Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Hypocholesterolemic Drugs and Coronary Heart Disease
When to Treat Hypercholesterolemias?
WHEN TO TREAT
HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIAS?
Principal risk factors for
heart disease are elevated lev-els of LDL cholesterol, a family history of
heart disease, and hypertension. Other risks include being male, smoking, low
levels of high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, diabetes mellitus,
hyperhomocystinemia, high levels of lipoprotein a (Lpa), and high blood levels
of C-reactive protein. (Table 23.1). C-Reactive protein is a marker for
cellular inflammation.
Homocysteine blood levels
(>15 mol/L) promote atherosclerosis, perhaps by stimulating proliferation of
arterial wall smooth muscle cells. Supplementing the diet with folic acid can
reduce high levels. Lpa is a mod-ified LDL particle that is both atherogenic
and pro-thrombic.
Although development and
clinical expression of coronary heart disease (CHD) are determined by the
interaction of numerous risk factors, lowering blood cholesterol is the major
approach to prevention and suppression of heart disease, the number one cause
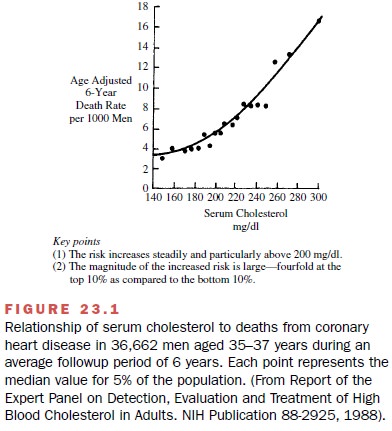
of death in Western society. The risk of CHD is directly proportional to blood
cholesterol levels (Fig. 23.1), and a lowering of cholesterol, specifically LDL
cholesterol, deceases the incidence of heart attacks.
The results of several large
clinical trials using the statin drugs (discussed later) show that the tested
drugs decreased the risk of both primary and secondary car-diovascular events.
The incidence of myocardial infarc-tion and death from cardiovascular disease
was reduced in patients with hypercholesterolemia who never had a heart attack
(primary prevention) and in those with heart disease (secondary prevention).
Furthermore, the statins decreased the risk of a first heart attack in
sub-jects with even average LDL cholesterol levels. In addi-tion to decreased
clinical expression of heart disease, aggressive lowering of blood cholesterol
with the statin drugs can partially reverse atherosclerosis in the sense of
reducing the degree of stenosis (closure) of coronary arteries. Guidelines for
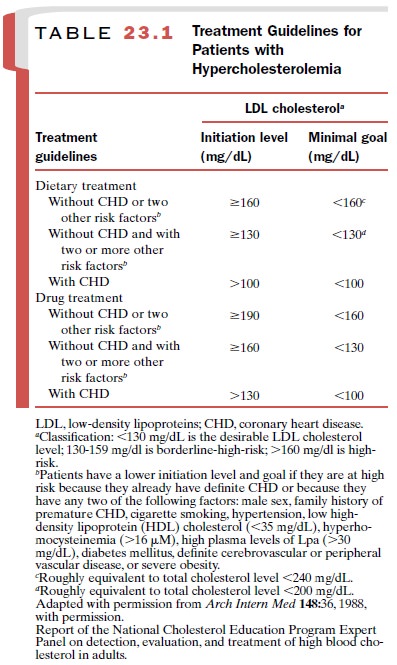
initiation and goals of treatment of hypercholesterolemias are outlined in
Table 23.1.
Related Topics