Chapter: Analog and Digital Communication
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Code division multiple access (CDMA)
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Code division multiple access (CDMA)
Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization group established in 1982 to create a common European mobile telephone standard that would formulate specifications for a pan-European mobile cellular radio system operating at 900 MHz. It is estimated that many countries outside of Europe will join the GSM partnership.
Throughout the evolution of cellular telecommunications, various systems havebeen developed without the benefit of standardized specifications. This presented many problems directly related to compatibility, especially with the development of digital radio technology. The GSM standard is intended to address these problems.
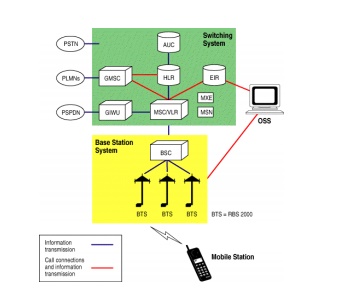
GSM network elements
GSM SERVICES
• Telephone Services
· Explanation
• Data Services
· Explanation
• Supplementary Services
GSM Features:
· Explanation
GSM System Architecture:
• Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
• Network and Switching Subsystem
• Operation Support Subsystem (OS
GSM interface:
• Abis interface
• –Ainterface
GSM channel Types:
• Traffic channels
• Control channels
Frame structure for GSM.
Different types of GSM services
• Telephone services
• Data services
• Supplementary services
Signaling tone :
The signaling tone is a 10 kbps data base which signals call termination by the subscriber. It is a special end of call message consisting of alternating 1s and 0s which is sent on the RVC by the subscriber unit for 200ms. The signaling tone alerts the base station that a subscriber has ended the call.
Telephone services in GSM: Teleservices provides communication between two end user applications according to a standard protocol. GSM mainly focuses on voice oriented tele services. This service includes emergency calling and facsimile. GSM also supports video text and tele text.
Handoff.
When a user/call moves to a new cell, then a new base station and new channel should be assigned (handoff)
• Handoffs should be transparent to users, while their number should be kept to minimum
• A threshold in the received power (Pr, handoff) should be determined to trigger the handoff process. This threshold value should be larger than the minimum acceptable received power (Pr, acceptable)
• Define: - Δ=Pr, handoff Pr, acceptable
–If D is large then too many handoffs
–If D is small then insufficient time to c
Features of CDMA
• Frequency reuse
• Soft capacity
• Multipath fading
• Data Rate
• Soft Handoff
• Self Jamming
• Flexibility.
Related Topics