Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
What problems may occur intraoperatively and postoperatively?
What problems may occur intraoperatively and postoperatively?
Meticulous attention should be paid to adequate
oxy-genation and ventilation of these neonates. There is an increased risk for
pneumothorax, especially on the contralat-eral side. If this should occur it
would be life-threatening. Efforts should be made to avoid using ventilation
pressures greater than 40 cm H2O to avoid causing a pneumothorax. No
attempt should be made to manually inflate the con-tralateral lung because of
this potential life-threatening risk. A diagnosis of a pneumothorax should be
considered when any abrupt change in the condition of the neonate occurs during
surgery. When in doubt of the diagnosis, a needle should be inserted into the
contralateral chest. This maneu-ver will both diagnose the presence of a
pneumothorax and treat it as well. A chest tube should be placed once the
diagnosis is made.
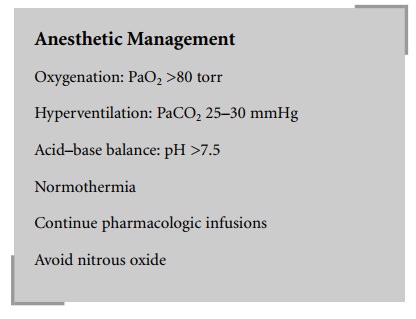
Postoperatively, these neonates may continue to
require oxygen and ventilatory support. There may be continued pulmonary
hypertension and the patient may continue to deteriorate despite surgical
correction. This deterioration is due to the severe degree of pulmonary hypoplasia
that existed preoperatively and the change in pulmonary mechanics after
surgery.
Related Topics