Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Cardiovascular system
Ventricular ectopic beats - Ventricular arrhythmias
Ventricular arrhythmias
Ventricular ectopic beats
Definition
A ventricular ectopic/extrasystole/premature beat is an extra myocardial depolarisation triggered by a focus in the ventricle.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
Ventricular ectopics are not uncommon in normal individuals and increase in incidence with advancing age. Common causes include ischaemic heart disease and hypertension. Ectopic beats may arise due to any of the mechanisms of arrhythmias, such as a re-entry circuit or due to enhanced automaticity (which may occur with electrolyte abnormalities, alcohol or nicotine excess, anaemia, medications such as ő≤ agonists or hypoxaemia). When ventricular ectopic beats occur regularly after each sinus beat, it is termed bigeminy, which is frequently due to digoxin.
Clinical features
Patients are usually asymptomatic but may feel uncomfortable or beaware of an irregular heart or missed beats. On examination the pulse may be irregular if ectopics are frequent.
Investigations
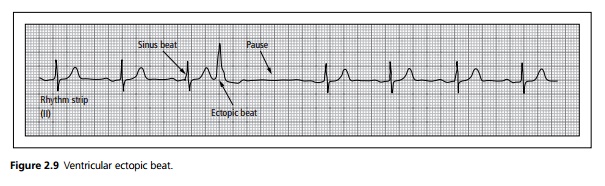
ECG shows broad bizarre QRS complexes without pre-ceding P, followed by an inverted T wave and then a pause before the next sinus beat (see Fig. 2.9).
Echocardiography and exercise testing may be used to look for underlying structural or ischaemic heart disease.
Management
Ventricular ectopic beats do not require treatment although any underlying cause should be identified and managed.
Prognosis
Ventricular ectopics worsen the prognosis in patients with underlying ischaemic heart disease but there is no evidence that anti-arrhythmic drugs improve this.
Related Topics