Chapter: Special Electrical Machines : Synchronous Reluctance Motors
Working of Synchronous Reluctance Motor
WORKING OF SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE
MOTOR
In order
to understand the working of synchronous reluctance motor, when a piece of
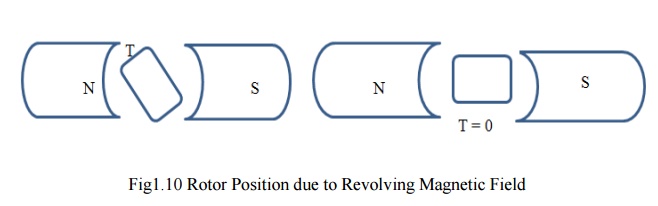
magnetic material is located in a magnetic field, a force acts on the material
tending to bring it into the desert portion of the field. The force tends to
align the specimen of the material in such a way that the reluctance of the
magnetic path that passes through the material will be minimum.
When
supply is given to the stator winding, the revolving magnetic field will exert
reluctance torque on the unsymmetrical rotor tending to align the salient pole
axis of the rotor with the axis of the revolving magnetic field, because in
this position, the reluctance of the magnetic path would be minimum. If the
reluctance torque is sufficient to start the motor and its load, the rotor will
pull into step with the revolving field and continue to run at the speed of the
revolving field. Actually the motor starts as an induction motor and after it
has reached its maximum speed as an induction motor, the reluctance torque
pulls its rotor into step with the revolving field, motor now runs as
synchronous motor by virtue of its saliency.
Reluctance
motors have approximately one third the HP rating they would have as induction
motors with cylindrical rotors. Although the ratio may be increased to 9one
half by proper design of the field windings, power factor and efficiency are
poorer than for the equivalent induction motor. Reluctance motors are subject
to cogging, since the locked rotor torque varies with the rotor position, but
the effect may be minimized by skewing the rotor bars and by not having the
number of poles.
Related Topics