Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs
Chemical Classification - Basic Pharmacology of Sedative Hypnotics
Chemical Classification
The
benzodiazepines are widely used
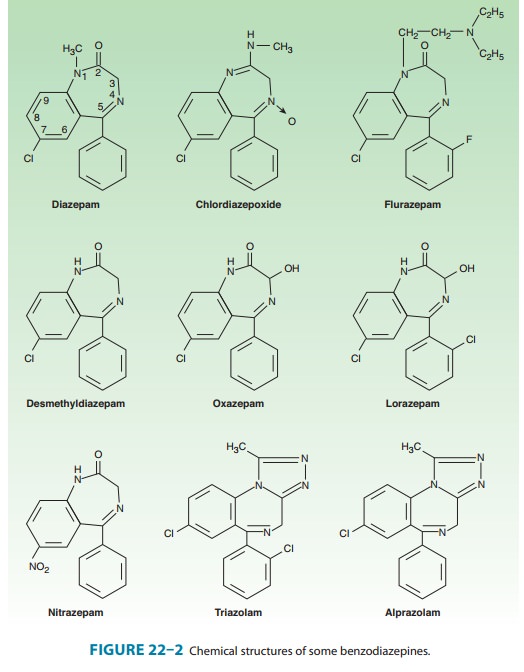
sedative-hypnotics. All of the structures shown in Figure 22–2 are
1,4-benzodiazepines, and most contain a carboxamide group in the 7-membered
heterocy-clic ring structure. An electronegative substituent in the 7
posi-tion, such as a halogen or a nitro group, is required for
sedative-hypnotic activity. The structures of triazolam and alprazo-lam include
the addition of a triazole ring at the 1,2-position.
The
chemical structures of some older and less commonly used sedative-hypnotics,
including several barbiturates, are
shown in Figure 22–3. Glutethimide and meprobamate are of distinctive chemical
structure but are practically equivalent to barbiturates in their pharmacologic
effects. They are rarely used.
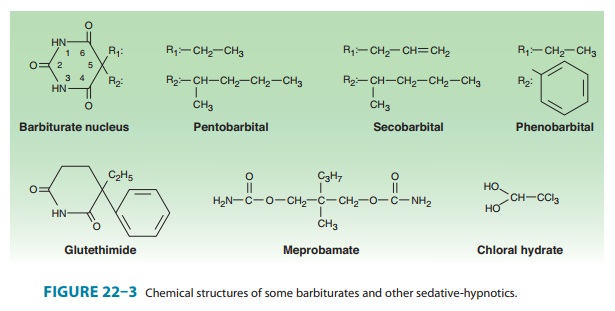
The sedative hypnotic
class also includes compounds of simpler chemical struc-ture, including ethanol
and chloral hydrate.Several
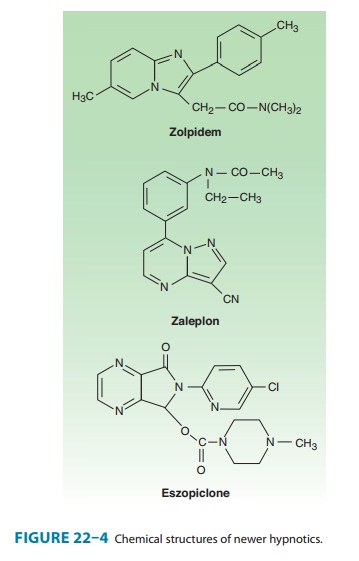
drugs with novel chemical structures have been intro-duced more recently for
use in sleep disorders. Zolpidem, an
imidazopyridine, zaleplon, a
pyrazolopyrimidine, and eszo-piclone,
a cyclopyrrolone (Figure 22–4), although structurallyunrelated to
benzodiazepines, share a similar mechanism of action, as described below.
Eszopiclone is the (S)-enantiomer of
zopiclone, a hypnotic drug that has been available outside the United States
since 1989. Ramelteon, a melatonin
receptor ago-nist, is a more recently introduced hypnotic drug (see Box: Ramelteon).
Buspirone is a slow-onset anxiolytic
agent whose actions are quite different from those of conventional
sedative-hypnotics.
Other
classes of drugs that exert sedative effects include anti-psychotics and many antidepressant drugs . The latter
are currently used widely in the manage-ment of chronic anxiety disorders.
Certain antihistaminic agents including diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine, and
promethazine cause sedation but commonly
also exert marked effects on the peripheral autonomic nervous system.
Antihistaminic drugs with sedative effects are available as over-the-counter
sleep aids.
Related Topics