Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Engine Exhaust Emission Control
Greenhouse effect (GHE)
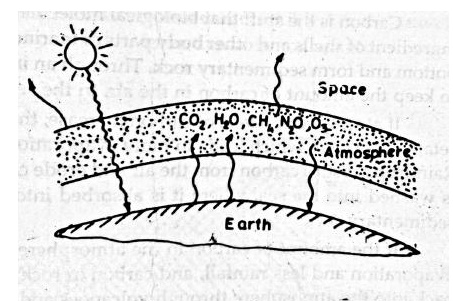
Greenhouse effect (GHE)
Radiation
from the sun always tries to passes through the earth. This wave length is
usually shorter. This shortwave radiation when strikes the inner earth surface
of green house, converts into heat long – wave radiation. This long wave
radiation is again reflected back into atmosphere from the inside surfaces but
it cannot go out as the atmosphere restricts the long wave going to out and
traps the heat. This trapped heat (which should have happened without glass)
contributes to warming of earth and provides energy for growth of plants.
Therefore, this effect is known as greenhouse effect.
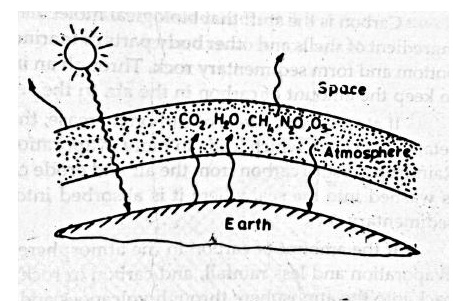
The
presence of CO2 in earth atmosphere gives it the warmth essential
for the substance of life. This happens because CO2 has peculiar
optical properties. CO2 absorbs a good part of this long wave
radiation, thus warming the globe. This is important life sustained that poses
a threat to the human life in the coming decades.
CO2
is the chief and also CH4, NO2 and certain CFCs have
similar effects. Collectively these gases are responsible for greenhouse
effect, threatening an average increase in earth temperature by 1.5 to 5°C by the middle of this century which will seriously affect sea level,
agriculture and forestry. From the ground, earth atmosphere is nearly invisible
and easy to take for granted. From space, it is perceived more readily as a
thin blanket of glasses, shielding the earth from sun’s UV – radiation and
trapping the sun’s warmth to keep Earth Rivers and oceans from freezing. The
greenhouse gases emitted into the atmospheric functions significantly,
degrading the UV-shielding of O3– layer and intensifying the heat
trapping properties of the atmosphere as a whole.
Factors affecting Greenhouse effect:
Carbon is
the stuff that biological molecules are made of. In the oceans, it serves as
the basic ingredients of shells and other body parts of marine organisms, which
eventually die and sink to the bottom and form sedimentary rock. Through an
intricate feedback system, the earth has contrived to keep the amount of carbon
in the air, in the sea on the land relatively constant.
If the
atmospheric levels of carbon increase, resulting greenhouse effect causes the
earth to retain more heat, which leads to more evaporation of water from oceans
and thus more rains. Rain drops absorb carbon from the air and erode carbon –
laden rock; eventually the excess carbon is washed into the sea, where it is
absorbed into seashells and returned to ocean bottom as sedimentary rocks.
If the
amount of carbon in the atmosphere decreases, the process is reversed. There is
less evaporation and less rainfall, carbon in rock at the ocean’s bottom
eventually works its way back into the atmospheric through volcanoes and
deep-sea vents.
The cycle
operates over millions of years; however human disturbances such as the burning
of fossils fuels and deforestation have outpaced this natural process,
resulting in atmospheric carbon.
Steps
taken to control greenhouse effect:
The
greenhouse effect is overwhelming in scope and will specially impact on using
departments dealing with energy. In accordance with this, some of the steps
have been taken by many countries which are as follows:
1. Increased
usage of Natural gases instead of fuels which highly emit CO2.
2. Finding
source and using more hydro-power.
3. Use of
alternative energy.
4. Increasing
the usage of nuclear power.
5. Using
efficient equipment that controls CO2.
6. Eliminating
the usage of CFC from refrigeration industry and finding the alternate
refrigerant.
7. Increasing
forestation and stopping deforestation.
8. Implementing
methodology of tax charges respect to carbon emission by industries.
Related Topics