Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
Spinal cord functioning
Spinal cord functioning
The spinal cord remains as a connecting, functional nervous structure in between the brain and sensory / effector organs. The sensory inputs received by sense organs are conducted towards appropriate regions of the brain. Similarly from the brain motor sensations are transmitted towards effector structures. Further as the brain, the spinal cord can effect motor initiation and bring about an effect. This activity is known as reflex action.
Reflex action
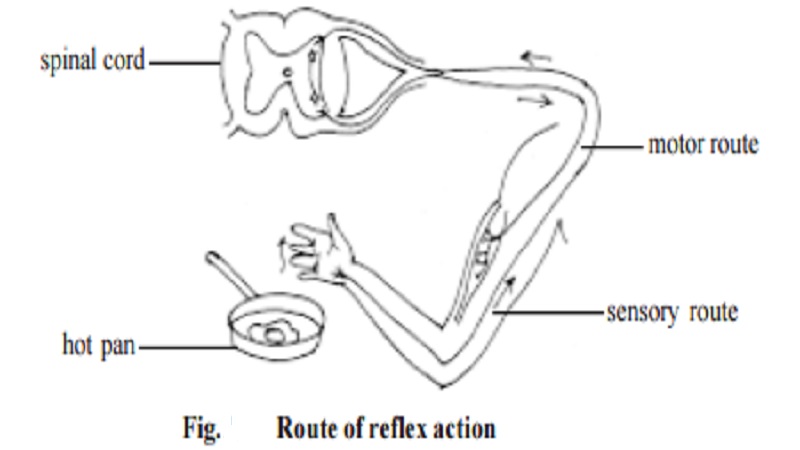
Reflex action is the spontaneously involuntary response caused due to stimulation of receptor organ. E.g. The quick closure of eye lid when some object touches the eyelashes.; the sudden withdrawl of hand when the hand touches hot pan.
A reflex action is an involuntary process and does not involve the intervention of consciousness. The anatomical basis of reflex action is the reflex arc. It is a nerve chain between receptor organ and effector organ. The reflex arc has the following route.
Sensory organ � sensory or afferent neuron � grey matter of the spinal cord � intermediary or relay neuron � efferent or motor neuron � effector organ.
Cerebro Spinal Fluid (CSF)
The ventricle of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord contain, a clear fluid similar to plasma called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is formed by a group of cells called the choroid plexus located inside the four ventricles. In human the volume of CSF is 150 ml and the rate of its secretion is 550 ml/day.
Functions:
1.CSF cushions the brain against mechanical shock when the head moves.
2. It acts as a protective covering for the CNS and confers buoyancy to brain.
3. The CSF also provides a reservoir of hormones and nutrition for the brain and spinal cord.
It acts as a mechanical buffer. Remaining inside and outside the CNS, it equalizes the mechanical pressure. If the intracranial pressure tends to rise the CSF is pressured out. If the pressure tends to fall, more CSF is retained.
Related Topics