to avoid oxidation. It is mostly connected to the negative polarity.
Two Basic Types of AW Electrodes
Consumable – consumed during welding process Source of filler metal in arc welding
Nonconsumable – not consumed during welding process
Filler metal must be added separately
Consumable Electrodes
Forms of consumable electrodes
• Welding rods (a.k.a. sticks) are 9 to 18 inches and 3/8 inch or less in diameter and must be changed frequently
• Weld wire can be continuously fed from spools with long
lengths of wire, avoiding frequent interruptions
In both rod and wire forms, electrode is consumed by arc and added to weld joint as filler metal.
Nonconsumable Electrodes
Made of tungsten which resists melting
Gradually depleted during welding (vaporization is principal mechanism) Any filler metal must be supplied by a separate wire fed into weld pool
3.Flux
A substance that prevents formation of oxides and other contaminants in welding, or dissolves them and facilitates removal
Provides protective atmosphere for welding Stabilizes arc
Reduces spattering
4.STEPS FOLOWED IN ARC WELDING :
• Prepare the edges to be joined and maintain the proper position
• Open the acetylene valve and ignite the gas at tip of the torch
• Hold the torch at about 45deg to the work piece plane
• Inner flame near the work piece and filler rod at about 30 – 40 deg
• Touch filler rod at the joint and control the movement according to
the flow of the material
Advantages
Most efficient way to join metals
Lowest-cost joining method
Affords lighter weight through better utilization of materials
Joins all commercial metals
Provides design flexibility
Disadvantages
• Manually applied, therefore high labor cost.
• Need high energy causing danger
• Not convenient for disassembly.
• Defects are hard to detect at joints.
Difference between Gas Welding and Arc Welding
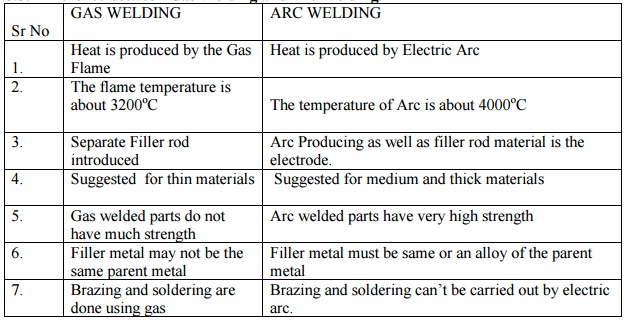
GAS WELDING
1. Heat is produced by the Gas Flame
2. The Flame temperature is about 3200oC
3. Separate Filler rod introduced
4. Suggested for thin materials
5. Gas welded parts do not have much strength
6. Filler metal may not be the same parent metal
7. Brazing and soldering are done using gas
ARC WELDING
1. Heat is produced by Electric Arc
2. The temperature of Arc is about 4000oC
3. Arc Producing as well as filler rod material is the electrode.
4. Suggested for medium and thick materials
5. Arc welded parts have very high strength
6. Filler metal must be same or an alloy of the parent metal
7. Brazing and soldering can’t be carried out by electric arc.
Related Topics