Chapter: Mathematics (maths) : Z-Transforms and Difference Equations
Z - Transforms and its Properties
Z - Transforms and its Properties
Definition
Let {fn} be a sequence defined for n = 0,1,2,…….,then its Z-transform F(z) is defined as
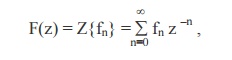
whenever the series converges and it depends on the sequence {fn}.
The inverse Z-transform of F(z) is given by Z-1{F(z)} = {fn}.
Note: If {fn} is defined for n = 0, ± 1, ± 2, …….,

Properties of Z-Transforms
1. The Z-transform is linear.
i.e, if F(z) = Z{fn} and G(z) = Z{gn}, then
Z{afn + bgn} = aF(z) + bG(z).


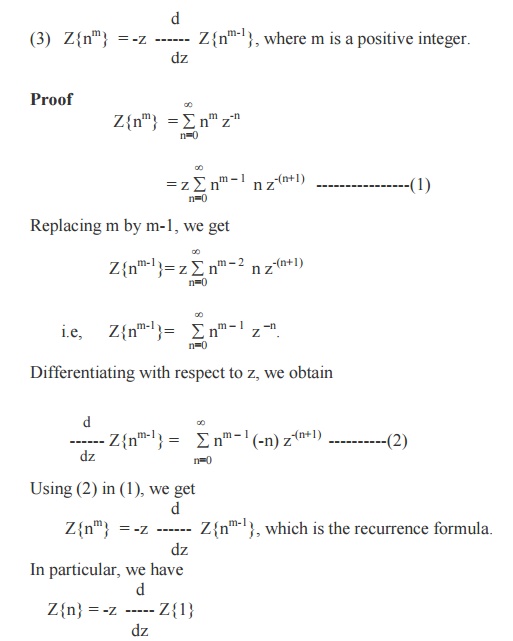
4. If Z{fn} = F(z), then
Z{fn+k}= zk{ F(z) –f0 –(f 1 / z ) - … - ( fk-1 / zk-1) } (k > 0)
Proof
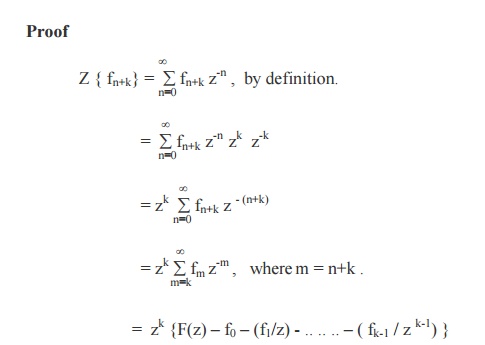
In Particular,
(i) Z{f n+1} = z {F(z) - f0}
(ii) Z{f n+2}= z2 { F(z) –f0 –(f1/z) }
Corollary
If Z{fn} = F(z), then Z{fn–k} = z-k F(z).
(5) Initial value Theorem
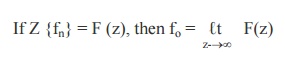
Proof
We know that F (z) = f0 + f1 z-1 + f2z-2 + . . .
Taking limits as z ® ¥on both sides, we get
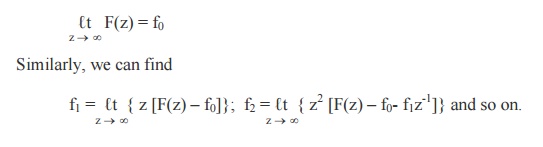
(6) Final value Theorem

SOME STANDARD RESULTS
1. Z{an} = z / (z-a), for |z| > |a|.
Proof
By definition, we have
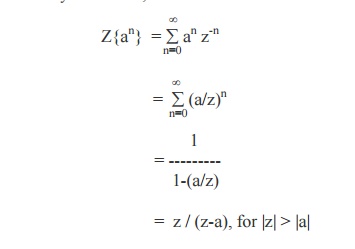
In particular, we have
Z{1} = z / (z-1), (taking a = 1).
and Z{(-1)n} = z / (z +1), (taking a = -1).
2. Z{nan} = az /(z-a)2
Proof: By property, we have
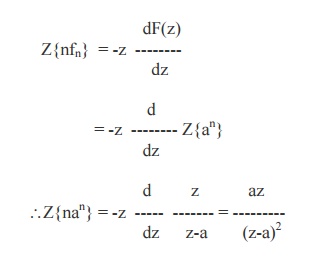
Similarly, we can prove
Z{n2an} = {az(z+a)}/ (z-a)3
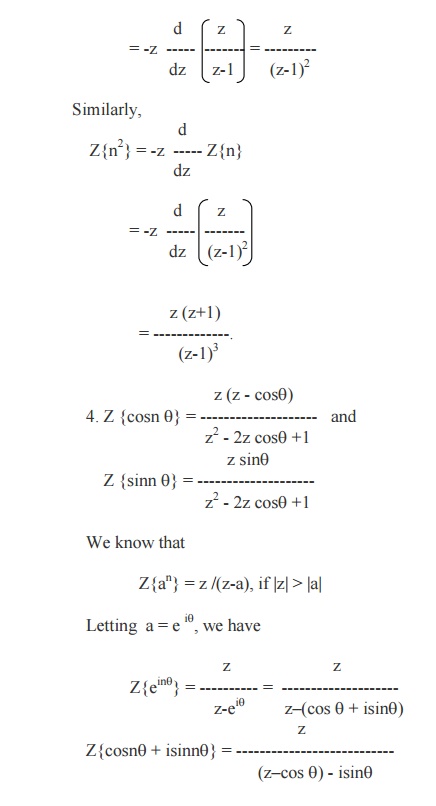
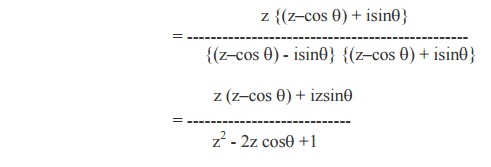
Equating the Real and Imaginary parts, we get

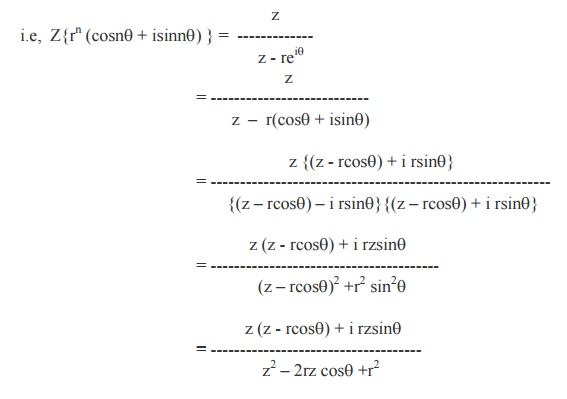
Equating the Real and Imaginary parts, we get
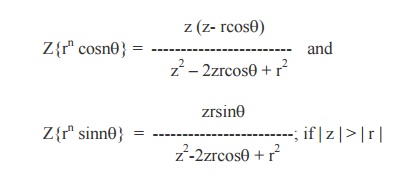
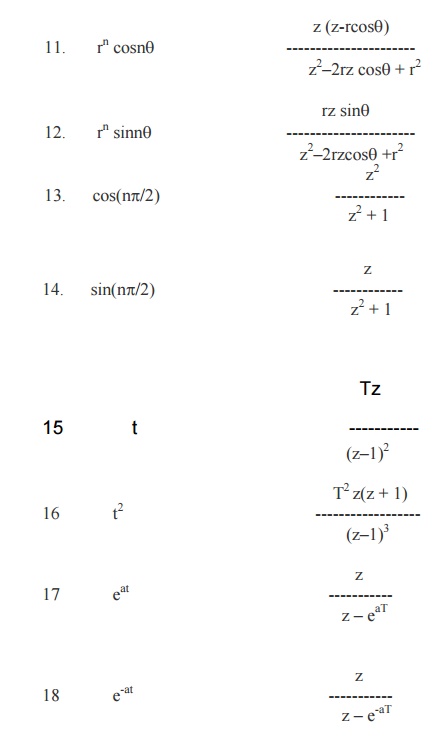
Table of Z –Transforms


Example 2
Find the Z–transform of
1. n(n-1)
2. n2 + 7n + 4
3. (1/2)( n+1)(n+2)
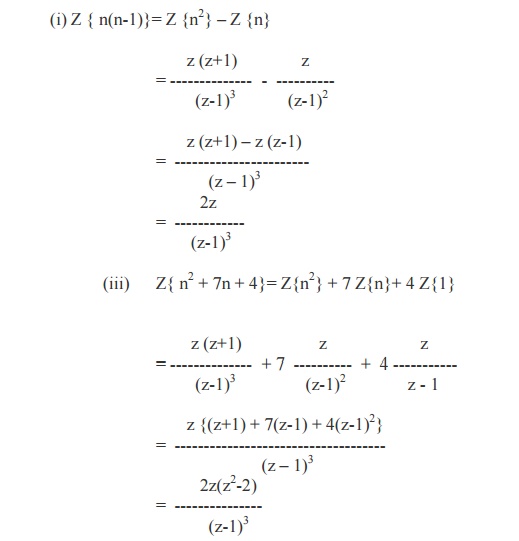
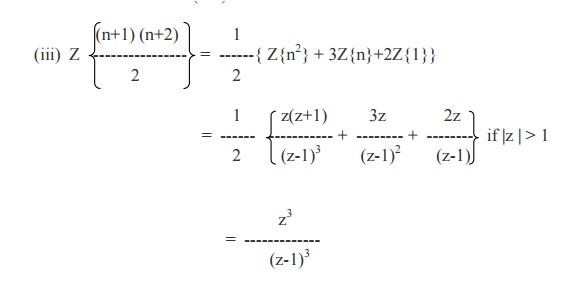
Example 3
Find the Z- transforms of 1/n and 1/n(n+1)
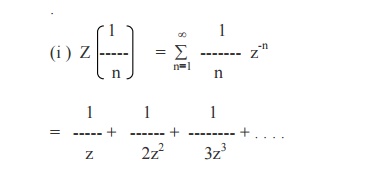
= - log (1 –1/z ) if |1/z| < 1
= - log (z-1 / z)
= log (z/z-1), if | z | >1.
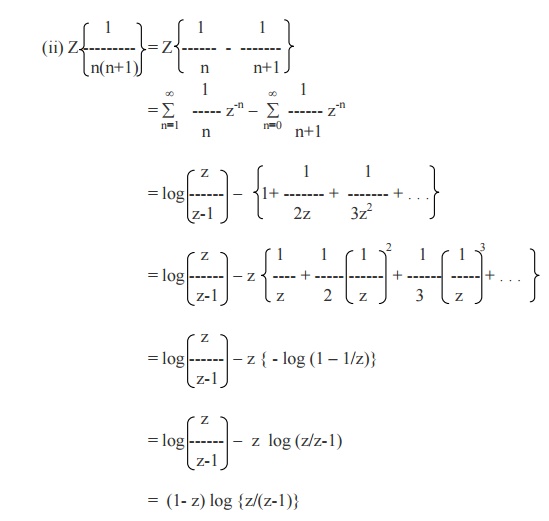
Example 4
Find the Z- transforms of
(i) cos np/2
(ii) sin np/2
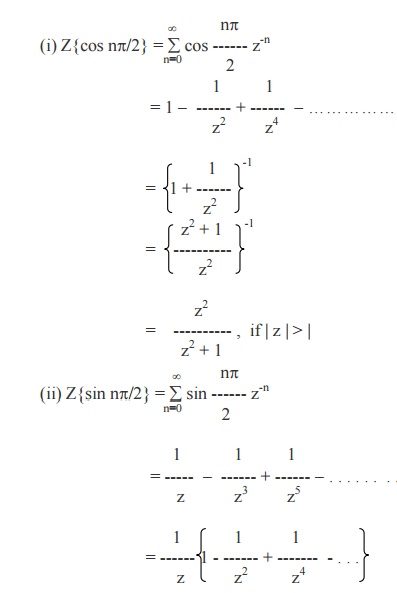
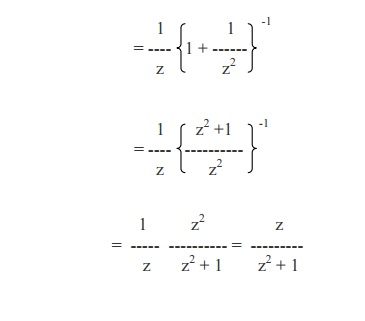
Example 5
Show that Z{1/ n!} = e1/z and hence find Z{1/ (n+1)!} and Z{1/ (n+2)!}
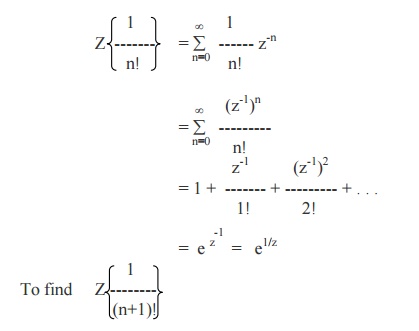
We know that Z{fn+1} = z { F(z) –f0}
Therefore,
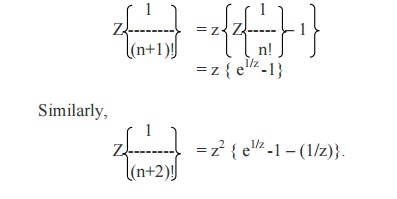
Example 6
Find the Z- transforms of the following

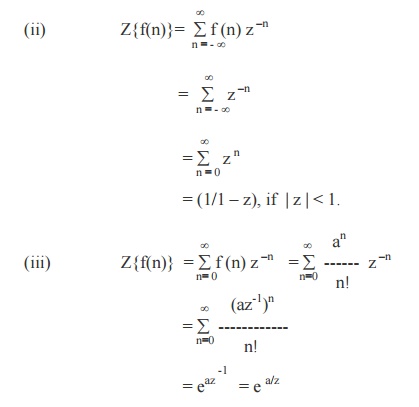

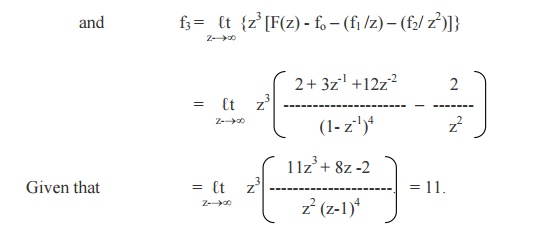
Related Topics