Problem Solving and Python Programming - Values and Data Types | Problem Solving and Python Programming : Data, Expressions, Statements
Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Data, Expressions, Statements
Values and Data Types
VALUES AND
DATA TYPES
Value:
Value can
be any letter ,number or string.
Eg, Values
are 2, 42.0, and 'Hello, World!'. (These values belong to different datatypes.)
Data type:
Every value in
Python has a data type.
It is a set of
values, and the allowable operations on those values.
Python has four standard data types:
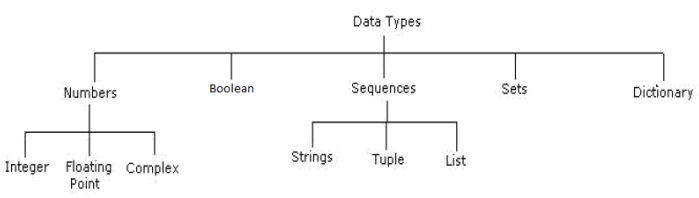
Numbers:
v Number data type stores Numerical Values.
v This data type is immutable [i.e. values/items
cannot be changed].
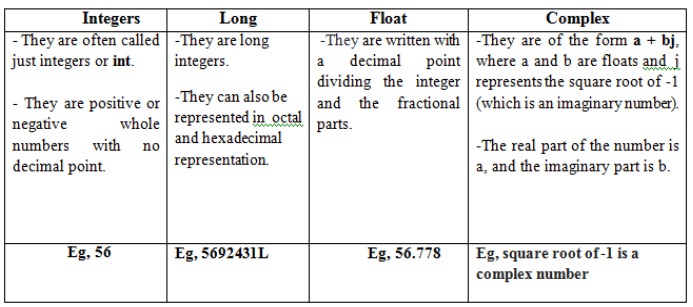
v Python supports integers, floating point
numbers and complex numbers. They are defined as,
Sequence:
v A sequence is an ordered collection of items, indexed by positive integers.
v It is a combination of mutable (value can be changed) and immutable (values cannot be changed) data types.
v There are three types of sequence data type
available in Python, they are
1.
Strings
2.
Lists
3.
Tuples
1. Strings
Ø A String in Python consists of a series or
sequence of characters - letters, numbers, and special characters.
Ø Strings are marked by quotes:
· single
quotes (' ') Eg, 'This a string in single quotes'
· double
quotes (" ") Eg, "'This a string in double quotes'"
·
triple quotes("""
""") Eg, This is a paragraph. It is made up of multiple lines
and sentences."""
Ø Individual character in a string is accessed
using a subscript (index).
Ø Characters can be accessed using indexing and
slicing operations
Strings are
immutable i.e. the contents of the string cannot be changed after it is
created.
Indexing:
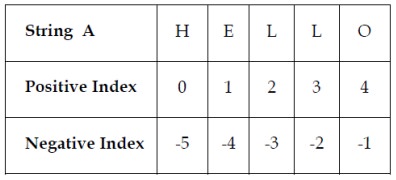
·
Positive
indexing helps in accessing the string from the beginning
·
Negative
subscript helps in accessing the string from the end.
·
Subscript 0 or
–ve n(where n is length of the string) displays the first element.
Example: A[0] or A[-5] will display “H”
·
Subscript 1 or
–ve (n-1) displays the second element.
Example: A[1] or A[-4] will display “E”
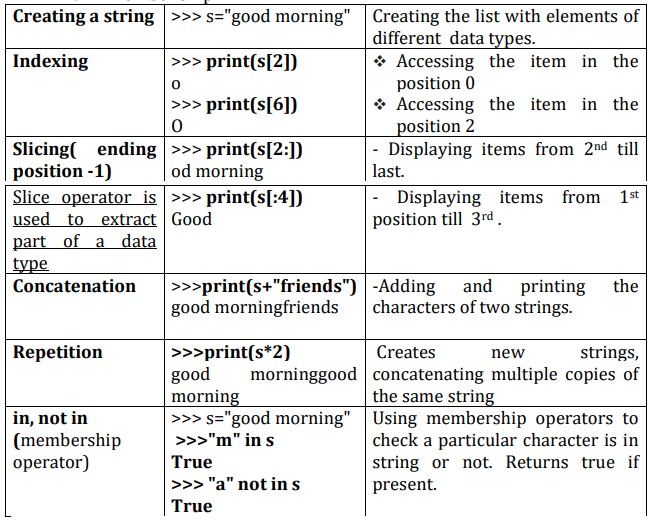
Operations on string:
i.
Indexing
ii.
Slicing
iii.
Concatenation
iv.
Repetitions
v.
Member ship
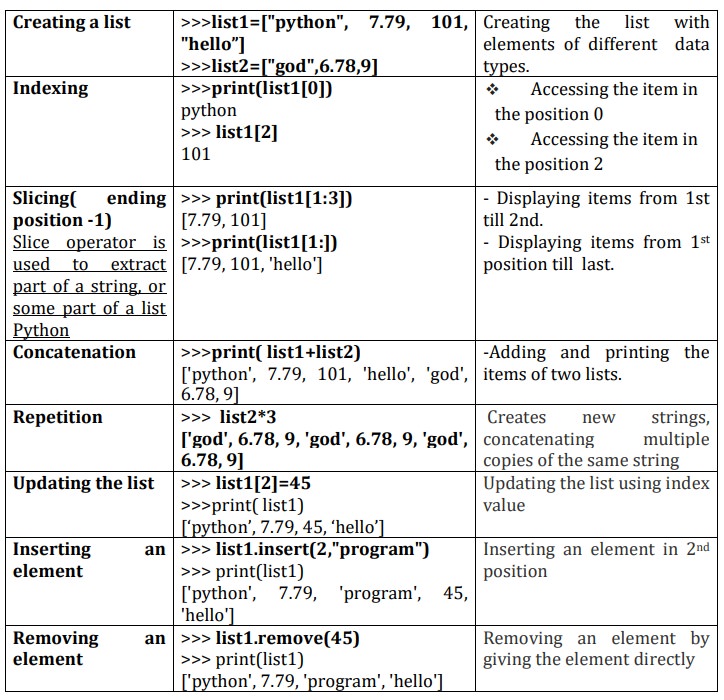
2. Lists
v List is an ordered sequence of items. Values
in the list are called elements / items.
v It can be written as a list of comma-separated
items (values) between square brackets[ ].
v Items in the lists can be of different data
types.
Operations on list:
Indexing
Slicing
Concatenation
Repetitions
Updation,
Insertion, Deletion
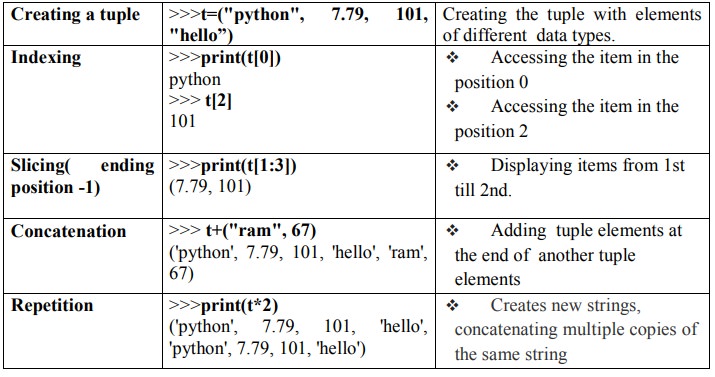
3. Tuple:
v A tuple is same as list, except that the set
of elements is enclosed in
parentheses instead of square brackets.
v A tuple is an immutable list. i.e. once a tuple has been created, you can't
add elements to a tuple or remove elements from
the tuple.
v Benefit of Tuple:
v Tuples are faster than lists.
v If the user wants to protect the data from
accidental changes, tuple can be used.
v Tuples can be used as keys in dictionaries,
while lists can't.
Basic Operations:
Altering the tuple data type leads to error. Following error occurs when user tries to do.
>>>
t[0]="a"
Trace
back (most recent call last):
File
"<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
Type
Error: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
Mapping
-This data type
is unordered and mutable.
-Dictionaries
fall under Mappings.
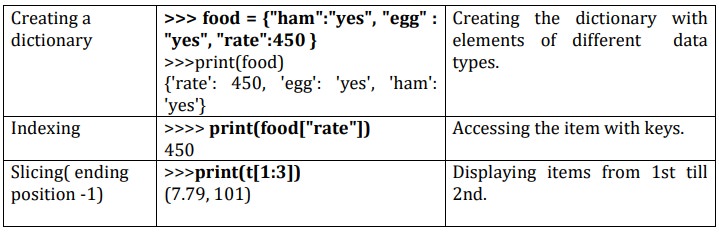
Dictionaries:
v Lists are ordered sets of objects, whereas dictionaries are unordered sets.
v Dictionary is created by using curly brackets. i,e. {}
v Dictionaries are accessed via keys and not via their position.
v A dictionary is an associative array (also
known as hashes). Any key of the dictionary is associated (or mapped) to a
value.
v The values of a dictionary can be any Python
data type. So dictionaries are
unordered key-value-pairs(The association of a key and a value is called
a key-value pair )
Dictionaries
don't support the sequence operation of the sequence data types like strings,
tuples and lists.
If you try to
access a key which doesn't exist, you will get an error message:
>>>
words = {"house" : "Haus",
"cat":"Katze"}
>>>
words["car"]
Traceback
(most recent call last):
File
"<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
KeyError:
'car'
Related Topics