Chapter: Digital Logic Circuits : VHDL
Important Short Questions and Answers: VHDL
VHDL
1. What
are the advantages of CMOS?
The advantages of CMOS are
Remarkable low static Power dissipation.
Its Propagation delay is low with improved noise margin.
These circuits take advantage of the fact that NMOS and PMOS Transistors
can be fabricated on the same substrate. It has lowest packaging density, high
speed and improved noise immunity.
2. Compare
ROM and PROM.
ROM or Read Only Memory, Computers
almost always contain a small amount of read-only memory that holds
instructions for starting up the computer. Unlike RAM, ROM cannot be written
to. It is non-volatile which means once you turn off the computer the
information is still there.
PROM, short for programmable
read-only memory A PROM is a memory chip on which data can be written only
once. Once a program has been written onto a PROM, it remains there forever.
Unlike RAM, PROM's retain their contents when the computer is turned off. The
difference between a PROM and a ROM (read-only memory) is that a PROM is
manufactured as blank memory, whereas a ROM is programmed during the
manufacturing process. To write data onto a PROM chip, you need a special
device called a PROM programmer or PROM burner. The process of programming a
PROM is sometimes called burning the PROM.
3.
Compare PAL and PLA
PAL is Programmable Array Logic and
PLA is Programmable Logic Array. In a PLA, both the OR gates and the AND gates
can have their inputs connected and disconnected. In a PAL, only the AND gates
can have their inputs connected and disconnected ("programmed"). This
makes PAL devices easier to program and less expensive than PLA. On the other
hand, since the OR array is fixed, it is less flexible than a PLA device.
4.
Classify the basic families that belong to the bipolar families and to the MOS
families.
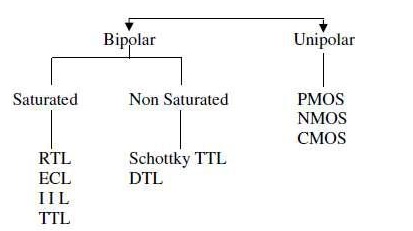
The Bipolar logic family is
classified into Saturated logic and Unsaturated logic. The RTL, DTL, TTL, I2L,
HTL logic comes under the saturated logic family. The Schottky TTL, and ECL
logic comes under the unsaturated logic family.
5.
What is FPGA?
FPGA refers to Field Programmable
Gate Array. The field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit
designed to be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing—hence
"field-programmable". The FPGA configuration is generally specified
using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an
application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). FPGAs can be used to implement
any logical function that an ASIC could perform. The ability to update the
functionality after shipping, and the low non recurring engineering costs
relative to an ASIC design (not withstanding the generally higher unit cost).
FPGAs contain programmable logic
components called "logic blocks", and a hierarchy of reconfigurable
interconnects that allow the blocks to be "wired together" somewhat
like a one-chip programmable breadboard. Logic blocks can be configured to
perform complex combinational functions,
or merely simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, the logic blocks
also include memory elements, which may be simple flipflops or more complete
blocks of memory.
6.
Draw the general structure of PAL.
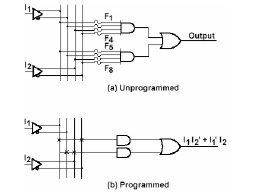
7.
Which memory is called volatile? Why?
RAM is called volatile memory,
because the content stored in this will be erased when power is switched off.
8.
What is PLA?
Programmable logic Array (PLA) is a
type of fixed architecture logic devices with programmable AND gates followed
by programmable OR gates.
9.
What is a EPROM ?
EPROM is a programmable ROM whose
content can be erased using ultra violet rays and the ROM can be subsequently
programmed
10.
How many address lines are required
for a 4K ROM?
The relation between address lines
and memory capacity is 2n = memory capacity.
Where n is the number of address
lines. Therefore 2n = 4096 gives n = 12
No of address lines required = 12
11.
Define address space and memory
space?
In virtual memory, the user gives a
larger address called virtual address. A set of such addresses is called
address space. The equivalent main memory address generated in the location of
physical address. A set of such location is called the memory space.
12.
Explain static memory. Define static
memory.
Memories that consist of circuits
capable of retaining their state as long as power is applied are known as
static memories. Eg RAM
13. What
is RAM?
We can read from and write into the
RAM, so it is called as read/write memory. It is a volatile memory, i.e. it
cannot hold data when power is turned off.
14.
Mention the two types of erasable PROM.
Two types of erasable PROM are
EPROM(Erasable programmable Read only memory) and EEPROM (Electrical Erasable
programmable Read only memory)
15.
How is individual location in a
EEPROM programmed or erased?
Data is stored as charge or no
charge on an insulated layer. The insulating layer is made very thin therefore
a voltage as low as 20 to 25V can be used to move charges across the thin
barrier in either direction for programming or erased. EEPROM allows selective
erasing at the register level.
16.
What is meant by static and dynamic
memories?
Memories that consist of circuits
capable of retaining their state as long as power is applied are known as
static memories. Dynamic RAM stores the data as a charge in capacitor.
17.
Whether ROM is classified as a nonvolatile storage device? Why?
It stores data that are used
repeatedly in system applications such as tables, conversions or programmed
instruction for system initialization and operations. ROM retains stored data
when power is off and are therefore nonvolatile memory.
Related Topics