Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Aminoglycosides & Spectinomycin
Amikacin
AMIKACIN
Amikacin
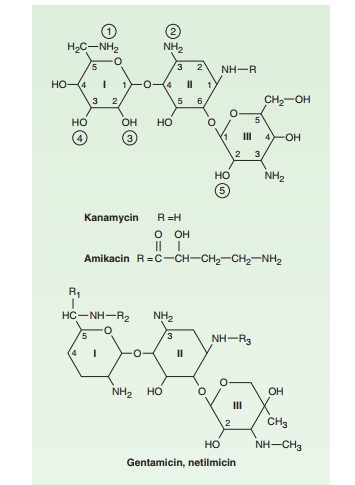
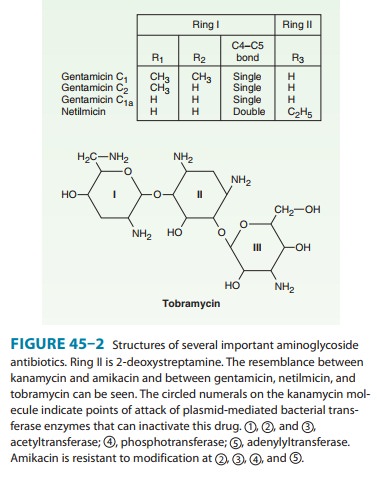
is a semisynthetic derivative of kanamycin; it is less toxic than the parent
molecule (Figure 45–2). It is resistant to many enzymes that inactivate
gentamicin and tobramycin, and it there-fore can be used against some
microorganisms resistant to the latter drugs. Many gram-negative bacteria,
including many strains of Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, and Serratia,
are inhibited by 1–20 mcg/mL amikacin in vitro. After injection of 500 mg of
amikacin every 12 hours (15 mg/kg/d) intramuscularly, peak levels in serum are
10–30 mcg/mL.Strains of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium
tuberculosis, including streptomycin-resistant strains, are usually
susceptible to amikacin. Kanamycin-resistant strains may be cross-resistant to
amikacin. The dosage of amikacin for tuberculosis is 7.5–15 mg/ kg/d as a
once-daily or two to three times weekly injection and always in combination
with other drugs to which the isolate is susceptible.
Like all
aminoglycosides, amikacin is nephrotoxic and ototoxic (particularly for the
auditory portion of the eighth nerve). Serum concentrations should be
monitored. Target peak serum concen-trations for an every-12-hours dosing
regimen are 20–40 mcg/mL, and troughs should be maintained between 4 and 8
mcg/mL.
Related Topics