Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Aggressive And Protective Factors For Gastroduodenal Mucosa
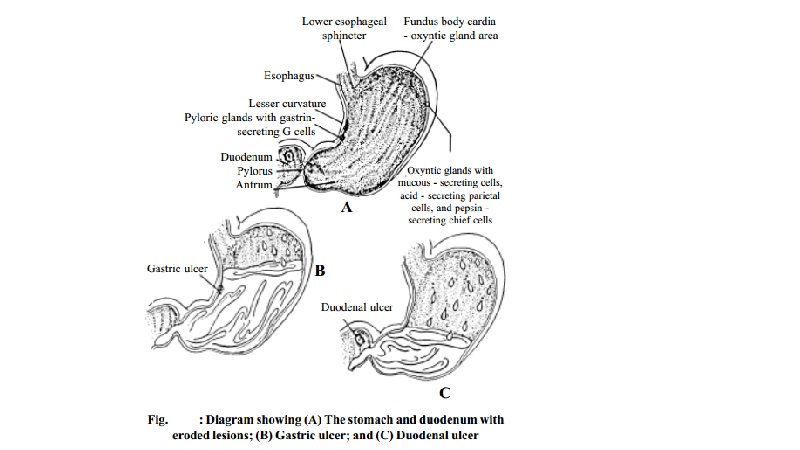
AGGRESSIVE AND PROTECTIVE FACTORS FOR GASTRODUODENAL
MUCOSA
Aggressive factors
1.
Bacterial infection : Helicobacter pylori, a spiral shaped, unipolar
flagellate is associated with inflammation of gastric mucosa which could be a
cause for peptic ulcer. This can be cleared by antibiotic treatment.
2.
Genetic factors : It is more common in persons
with blood group O. First degree relatives of patients with duodenal ulcer have
an increased risk.
3.
Sex : Men are affected two to three times more
frequently than women.
4.
Age : The incidence is high between 20 and 40
years during which time career and personal strivings are at a peak.
5.
Stress : Highly nervous and emotional
individuals are more susceptible as worry, fear and anxiety lead to
hypersecretion of acid and hypermotility of the stomach.
6.
Potentially irritant substances : Caffeine,
aspirin and nicotine may delay healing the ulcer. Chillies, pepper, ginger,
strong tea and coffee increase the secretion of hydrochloric acid and aggravate
the condition.
7.
Hydrochloric acid
8.
Pepsin
9.
Rapid gastric emptying
10.
Smoking
11.
Alcohol
Protective Factors
1.
Prostaglandin
2.
Bicarbonate secreted by stomach
3.
Mucus
4.
Mucosal blood flow.
Symptoms
1.
Epigastric pain
2.
Heart burn occurring as deep hunger contractions
1 to 3 hours after meals is the chief complaint.
3.
The pain is dull, piercing and burning and is
usually relieved by taking food.
4.
Discomfort and flatulence in the upper part of
the abdomen may be present.
5.
Low plasma protein levels delay rapid and
complete healing of the ulcer.
6.
Weight loss and iron deficiency anemia are
common.
Treatment :
Therapeutic goals :
1.
To relieve the symptoms
2.
To allow healing of ulcer
3.
To prevent complications like surgery
Related Topics