Animals in Daily Life | Term 3 Unit 5 | 7th Science - Animal products used as clothing or Animal Fibres | 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 5 : Animals in Daily Life
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 3 Unit 5 : Animals in Daily Life
Animal products used as clothing or Animal Fibres
Animal products used as clothing
Animal
hair has a great demand. The hair from goat and sheep is used for manufacturing
woollen clothes, shawls and blankets, mufflers and socks. Similarly horse
hair is used as bristles in small painting brushes. Even fur of animals
including the skin is used to make warm and modern style clothes.
Animal Fibres
Some
fabric fibres such as cotton, jute, silk are called natural fibres. Cotton and
jute are examples of plant fibres. Wool and silk fibres are examples of animal
fibres. Wool is obtained from the fleece of sheep or goat. It is also obtained
from the hair of rabbit, yak and camel. Silk fibre is obtained from the cocoon
of silkworm.
1. Wool
What type of
clothes are being used by people of snow capped region? Why such kind of clothing is
preferred by them?

Wool is the fibre derived from the
fur of animals of the Caprinae family principally sheep. The hair of other
mammals like goat, yak, alpaca and rabbit may also be called wool. Mostly, wool
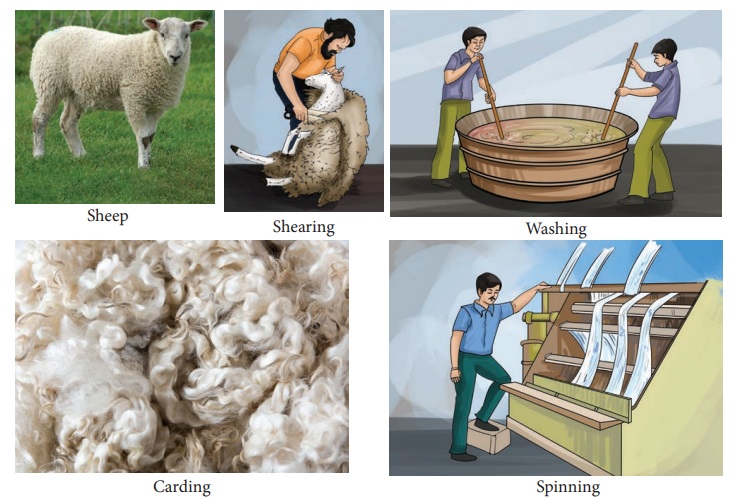
is produced from the outer coat of sheep. The processing of wool involves five
major steps. They are as follows Shearing, Grading (or) Sorting, Washing (or)
Scouting, Carding and Spinning.

Shearing:- The flesh of the sheep is removed
from its body. This is called shearing.
Grading (or) Sorting:- The fleece from the same
sheep may be different from different parts of the body. It is sorted out into
separate piles of similar nature. This is known as Grading (or) Sorting.
Washing (or) Scouting:- The sheared skin is washed
thoroughly with soap (or) detergents to remove dirt, dust and grease.
Carding:- The dried wool is carefully removed.
These fibres then passed through the rollers which are covered with fine sheet
of thin wire teeth. This process arranges the wool into a flat sheet called a
web.
Spinning:- The web is drawn into narrow strand
and then passed through spinning machines. The spinning machines twist the strands
into yarn. The yarn is wound to form balls of wool. This yarn is either weaved
into fabric (or) retained for knitting.
Characteristic
features of wool
*
It is resistant to heat, water, wear and tear.
*
It absorbs moisture.
*
Wool insulates against cold. So wool is a good insulator.
*
It does not wrinkle easily.
Uses of
wool
Wool is a multifunctional fibre with
a range of diameters that makes it suitable for clothing, household fabrics and
technical textiles. Two third of wool is used in the manufacture of garments
including sweaters, dresses, coats and active sportswear. Blended with other
natural (or) synthetic fibres wool used as adds drape and crease resistance
blankets, anti-static and noise absorbing carpets.
2. Silk
Have you ever attended marriage
functions? What type of dresses the bride and bridegroom wear? What is it made
up of?

Silk is the secretions of the silk
moth. Silk is obtained from the cocoon of silk worms, which feed on the
mulberry leaves. Silk worms live for a very short time, only about two months.
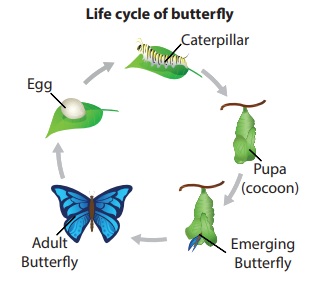
During this period they pass through four stages of development. They are eggs,
caterpillars, cocoon and adult moth. These stages are called as life cycle of a
silk worm.
The cultivation and production of
silk is known as Sericulture. An adult female silk moth lays about 500 eggs.
The eggs are then kept in cold storage for six weeks.
The eggs are placed in the
incubator. After about ten days, the eggs hatch out and the larvae spend the
next 35 days eating mulberry leaves.

The silk worms spend about five days producing silk and
spinning its cocoon of a single long thread. The cocoons are boiled to make it
easier to unwind the silk and kill the pupae inside. If the silk moths were
allowed to hatch, the long silk fibres will get turned by the hatching of moth.
Cocoons are unwind and then the individual silk filament is reeled together to
form a thread large enough for weaving. The silk thread is cleaned, dyed, woven
into fabric.
Characteristic features of
Silk
* It is very soft, comfortable and versatile
* It can be easily dyed.
* It is the strongest natural fibre.
* It has a poor resistance to
sunlight exposure.
Uses of
Silk
Silk has natural beauty and
elegance. It gives comfort in warm weather and warmth during colder months. It
is used in the manufacture of classical and high fashion clothes, modern
dresses particularly silk sarees, the elegant of beautiful dresses. It is also
used in household for making wall hangings, curtains, rugs and carpets. It is
also being used in the manufacture of surgical threads for sutures.
India is the world’s
second largest silk producing country. Kancheepuram, Thirubhuvanam and Arani
are famous places for silk production in Tamil Nadu.
Related Topics