Chapter: Special Electrical Machines : Synchronous Reluctance Motors
Primary Design Considerations - Synchronous Reluctance Motor
PRIMARY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
v High
output power capability.
v Ability
of the rotor to with stand high speeds.
v Negligible
zero torque spinning losses.
v High
reliability.
v High
efficiency.
v Low cost.
(a) Power factor:
The
maximum achievable power factor PFmax of a synchronous reluctance
machine given as
PFmax
= Ld/Lq - 1/ Ld/Lq + 1
Higher Ld/Lq
ratio yield higher power factors, which corresponds to reduced I2R
losses and reduced volt ampere ratings of the inverter driving the machine.
(b) Copper loss and core loss:
Copper
loss = 3 I2Rs
= 3V2Rs/(Rs2
+ω2LdLq)2 { Rs2 + Rs ω(Ld-Lq)
sin 2Ȣ }+ω2
[Ld2+Lq2/2 – Lq2
– Ld2/2 cos 2Ȣ ]
Where
Rs –
Stator resistance
Ld ,Lq - direct and quadrature
inductance
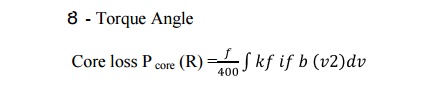
The core
losses are calculated corresponding to the fundamental component of flux
density in the stator iron core. There will also be significant core losses in
the stator and rotor due to the winding and slot harmonics. The losses are
difficult to estimate reliably.
Related Topics