Chapter: Biology: Practical Zoology
Earthworm: Classification, External Features, Digestive System, Method of Dissection
Earthworm
Classification of Earthworm:
kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Annelida
Class: Oligochaeta
Order: Neo-oligochaeta
Family: Megascolecidae
Genus: Metaphire (Pheretima)
species: Metaphire posthuma
Earthworm belongs to the phylum Annelida. it leaves in soil.
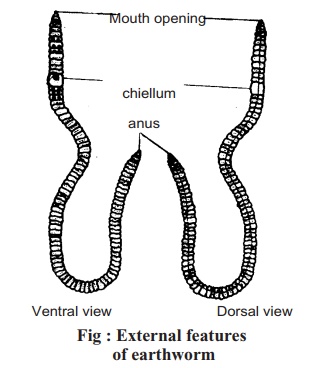
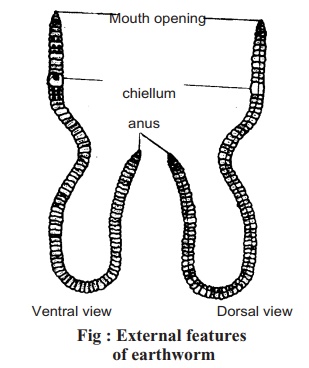
External Features:
1. The body of earthworm in cylindrical and the two ends are tapering.
2. Its body is clay-coloured, deeper dorsally and lighter ventrally. There is a fine, long black line on the dorsal side.
3. The body is segmented both externally and internally. There are about 100 segments in the body.
4. At the anterior end the mouth opening and at the posterior end the anal opening is present.
5. 5.Near the front end on 14th , 15th and 16th segments, there is a fleshy band like covering surrounding the three segments mentioned above, known as clitellum.
6. The integument has spine- like organs known as setae.
7. On the ventral side single female genital pore and a pair of male genital pores present.
Digestive System:
Dissection: All invertebrates animal are to dissect on the dorsal side. Earthworm is a invertebrate animal. So it is dissected on the dorsal side. The alimentary canal is extended within the body of earthworm from the anterior end to the posterior end and that is divided into seven regions, namely:
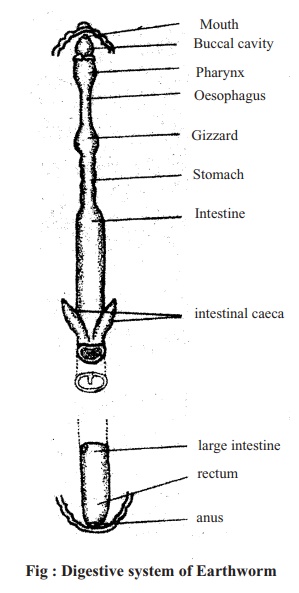
Mouth and Buccal Cavity: In the middle of first segment, there is mouththrough which foods enter into the buccal cavity. It lies behind the mouth. It is a wide cavity.
Pharynx: Behind the buccal cavity themuscular pharynx present, it crushes the food.
Oesophagus: Next to pharynx, the tubularportion is the oesophagus through which the food goes to the gizzard.
Gizzard: Behind the oesophagus lies thegizzard. It is muscular.
Stomach or Preintestine: Next to gizzardstomach or preintestine is situated. It is tubular and the food is digested here.
Intestine: The intestine follows thestomach. It is also tubular and is the longest part of the gut where food is digested and digested food is absorbed.
Rectum: At the posterior end of thealimentary canal the rectum is formed with 25 segments where faeces stored. Behind the rectum, at the posterior end there is anal pore.
Method of Dissection:
1. The two ends of the earthworm are stuck in the dissecting tray, keeping the dorsal side upward.
2. Following the black, thread like line on the dorsal side, it is to be cut straight with blade or scissors.
3. By removing the body wall on the dorsal side, the tubular long alimentary canal is to be found.
4. Now observe the different regions of alimentary canal.
Related Topics