Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
What is the preoperative management of CDH?
What is the preoperative management of CDH?
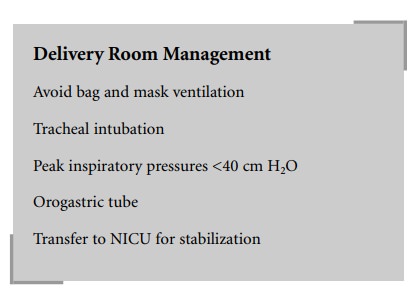
In the delivery room, once the diagnosis of CDH
is suspected, mask ventilation should be avoided to prevent distention of the
abdominal organs in the thorax, which would further impair oxygenation and
ventilation. The tra-chea should be intubated and inflation pressures limited
to less than 40 cm H2O to avoid causing a pneumothorax. A
pneumothorax will most likely occur in the contralateral lung, which is where
most of the gas exchange occurs. An orogastric tube should be inserted to
assist in deflation of the stomach. If transfer to the neonatal intensive care
unit (NICU) is delayed, an arterial and intravenous catheter should be inserted
to guide therapy and for administration of pharmacologic agents. If possible,
the arterial line should be placed in the right radial artery so that preductal
oxygenation is measured.
Measures to both prevent further increases in
PVR and promote a decrease in PVR, thereby increasing pulmonary blood flow,
should be instituted. These include increased oxygenation, hypocarbia,
alkalosis, avoiding sympathetic stimulation, and normothermia. Pharmacologic
vasodilator therapy may be necessary. Tolazoline is most commonly used for this
purpose. However, there may be systemic hypotension associated with its use and
pharmacologic support of the systemic blood pressure may be necessary. Nitric
oxide, a specific pulmonary vasodilator, has been used in these patients with
variable results. If these meas-ures do not improve the neonate’s condition,
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be utilized.
Related Topics