Introduction, Definition, Features, Specimen, Important terms | Accountancy - Bills of exchange | 11th Accountancy : Chapter 6 : Subsidiary Books - I
Chapter: 11th Accountancy : Chapter 6 : Subsidiary Books - I
Bills of exchange
Bills of exchange
Introduction
To increase
the sales, a seller sells the goods on credit to his customers. If sale is made
on credit, cash will not be received immediately. The seller may draw a bill on
the customer for the amount due from him. If the customer accepts it, the
seller can get the same discounted with the bank and get cash immediately.
Definition of bill of exchange
According to
the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, “Bill of exchange is an instrument in
writing containing an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a
certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of a
certain person or to the bearer of the instrument”.
Features of bills of exchange
An analysis
of the definition given above, highlights the following important features of a
bill of exchange:
·
It is a
written document.
·
It is an
unconditional order.
·
It is an
order to pay a certain sum of money.
·
It is
signed by the drawer.
·
It bears
stamp or it is drafted on a stamp paper.
·
It is to
be accepted by the acceptor.
·
The
amount of the bill is paid to the drawer or the endorsee.
Specimen of bill of exchange
Bill of exchange

Important terms
Explanation of some terms connected with bill of
exchange is given below:
(i) Drawing of a bill
The seller (creditor) prepares the bill in the form
presented above. The act of preparing the bill by the seller or creditor in its
complete form with the signature is known as ‘drawing’ a bill.
(ii) Parties
There are three parties to a bill of exchange as
under:
Drawer: The person
who prepares the bill is called the drawer, i.e., a creditor
Drawee: The person
who has to make the payment or who accepts to make the payment is called the
drawee, i.e., a debtor
Payee: The person
who receives the payment is payee. He may be a third party or the drawer
of the bill.
In the above
specimen, drawer and payee is Ramesh Babu. Jothi Kumar is the drawee.
(iii) Acceptance
In a bill,
drawee gives his/her acceptance by writing the word ‘accepted’ and signs the
same with the date. Now the bill becomes a legal document enforceable in the
court of law.
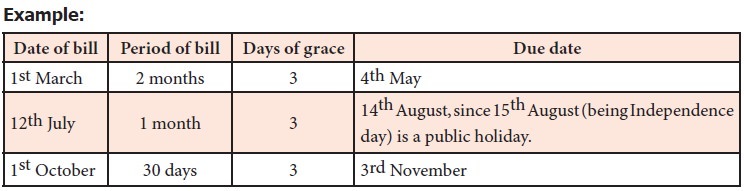
(iv) Due date and days of grace
When a bill
is drawn payable after a specified period, the date on which the payment should
be made is called ‘Due date’. In the
calculation of the due date, three extra days are added to the specified period
of the bills called ‘Days of grace’.
If the date of maturity falls on a holiday, the bill will be due for payment on
the preceding day.
Example:
(v) Endorsement
Endorsement
means signing on the face or back of a bill for the purpose of transferring the
title of the bill to another person. The person who endorses is called the
“Endorser”. The person to whom a bill is endorsed is called the “Endorsee”. The
endorsee is entitled to collect the money.
(vi) Discounting
When the
holder of a bill is in need of money before the due date of a bill, cash can be
received by discounting the bill with the banker. This process is referred to
as the discounting of bill. The banker deducts a small amount of the bill which
is called discount and pays the balance in cash immediately to the holder of
the bill.
(vii) Retiring of bill
An acceptor
may make the payment of a bill before its due date and may discharge the
liability on the bill. It is called as retirement of a bill. Usually, the
holder of the bill allows a concession called rebate to the drawee for the
unexpired period of the bill.
(viii) Renewal
When the
acceptor of a bill knows in advance that he/she will not be able to meet the
bill on its due date, he/she may request the drawer for extension of time for
payment. The drawer of the bill may agree to cancel the original bill and draw
a new bill for the amount due with interest thereon. This is referred to as
renewal.
(ix) Dishonour
Dishonour of
the bill means the non payment of the amount of the bill, when it is presented
for payment.
Related Topics