Chapter: Medical Physiology: Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation
Sinus Arrhythmia - Abnormal Sinus Rhythms
Sinus Arrhythmia
Figure 13–3 shows a cardiotachometer recording of the heart rate, at first during normal and then (in the second half of the record) during deep respiration. A cardiota-chometer is an instrument that records by the height ofsuccessive spikes the duration of the interval betweenthe successive QRS complexes in the electrocar-diogram. Note from this record that the heart rate increased and decreased no more than 5 per cent during
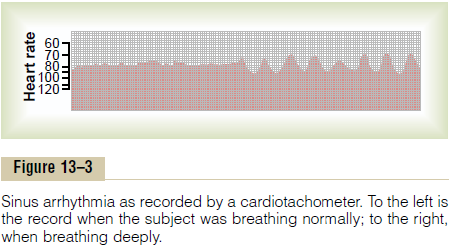
quiet respiration (left half of the record). Then, duringdeep respiration, the heart rate increased and decreasedwith each respiratory cycle by as much as 30 per cent.
Sinus arrhythmia can result from any one of many cir-culatory conditions that alter the strengths of the sym-pathetic and parasympathetic nerve signals to the heart sinus node. In the “respiratory” type of sinus arrhyth-mia, as shown in Figure 13–3, this results mainly from “spillover” of signals from the medullary respiratory center into the adjacent vasomotor center during inspi-ratory and expiratory cycles of respiration. The spillover signals cause alternate increase and decrease in the number of impulses transmitted through the sympa-thetic and vagus nerves to the heart.
Related Topics