Chapter: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Fundamentals and Applications : Interferons and Interleukins
Anakinra - Therapeutic Use of Recombinant Interleukins
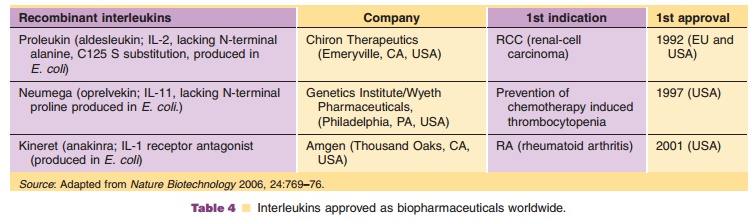
Anakinra
Kineret (anakinra) is a recombinant, nonglycosylatedform of the human IL-1
receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) produced using an E. coli
bacterial expression system. It consists of 153 amino acids, has a molecular
weight of 17.3 kDa, and differs from native human IL-1Ra in that it has the
addition of a single methionine residue at its amino terminus. The absolute
bioavailability of Kineret
after a 70 mg SC bolus injection is 95%. Cmax occurs 3 to 7 hr after SC administration at clinically relevant doses
(1 to 2 mg/kg) with half-life ranging from 4 to 6 hr. There is no accumulation
of Kineret after daily SC doses for up to 24 weeks. The mean plasma clearance
with mild and moderate (creatinine clearance 50–80 mL/ min and 30–49 mL/min)
renal insufficiency was reduced by 16% and 50%, respectively. In severe renal
insufficiency and end-stage renal disease (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min), mean plasma clearance de-clined by 70% and 75%,
respectively. Less than 2.5% of the administered dose is removed by
hemodialysis or continuous peritoneal dialysis. A dose schedule change should
be considered for subjects with severe renal insufficiency or end-stage renal
disease.
Kineret is supplied in single-use prefilled glass syringes with 27 gauge
needles as a sterile, clear, preservative-free solution for daily SC
administration. Each prefilled glass syringe contains: 0.67 mL (100 mg) of
anakinra in a solution (pH 6.5) containing 1.29 mg sodium citrate, 5.48 mg
sodium chloride, 0.12 mg disodium EDTA, and 0.70 mg polysorbate 80 in water for
injection. It is indicated for the reduction in signs and symptoms and slowing
the progression of struc-tural damage in moderately to severely active
rheuma-toid arthritis and can be used alone or in combination with DMARDs other
than TNF-blocking agents. The recommended dose for the treatment of patients
with rheumatoid arthritis is 100 mg/day. Patients with severe renal
insufficiency or end-stage renal disease should receive 100 mg every other day.
Anakinra is generally well-tolerated, the most common adverse reaction is
injection-site reactions, the most serious adverse reactions neutropenia,
particularly when used in combination with TNF-blocking agents, and serious
infections. For a detailed reporting of all adverse events, rarely severe, the
reader is referred to the product information for Kineret.
Related Topics