Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Data, Expressions, Statements
Type of operators in Python
Type of operators in Python
Arithmetic
operators
Comparison
(Relational) operators
Logical
(Boolean) operators
Bitwise
operators
Assignment
operators
Special
operators
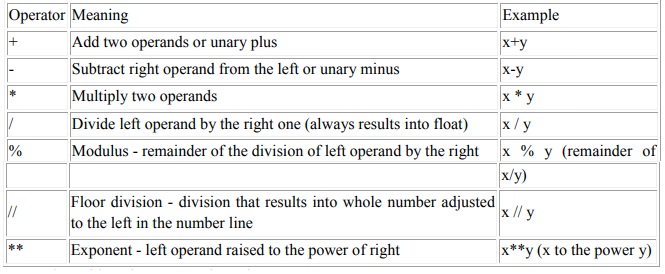
Arithmetic operators
Arithmetic
operators are used to perform mathematical operations like addition,
subtraction,
multiplication etc.
Arithmetic
operators in Python
Example:
Arithmetic operators in Python
x = 15
y = 4
# Output:
x + y = 19
print('x
+ y =',x+y)
# Output:
x - y = 11
print('x
- y =',x-y)
# Output:
x * y = 60
print('x
* y =',x*y)
# Output:
x / y = 3.75
print('x
/ y =',x/y)
# Output:
x // y = 3
print('x
// y =',x//y)
# Output:
x ** y = 50625
print('x
** y =',x**y)
When you
run the program, the output will be:
x + y =
19
x - y =
11
x * y =
60
x / y =
3.75
x // y =
3
x ** y =
50625
Comparison operators
Comparison
operators are used to compare values. It either returns True or False
according
to the condition.

Example:
Comparison operators in Python
x = 10
y = 12
# Output:
x > y is False
print('x
> y is',x>y)
# Output:
x < y is True
print('x
< y is',x<y)
# Output:
x == y is False
print('x
== y is',x==y)
# Output:
x != y is True
print('x
!= y is',x!=y)
# Output:
x >= y is False
print('x
>= y is',x>=y)
# Output:
x <= y is True
print('x
<= y is',x<=y)
Output:
x > y
is False
x < y
is True
x == y is
False
x != y is
True
x >= y
is False
x <= y
is True
Logical operators
Logical
operators are and, or, not operators.

Example:
Logical Operators in Python
x = True
y = False
# Output:
x and y is False
print('x
and y is',x and y)
# Output:
x or y is True
print('x
or y is',x or y)
# Output:
not x is False
print('not
x is',not x)
Output:
x and y
is False
x or y is
True
not x is
False
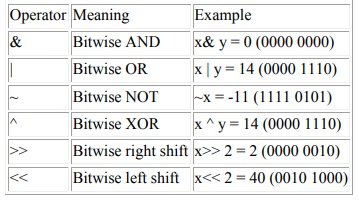
Bitwise operators
Bitwise
operators act on operands as if they were string of binary digits. It operates
bit by bit, hence the name.
For
example, 2 is 10 in binary and 7 is 111.
In the
table below: Let x = 10 (0000 1010 in binary) and y = 4 (0000 0100 in binary)
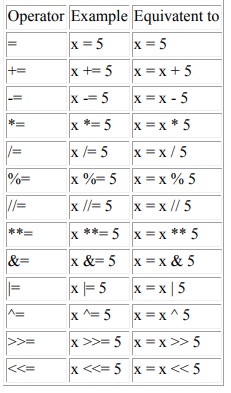
Assignment operators
Assignment
operators are used in Python to assign values to variables. a = 5 is a simple assignment
operator that assigns the value 5 on the right to the variable a on the left.
There are
various compound operators in Python like a += 5 that adds to the variable and later
assigns the same. It is equivalent to a = a + 5.
Assignment
operators in Python
Example:
Assignment operators in Python
x = 15
y = 4
x+=y
# Output:
x + y = 19
print('x
+ y =',x)
x = 15
y = 4
x-=y
# Output:
x - y = 11
print('x
- y =',x)
x = 15
y = 4
x*=y
# Output:
x * y = 60
print('x
* y =',x)
x = 15
y = 4
x/=y
# Output:
x / y = 3.75
print('x
/ y =',x)
x = 15
y = 4
x//=y
# Output:
x // y = 3
print('x // y =',x)
x = 15
y = 4
x**=y
# Output:
x ** y = 50625
print('x
** y =',x)
Special operators
Python
language offers some special type of operators like the identity operator or
the membership operator.
Identity operators
is and is
not are the identity operators in Python. They are used to check if two values
(or variables) are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that
are equal does not imply that they are identical.
Identity
operators in Python

Example:
Identity operators in Python
x1 = 5
y1 = 5
x2 =
'Hello'
y2 =
'Hello'
x3 =
[1,2,3]
y3 =
[1,2,3]
# Output:
False
print(x1
is not y1)
# Output:
True
print(x2
is y2)
# Output:
False
print(x3
is y3)
Output:
False
True
False
Here, we
see that x1 and y1 are integers of same values, so they are equal as well as
identical.
Same is the case with x2 and y2 (strings).
But x3
and y3 are list. They are equal but not identical. Since list are mutable (can
be changed), interpreter locates them separately in memory although they are
equal.
Membership operators
in and
not in are the membership operators in Python. They are used to test whether a value
or variable is found in a sequence (string, list, tuple, set and dictionary).
In a
dictionary we can only test for presence of key, not the value.

Example:
Membership operators in Python
x =
'Hello world'
y =
{1:'a',2:'b'}
# Output:
True
print('H'
in x)
# Output:
True
print('hello'
not in x)
# Output:
True
print(1
in y)
# Output:
False
print('a'
in y)
Output:
True
True
True
False
Here, 'H'
is in x but 'hello' is not present in x (remember, Python is case sensitive).
Similary,
1 is key and 'a' is the value in dictionary y. Hence, 'a' in y returns False.
Related Topics