Chapter: Control Systems : Systems and their Representation
AC Servo Motors - Control Systems
AC Servo Motors
An AC
servo motor is essentially a two phase induction motor with modified
constructional features to suit servo applications.
The
schematic of a two phase or servo motor is shown
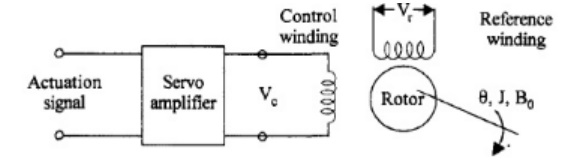
It has
two windings displaced by 90oon the stator One winding, called as
reference winding, is supplied with a constant sinusoidal voltage.
The second winding, called control winding, is supplied with a variable control voltage which is displaced by -- 90o out of phase from the reference voltage.
The major differences between the normal induction motor and an AC servo motor are
The rotor
winding of an ac servo motor has high resistance (R) compared to its inductive
reactance (X) so that its X / R ratio
is very low.
For a
normal induction motor, X / R ratio
is high so that the maximum torque is obtained in normal operating region which
is around 5% of slip.
The
torque speed characteristics of a normal induction motor and an ac servo motor
are shown in fig
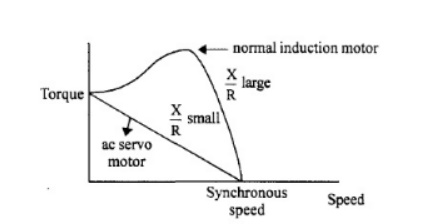
The
Torque speed characteristic of a normal induction motor is highly nonlinear and
has a positive slope for some portion of the curve.
This is
not desirable for control applications. as the positive slope makes the systems
unstable. The torque speed characteristic of an ac servo motor is fairly linear
and has negative slope throughout.
The rotor
construction is usually squirrel cage or drag cup type for an ac servo motor.
The diameter is small compared to the length of the rotor which reduces inertia
of the moving parts.
Thus it
has good accelerating characteristic and good dynamic response.
The supplies
to the two windings of ac servo motor are not balanced as in the case of a
normal induction motor.
The
control voltage varies both in magnitude and phase with respect to the constant
reference vulture applied to the reference winding.
The
direction of rotation of the motor depends on the phase (± 90°) of the control
voltage with respect to the reference voltage.
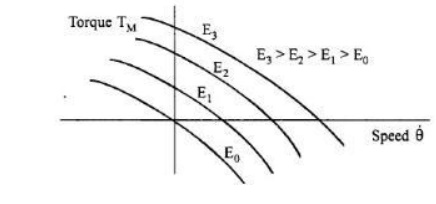
For
different rms values of control voltage the torque speed characteristics are
shown in Fig.
The
torque varies approximately linearly with respect to speed and also controls
voltage. The torque speed characteristics can be linearised at the operating
point and the transfer function of the motor can be obtained.
Related Topics