Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Data, Expressions, Statements
Operators and Types of Operators - Python
OPERATORS:
v Operators are the constructs which can
manipulate the value of operands.
v Consider the expression 4 + 5 = 9. Here, 4 and 5 are called operands and + is called operator
Types of Operators:
-Python language
supports the following types of operators
·
Arithmetic
Operators
·
Comparison
(Relational) Operators
·
Assignment
Operators
·
Logical
Operators
·
Bitwise
Operators
·
Membership
Operators
·
Identity
Operators
Arithmetic operators:
They are used to
perform mathematical operations like
addition, subtraction, multiplication etc. Assume,
a=10 and b=5
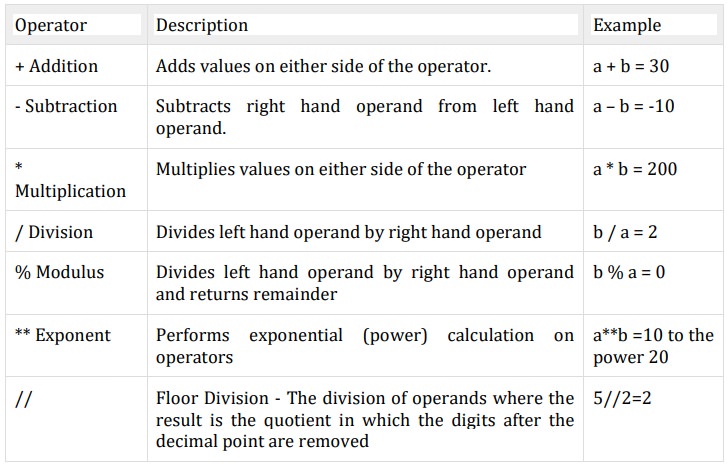
Examples
a=10
b=5
print("a+b=",a+b)
print("a-b=",a-b)
print("a*b=",a*b)
print("a/b=",a/b)
print("a%b=",a%b)
print("a//b=",a//b)
print("a**b=",a**b)
Output:
a+b= 15
a-b= 5
a*b= 50
a/b= 2.0
a%b= 0
a//b= 2
a**b= 100000
Comparison (Relational) Operators:
·
Comparison operators
are used to compare values.
·
It either
returns True or False according to the condition. Assume, a=10 and b=5

Example
a=10
b=5
print("a>b=>",a>b)
print("a>b=>",a<b)
print("a==b=>",a==b)
print("a!=b=>",a!=b)
print("a>=b=>",a<=b)
print("a>=b=>",a>=b)
Output:
a>b=> True
a>b=>
False
a==b=> False
a!=b=> True
a>=b=>
False
a>=b=>
True
Assignment Operators:
-Assignment
operators are used in Python to assign values to variables.
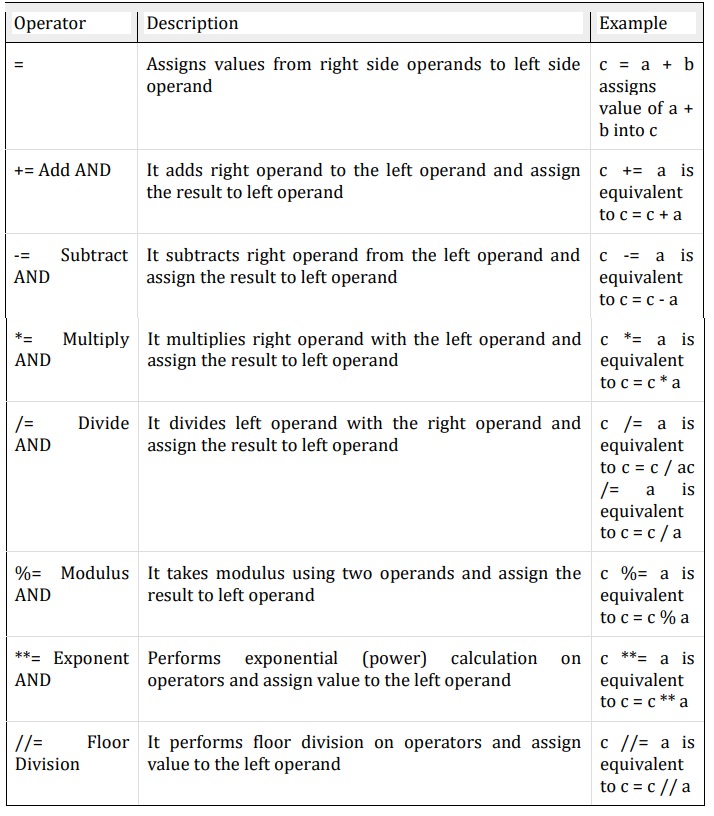
Example
a = 21
b = 10
c = 0
c = a + b
print("Line
1 - Value of c is ", c)
c += a
print("Line
2 - Value of c is ", c)
c *= a
print("Line
3 - Value of c is ", c)
c /= a
print("Line
4 - Value of c is ", c)
c= 2 c %= a
print("Line
5 - Value of c is ", c) c **= a
print("Line
6 - Value of c is ", c) c //= a
print("Line
7 - Value of c is ", c)
Output
Line 1 - Value
of c is 31
Line 2 - Value
of c is 52
Line 3 - Value
of c is 1092
Line 4 - Value
of c is 52.0
Line 5 - Value
of c is 2
Line 6 - Value
of c is 2097152
Line 7 - Value
of c is 99864
Logical Operators:
-Logical
operators are the and, or, not operators.

Example
a = True
b = False
print('a and b
is',a and b)
print('a or b
is',a or b)
print('not a
is',not a)
Output
x and y is False
x or y is True
not x is False
Bitwise Operators:
A bitwise
operation operates on one or more bit
patterns at the level of individual Bits
Example:
Let x = 10 (0000
1010 in binary) and
y = 4 (0000 0100
in binary)
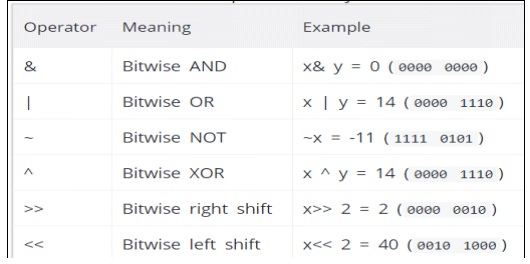
Example
a = 60 # 60 = 0011 1100
b = 13 # 13 = 0000 1101
c = 0
c = a & b; # 12 = 0000 1100
print "Line
1 - Value of c is ", c
c = a | b; # 61 = 0011 1101
print "Line
2 - Value of c is ", c
c = a ^ b; # 49 = 0011 0001
print "Line
3 - Value of c is ", c
c = ~a; # -61 = 1100 0011
print "Line
4 - Value of c is ", c
c = a <<
2; #
240 = 1111 0000
print "Line
5 - Value of c is ", c
c = a >>
2; #
15 = 0000 1111
print "Line
6 - Value of c is ", c
Output
Line 1 - Value
of c is 12
Line 2 - Value
of c is 61
Line 3 - Value of c is 49
Line 4 - Value of c is -61
Line 5 - Value of c is 240
Line 6 - Value of c is 15
Membership Operators:
v Evaluates to find a value or a variable is in
the specified sequence of string, list, tuple, dictionary or not.
v Let, x=[5,3,6,4,1].
To check particular item in list or not,
in and not in operators are used.
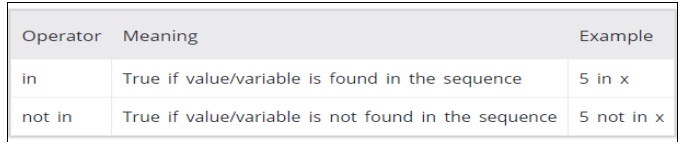
Example:
x=[5,3,6,4,1]
>>> 5
in x
True
>>> 5
not in x
False
Identity Operators
They are used to
check if two values (or variables) are located on the same part of the memory.

Example
x = 5
y = 5
x2 = 'Hello'
y2 = 'Hello'
print(x1 is not
y1)
print(x2 is y2)
Output
False
True
Related Topics