Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Gross Anatomy of the Cerebral Hemispheres
An Introduction to Some Structures within the Cerebral Hemispheres
AN INTRODUCTION TO SOME STRUCTURES WITHIN THE CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES
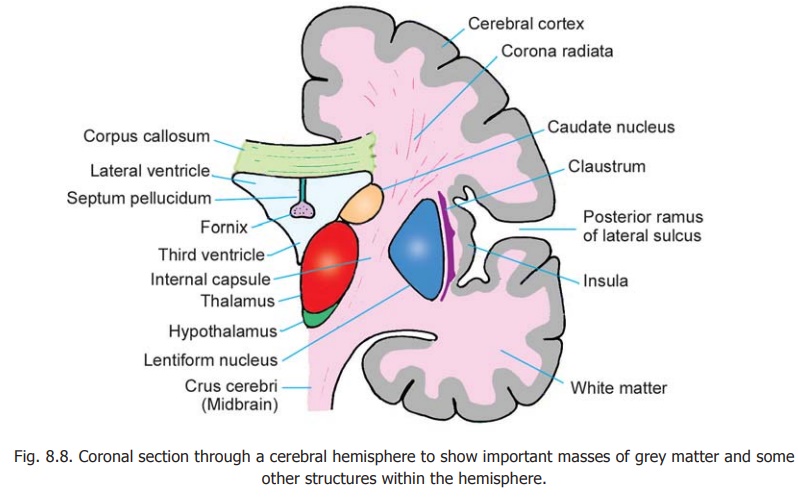
The surface of the cerebral hemisphere is covered by a thin layer of grey matter called the cerebralcortex. The cortex follows the irregular contour of the sulci and gyri of the hemisphere and extendsinto the depths of the sulci. As a result of this folding of the cerebral surface, the cerebral cortex acquires a much larger surface area than the size of the hemispheres would otherwise allow.
The greater part of the cerebral hemisphere deep to the cortex is occupied by white matter within which are embedded certain important masses of grey matter. Immediately lateral to the third ventricle
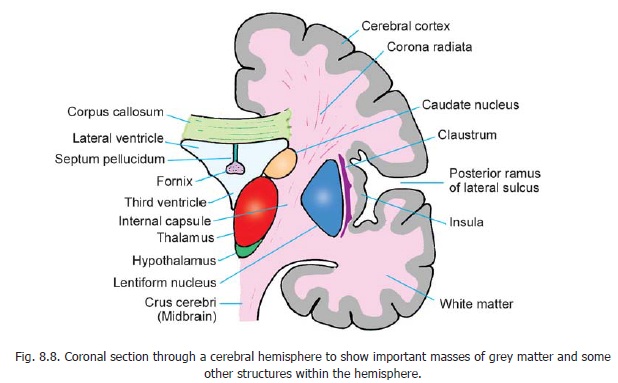
there are the thalamus and hypothalamus (and certain smaller masses) derived from the diencephalon. More laterally there is thecorpus striatum which is derived from the telecephalon. It consists of two masses of grey matter, the caudate nucleus and thelentiform nucleus. A little lateral to the lentiform nucleus we see the cerebral cortex in the region of the insula. Between the lentiform nucleus and the insula there is a thin layer of grey matter called the claustrum. The caudate nucleus, the lentiform nucleus, the claustrum and some other masses of grey matter (all of telencephalic origin) are referred to as basal nuclei or as basal ganglia.
The white matter that occupies the interval between the thalamus and caudate nucleus medially, and the lentiform nucleus laterally, is called the internal capsule. It is a region of considerable importance as major ascending and descending tracts pass through it. The white matter that radiates from the upper end of the internal capsule to the cortex is called the corona radiata.
The two cerebral hemispheres are interconnected by fibres passing from one to the other. These fibres constitute thecommissures of the cerebrum. The largest of these is the corpus callosum which is seen just above the lateral ventricles in Fig. 8.8.
Related Topics