Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Spinal Anesthesia
Describe the advantages of spinal anesthesia over general anesthesia
Describe the advantages of spinal anesthesia over general
anesthesia.
Although general anesthesia frequently provides
airway control for the anesthesiologist, spinal anesthesia offers many
advantages over general anesthesia. Both orthopedic and vascular surgeries on
the lower extremities are associ-ated with diminished blood loss under spinal
anesthesia compared with general anesthesia. The inference, which has been
proven to be true, is that patients undergoing these procedures with spinal
anesthesia receive less transfused blood. The risk of receiving the human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and other communicable diseases through blood
transfusion is therefore reduced also (Table 56.2).
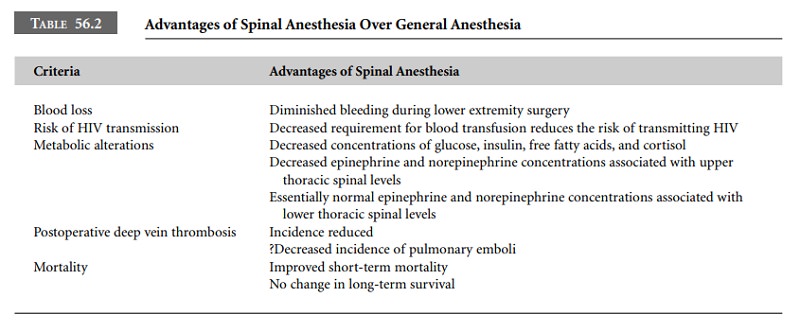
Metabolic alterations associated with general
anesthesia and surgery are well described. Increases in energy-liberating
hormones, such as epinephrine, norepinephrine, cortisol, and growth hormone
occur. Glucose levels may also increase in patients undergoing surgery and
general anes-thesia. Spinal anesthesia to the upper thoracic levels is
associated with decreased epinephrine and norepinephrine concentrations, while
lower thoracic levels allow epineph-rine and norepinephrine levels to remain
essentially unchanged. Surgery under spinal anesthesia is associated with
depressed levels of cortisol, insulin, and free fatty acids. Glucose
concentrations under spinal anesthesia increase slightly and then tend to fall
slightly.
It is postulated that spinal anesthesia
prevents increases in metabolic hormone concentrations by afferent and efferent
neural blockade. Inhibition of adrenal medullary catecholamine release is
probably secondary to efferent autonomic blockade. Inhibition of pituitary
hormone release is probably due to afferent pathway interruption.
Ablation of the hyperglycemic response seen
under spinal anesthesia may be secondary to efferent sympathetic block-ade to
the liver as well as inhibition of catecholamine release from the adrenal
medulla.
The incidence of deep vein thrombosis following
lower extremity orthopedic surgery is reduced under spinal anesthesia compared
with general anesthesia. Although one would anticipate the incidence of pulmonary
emboli to be reduced following spinal anesthesia, this has not been documented.
Elderly patients undergoing surgery for femoral
neck fractures under spinal anesthesia demonstrate an improved short-term
survival rate. Interestingly, the long-term sur-vival rate of patients
undergoing similar surgery under spinal anesthesia is approximately the same as
that for patients who had undergone general anesthesia. Pulmonary embolism was
a frequent cause of death for those who received general anesthesia and who
died within 1 month of surgery.
Related Topics