Chapter: Business Science : International Business Management
Protectionism and Trade Liberalisation
Protectionism and Trade Liberalisation
Protectionism:
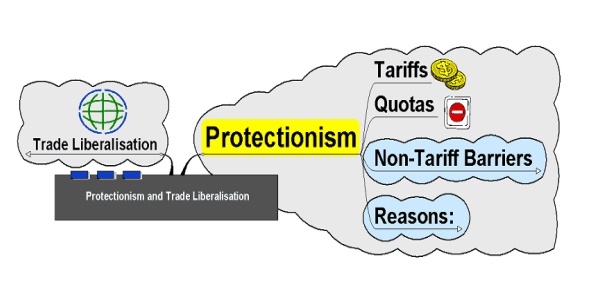
Protectionism means by which trade between
countries is restricted in some way – normally through measures to reduce the number of imports coming into a
country
Main
means are:
Tariffs - A tax on a good coming into a
country. increases the price of the good and makes it less competitive
Quotas - Physical restriction on the number of goods
coming
into a country.
Non-Tariff Barriers - Any
methods not covered by a tariff, most usually:
Rules
Regulations
Voluntary Export Restraints (VERs)
Legislation
Exacting Standards or Specifications
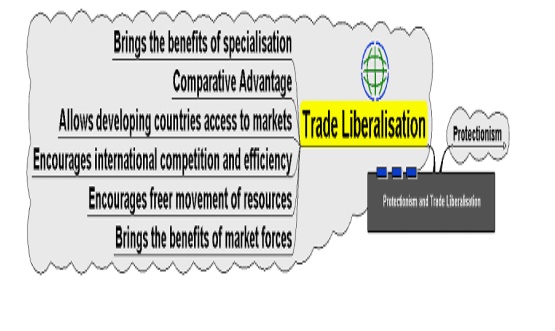
Trade Liberalisation
The
removal of or reduction in the trade practices that thwart free flow of goods
and services from one nation to another. It includes dismantling of tariff
(such as duties, surcharges, and export subsidies) as well as nontariff
barriers (such as licensing regulations, quotas, and arbitrary standards).
In economy and trade
Privatization,
also spelled as privatization, may have several meanings. Primarily, it is the
process of transferring ownership of a business, enterprise, agency, public
service or public property from the public sector (a government) to the private
sector, either to a business that operates for a profit or to a nonprofit
organization. It may also mean government outsourcing of services or functions
to private firms, e.g. revenue collection, law enforcement, and prison
management
Privatization
has also been used to describe two unrelated transactions. The first is the
buying of all outstanding shares of a publicly traded company by a single
entity, making the company privately owned. This is often described as private
equity. The second is a demutualization of a mutual organization or cooperative
to form a joint-stock company..
Although
economic liberalization is often associated with privatization, the two are
distinct concepts. For example, the European Union has liberalized gas and
electricity markets, instituting a competitive system, but some leading
European energy companies such as France's EDF and Sweden's Vattenfall remain
partially or completely in government ownership.
Liberalized
and privatized public services may be dominated by just a few big companies
particularly in sectors with high capital costs, or high water, gas, or
electricity costs. In some cases they may remain legal monopolies, at least for
some segments of the market (like small consumers).
Liberalization
is one of three focal points (the others being privatization and stabilization)
of the Washington Consensus's trinity strategy for economies in transition.
There is
also a concept of hybrid liberalization as, for instance, in Ghana where cocoa
crop can be sold to a variety of competing private companies, but there is a
minimum price for which it can be sold and all exports are controlled by the
state
Related Topics