Chapter: Paediatrics: Neurology
Paediatrics: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
ADEM is an immune mediated
disease. It usually occurs following a viral infection, but may follow other
infections or vaccination. It involves auto-immune demyelination, it is similar
to multiple sclerosis- although mono-phasic. ADEM produces multiple
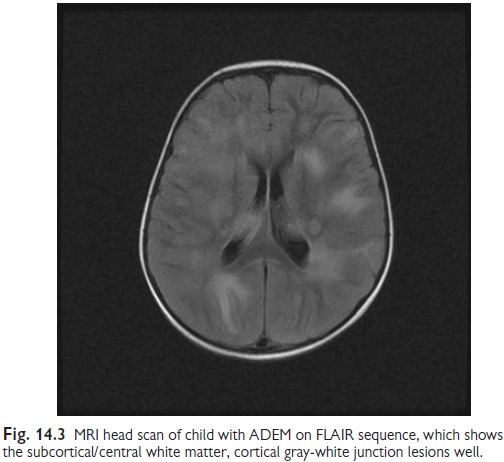
inflammatory lesions in the brain and spinal cord, particularly in the white
matter. Usually these are found in the subcortical/central white matter and
cortical gray-white junction of both cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum,
brainstem, and spinal cord, but other areas including the basal ganglia may
also be involved.
Presentation
· The average age around 5–8yrs old.
· Abrupt onset and a monophasic
course.
· Symptoms usually begin 1–3wks
after infection or vaccination and include fever, headache, drowsiness, coma,
and seizures.
· Average time to maximum severity
about four and a half days.
· Additional symptoms include
hemiparesis, paraparesis, and cranial nerve palsies.
Diagnosis
This is based on finding typical
changes on MRI- as above in the subcor-tical/central white matter, cortical
gray-white junction, cerebellum, brain-stem, and spinal cord. The basal ganglia
may also be involved (Fig. 14.3). CSF may show a mild lymphocytosis, with
normal glucose, but there may be a mild rise in protein.
Treatment
It is important to exclude other
causes of encephalopathy. Then supportive measures such as hydration/feeding,
bulbar func-tion and respiration should be instituted. Pulsed intravenous
methylpred-nisolone is widely recommended as definitive treatment, and is
normally associated with improvement within days.
ADEM may relapse once or twice, it
is then called M(ultiple)DEM. Multiple Sclerosis rarely occurs in childhood,
but becomes more common as children approach adulthood. It presents with
demyelinating plaques, which differ from ADEM in their distribution- more periventricu-lar
white matter, and with much less encephalopathy, seizures, and coma, but more
focal neurological signs.
Related Topics