Principle, Steps, Application | Immunology - Western Blot techniques | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 11 : Immunology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 11 : Immunology
Western Blot techniques
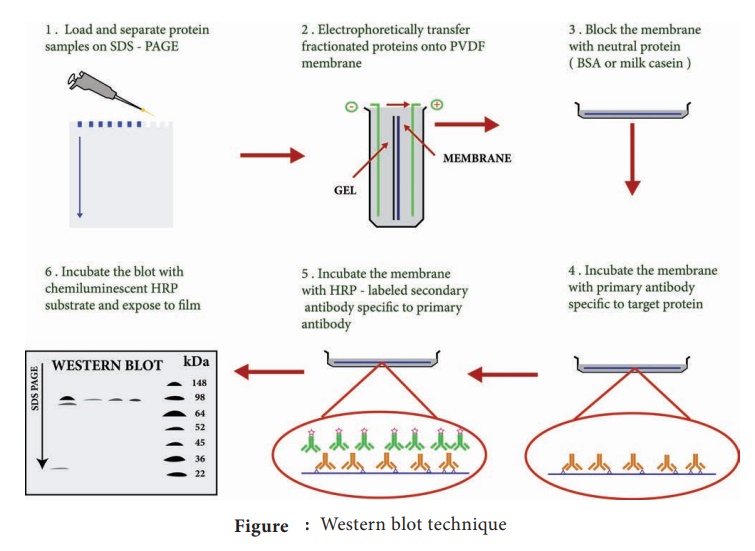
Western Blot techniques
Macromolecules
immobilized or fixed on nitrocellulose membrane i.e., blotted can be subjected
to a variety of analytical techniques more easily. Southern blotting was the
first blotting technique developed which made the analysis and recording of DNA
easy. Later the technique was extended for analysis of RNA and proteins and
they have acquired the jargon terms Northern and Western Blotting respectively.
Western blotting is also known as immunoblotting because it uses antibodies to
detect the protein. Western blotting is a quantitative test to determine the
amount of protein in sample.
Principle
Western
blotting technique is used for the identification of a particular protein from
the mixture of a proteins. In this method, the proteins are first extracted
from the sample. Extracted proteins are subjected to Poly Acryl - amide Gel
Electrophoresis (PAGE). Transfer of proteins from poly acryl amide to the
nitrocellulose paper is achieved by applying electric field. When radio
labelled specific antibody is added on such membrane it binds to the specific
complementary protein. Finally the proteins on the membrane can be detected by
staining or through ELISA technique.
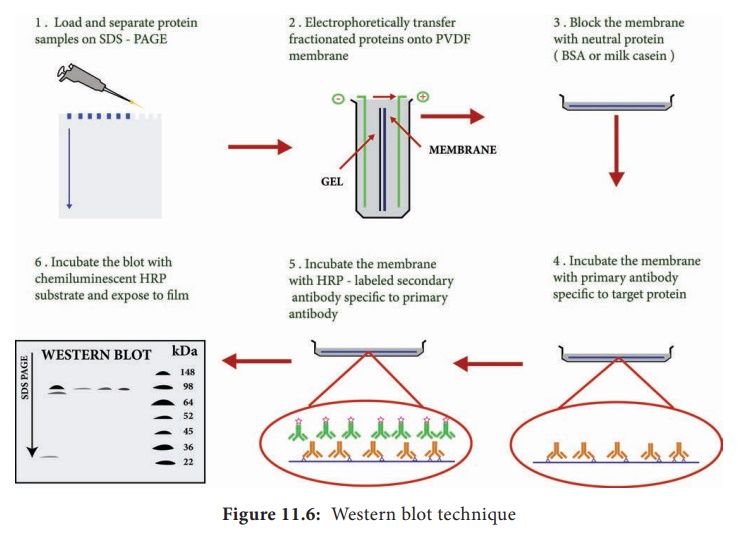
Steps
Step I: Extraction of Protein
The most
common protein sample used for Western blotting is cell lysate. The protein
from the cell is generally extracted by mechanical means or by adding chemicals
which can lyse the cell. The extraction step is termed as tissue preparation.
Protease inhibitor is used to prevent
the denaturing of proteins. Using spectroscopy the concentration of the protein
sample is analysed and diluted in loading buffer containing glycerol. This will
help the sample to sink in the well. Bromothymol blue is used as tracking dye
and is used to monitor the movement of the sample.
Step II: Gel electrophoresis
The
protein sample is loaded in well of SDS-PAGE (Sodium dodecyl sulfate-poly
-acryl amide gel electrophoresis). The proteins are separated on the basis of
electric charge, isoelectric point, molecular weight, or combination of all
these. Proteins are negatively charged, so they move toward positive (anode)
pole as electric current is applied. Smaller proteins move faster than the
larger proteins.
Step III: Blotting
Blotting
refers to the transfer of the protein from the gel to the nitrocellulose paper
by capillary action. Electro blotting is done nowadays to speed up the process.
In electro-blotting nitrocellulose membrane is sandwich between gel and
cassette of filter paper and then electric current is passed through the gel
causing transfer of protein to the membrane
Step IV: Blocking
The
nitrocellulose membrane is non-specifically saturated or masked by using casein
or Bovine serum albumin (BSA) before adding the primary antibody. This blocking
step is very important in western blotting as antibodies are also proteins and
they are likely to bind to the nitrocellulose paper.
Step V: Treatment with primary and secondary antibody
The
primary antibody is specific to desired protein so it forms Ag-Ab complex. The
secondary antibody is enzyme labelled and is against primary antibody
(anti-antibody) so it can bind with Ag-Ab complex. Alkaline phosphatase or
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is labelled with secondary antibody.
Step VI: Treatment with suitable substrate
Finally,
the reaction mixture is incubated with specific substrate. The enzyme convert
the substrate to give visible coloured product, so band of colour can be
visualized in the membrane (Figure 11.6)
Application
1. The
size and concentration of protein in given sample is determined by western
blotting.
2. It is
used in the detection of antibody against virus or bacteria in serum and helps
in the disease diagnosis.
3. Western
blotting technique is the confirmatory test for HIV. It detects anti HIV
antibody in patient’s serum.
4. Useful
to detect defective proteins
Related Topics