Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Bullous diseases
Acquired epidermolysis bullosa
Acquired
epidermolysis bullosa
This
can also look like pemphigoid, but has two im-portant extra features: many of
the blisters are a response to trauma and arise on otherwise normal skin; and
milia are a feature of healing lesions. The target of the autoantibodies is
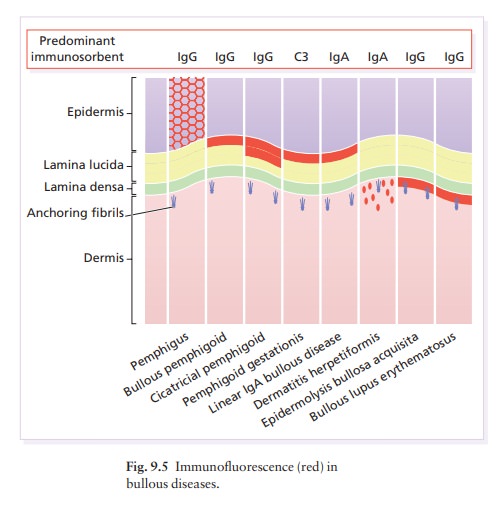
type VII collagen in anchoring fibrils (see Fig. 9.5). The antigen lies on the
dermal side of the lamina densa, in contrast to the pemphigoid antigens, which
lie on the epidermal sideaa difference that can be demonstrated when the
basement membrane is split by incubating skin in a saline solution (the
ŌĆśsalt-splitŌĆÖ technique). The condi-tion responds poorly to systemic
corticosteroids or immunosuppressive agents.
Related Topics